CG Drives & Automation 01-7492-01r1 Functional description 131
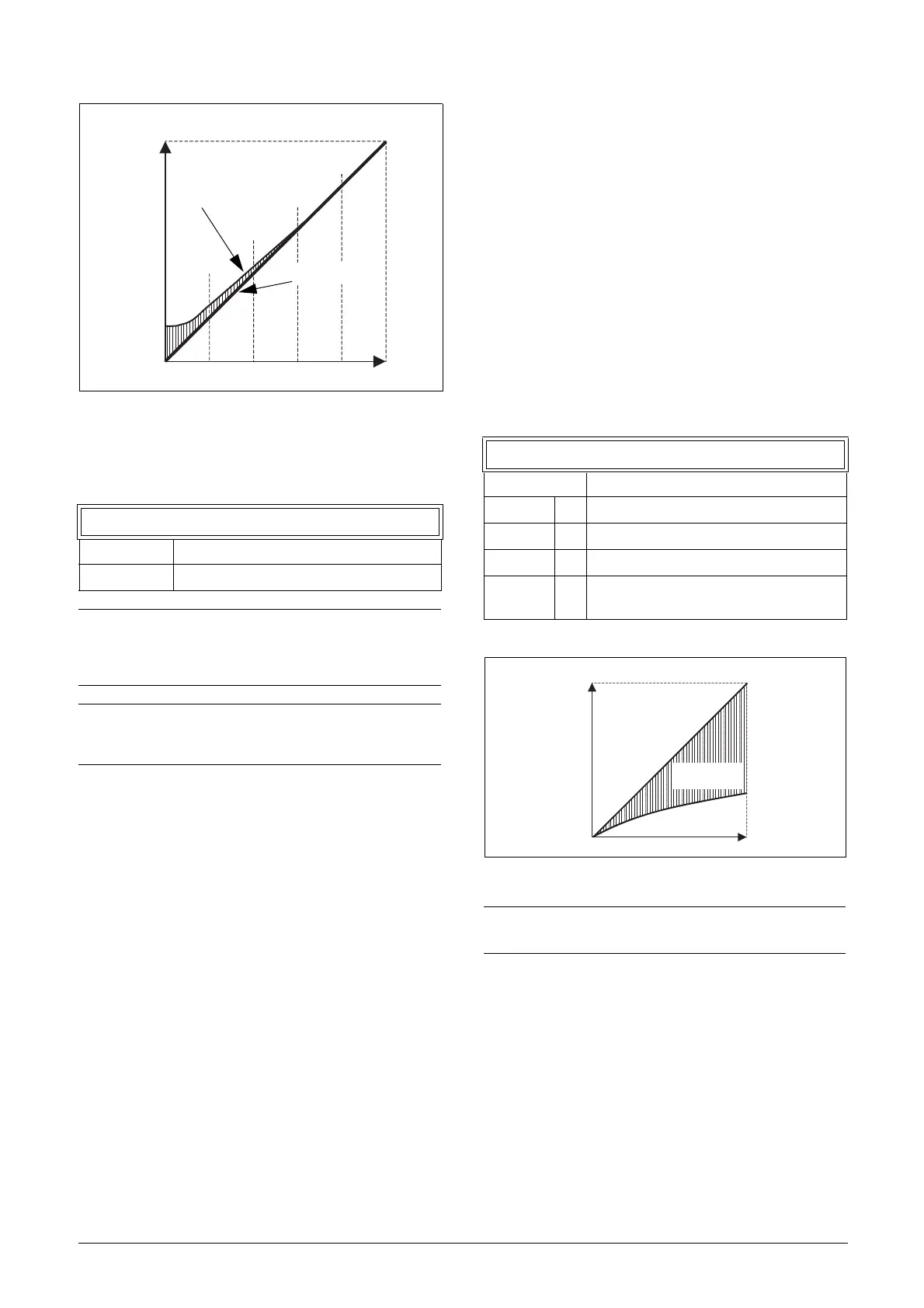
Fig. 106 IxR Comp at Linear V/Hz curve.
IxR Comp user [353]
Only visible if User-Defined is selected in previous menu.
Flux Optimization [354]
Asynchronous motors
Flux Optimization for asynchronous motors reduces the
energy consumption and the motor noise, at low or no load
conditions. Flux Optimization automatically decreases the
V/Hz ratio, depending on the actual load of the motor when
the process is in a steady state. fig. 107 shows the area within
which the Flux Optimization is active.
Permanent magnet synchronous and
synchronous reluctance motors
Flux optimization for permanent magnet synchronous
motors and synchronous reluctance motors adjusts the
V/Hz ratio, to either minimize the current or by predicting a
suitable level based on the torque (and speed). Note that
IxR compensation is needed for synchronous motors to get a
good start, also when flux optimization is activated.
Fig. 107 Flux Optimizing
353 IxR CompUsr
Default: 0.0%
Range: 0-25% x U
NOM
(0.1% of resolution)
NOTE: A too high level of IxR Compensation could
cause motor saturation. This can cause a “Power
Fault” trip. The effect of IxR Compensation is
stronger with higher power motors.
NOTE: The motor may be overheated at low speed.
Therefore it is important that the Motor I
2
t Current
[232] is set correctly.
10 20 30 40 50
Hz
f
25
%
U
100
354 Flux optim
Default: Off
Off 0 Function disabled
On (lmin) 1 Flux controlled to minimize current
On (n, T) 2 Flux adjusted based on the torque
On (cos
ϕ)3
Flux controlled to minimize reactive
power.
NOTE: Flux optimization works best at stable
situations in slow changing processes.

 Loading...
Loading...