12 General description CG Drives & Automation 01-7318-01r1
2.1 AC drive types
2.1.1 Standard AC drive (as
comparison)
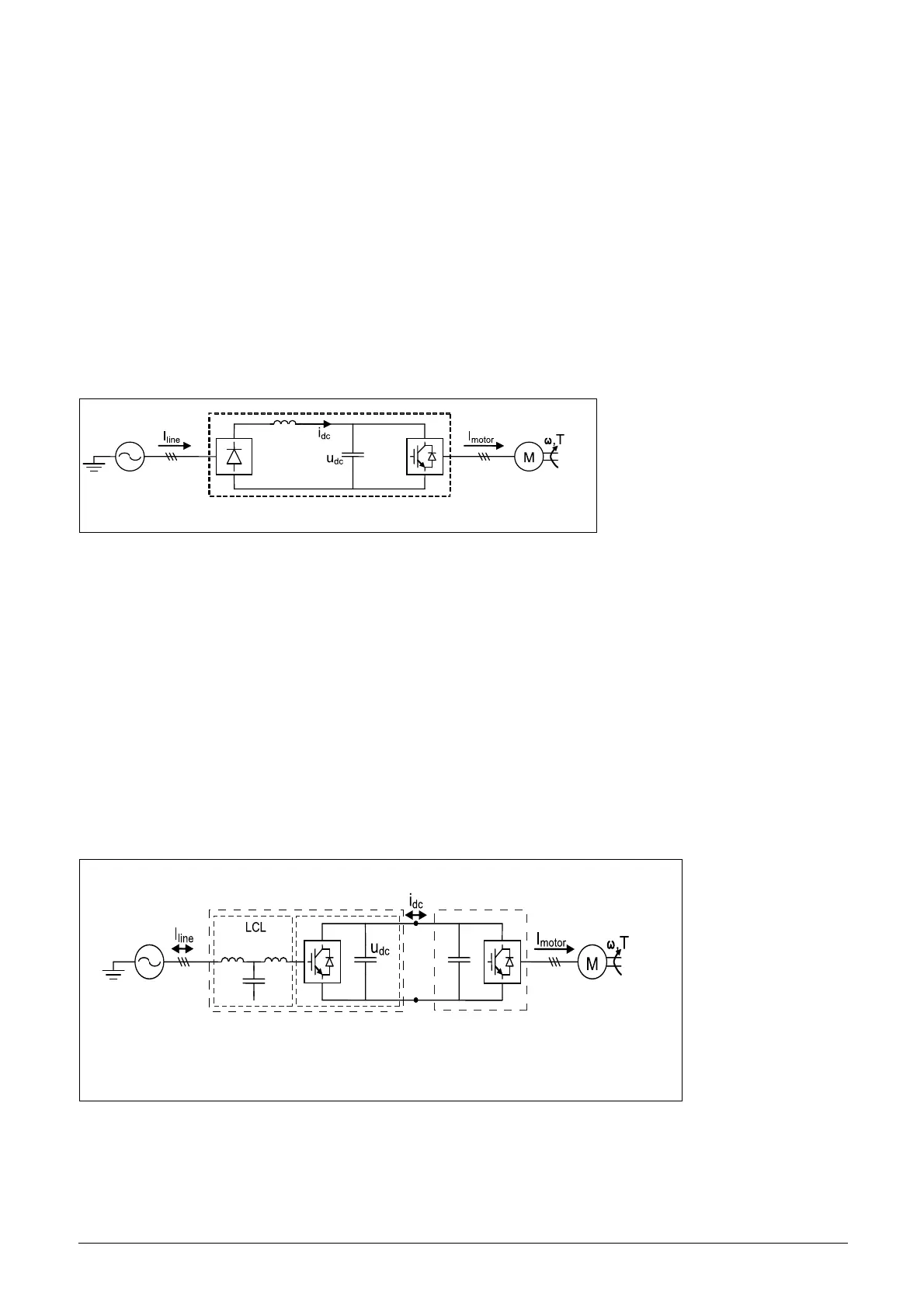
A standard AC drive consists of a rectifier module and an
inverter module. The rectifier module (front-end) consists of
a 6-pulse diode bridge, i.e. diode front-end (DFE) while the
inverter module (VSI) consists of IGBTs with anti-parallel
free wheeling diodes, see Figure 2. The main advantages of
DFEs are the simple and robust design together with their
high efficiency, i.e. low losses. The main disadvantages are
unidirectional power flow and the high harmonic content in
the line current, typically THD 30- 40%.
Fig. 2 Standard AC drive.
2.1.2 AC drive with AFR or AFG
(FDUL/VFXR/FDUG/VFXG)
An AFE unit is basically a VSI towards the supply (via a
filter) where the IGBTs are used as an active rectifier, see
Figure 3. The main advantages are inherent 4Q-operation,
i.e. bi-directional power flow, and sinusoidal supply
currents, i.e. low harmonics, regeneration and improved
power factor.
The AFE unit is controlled in such a way to keep the energy
between motor and supply in balance. This is achieved by
controlling the DC-link voltage (U
dc
). Other features are
the possibility for reactive power compensation and boosted
DC-link voltage.
Fig. 3 VSI with AFR/AFG.
VSI
AFR/AFG = AFE + LCL-filter
FDUL/VFXR = AFR + VSI (FDU/VFX)
AFR/AFG
FDUG/VFXG = AFG + VSI (FDU/VFX)

 Loading...
Loading...