xStack
®
DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch
How ARP Spoofing Attacks a Network
ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a method to attack an Ethernet network which may allow an attacker to sniff data
frames on a LAN, modify the traffic, or stop the traffic altogether (known as a Denial of Service – DoS attack). The principle of
ARP spoofing is to send the fake or spoofed ARP messages to an Ethernet network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's
or random MAC address with the IP address of another node (such as t he default gateway). Any traffic meant for that IP address
would be mistakenly re-directed to the node specified by the attacker.
IP s poofing at tack is cau sed by G ratuitous ARP that occurs w hen a host sen ds an AR P re quest t o resolve i ts own IP address.
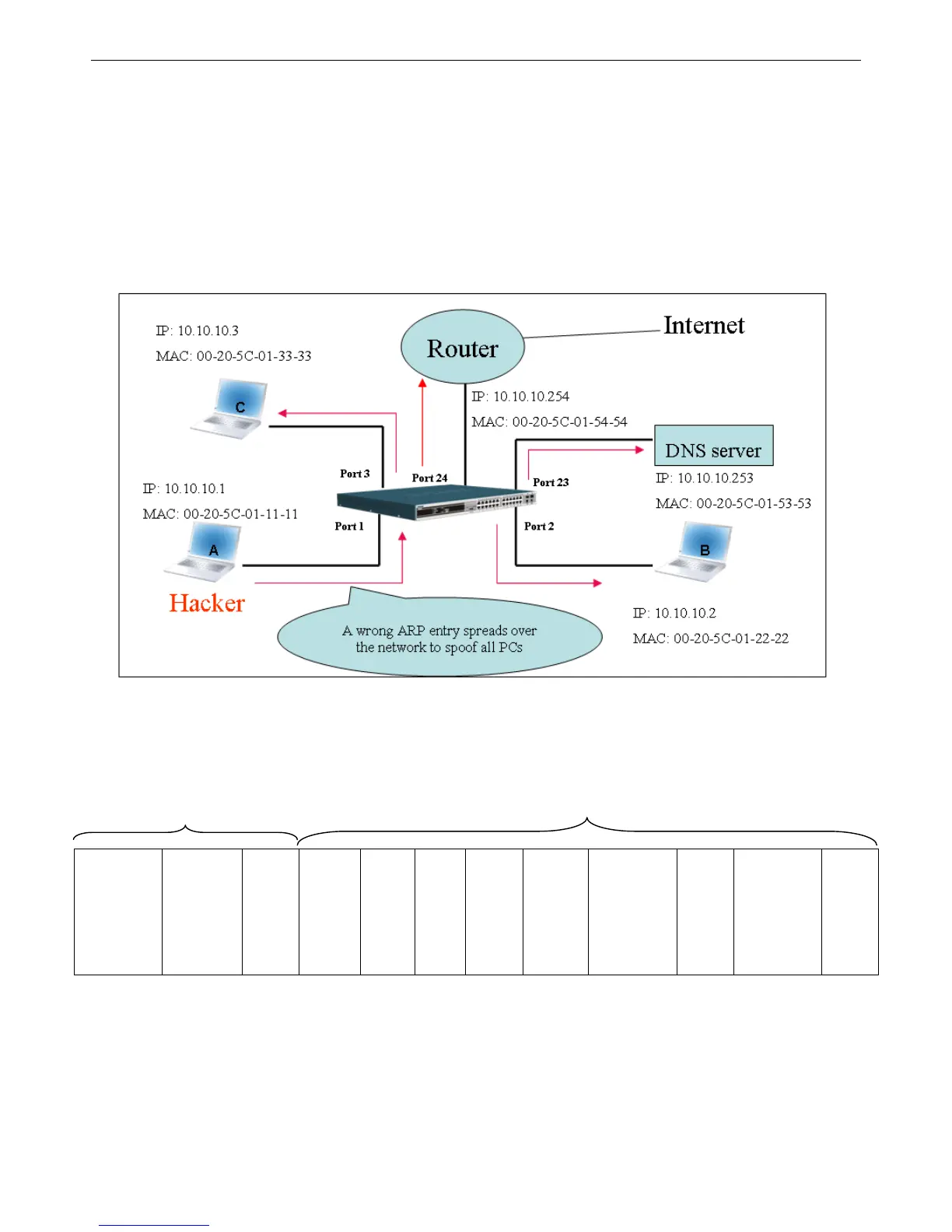
Figure-4 shows a hacker within a LAN to initiate ARP spoofing attack.
Figure 4
In the Gratuitous ARP p acket, the “Sender protocol address” and “Target p rotocol add ress” are filled with th e same sou rce IP
address itself. The “Sender H/W Address” and “Target H/W address” are filled with the sam e source MAC address itself. Th e
destination MAC address is the Ethernet broadcast address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF). All nodes within the network will immediately
update their own ARP table in accordance with the sender’s MAC and IP address. The format of Gratuitous ARP is shown in the
following table
.
Tab le 5
260
Destination
Address
Source
Address
Ethernet
Type
H/W Type Protocol
Type
H/W
Address
Length
Protocol
Address
Length
Operation Sender H/W
Address
Sender
Protocol
Address
Target H/W
Address
Target
Protocol
Address
(6-byte) (6-byte) (2-byte) (2-byte) (2-byte) (1-byte) (1-byte) (2-byte) (6-byte) (4-byte) (6-byte) (4-byte)
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF 00-20-5C-01-11-11
0806
ARP relay 00-20-5C-01-11-11 10.10.10.254 00-20-5C-01-11-11 10.10.10.254
A common DoS attack today can be done by associating a nonexistent or an y sp ecified MA C a ddress to th e IP ad dress of th e
network’s default gateway. The malicious attacker only needs to broadcast one Gratuitous ARP to the network claiming it is the
gateway so that the whole network operation will be turned down as all packets to the Internet will be directed to the wrong node.
Likewise, the attacker can either choose to forward the traffic to th e actual default gateway (passive sniffing) or modify the data
before forwarding it (m an-in-the-middle attack). The hacker cheats the victim PC that it is a router and cheats the router that it is
the victim. As can be seen in Figure 5 all traffic will be then sniffed by the hacker but the users will not discover.
Gratuitous ARP
Ethernet Header
 Loading...
Loading...











