7-12
7.1.3.4 Calculating the RMS rating of the motor
In case of the load which is repeatedly and very frequently driven by a motor, the load current fluctuates
largely and enters the short-time rating range of the motor repeatedly. Therefore, you have to review the
thermal allowable rating of the motor. The heat value is assumed to be approximately proportional to the
square of the load current.
If an inverter drives a motor in duty cycles that are much shorter than the thermal time constant of the motor,
calculate the "equivalent RMS current" as mentioned below, and select the motor so that this RMS current
will not exceed the rated current of the motor.
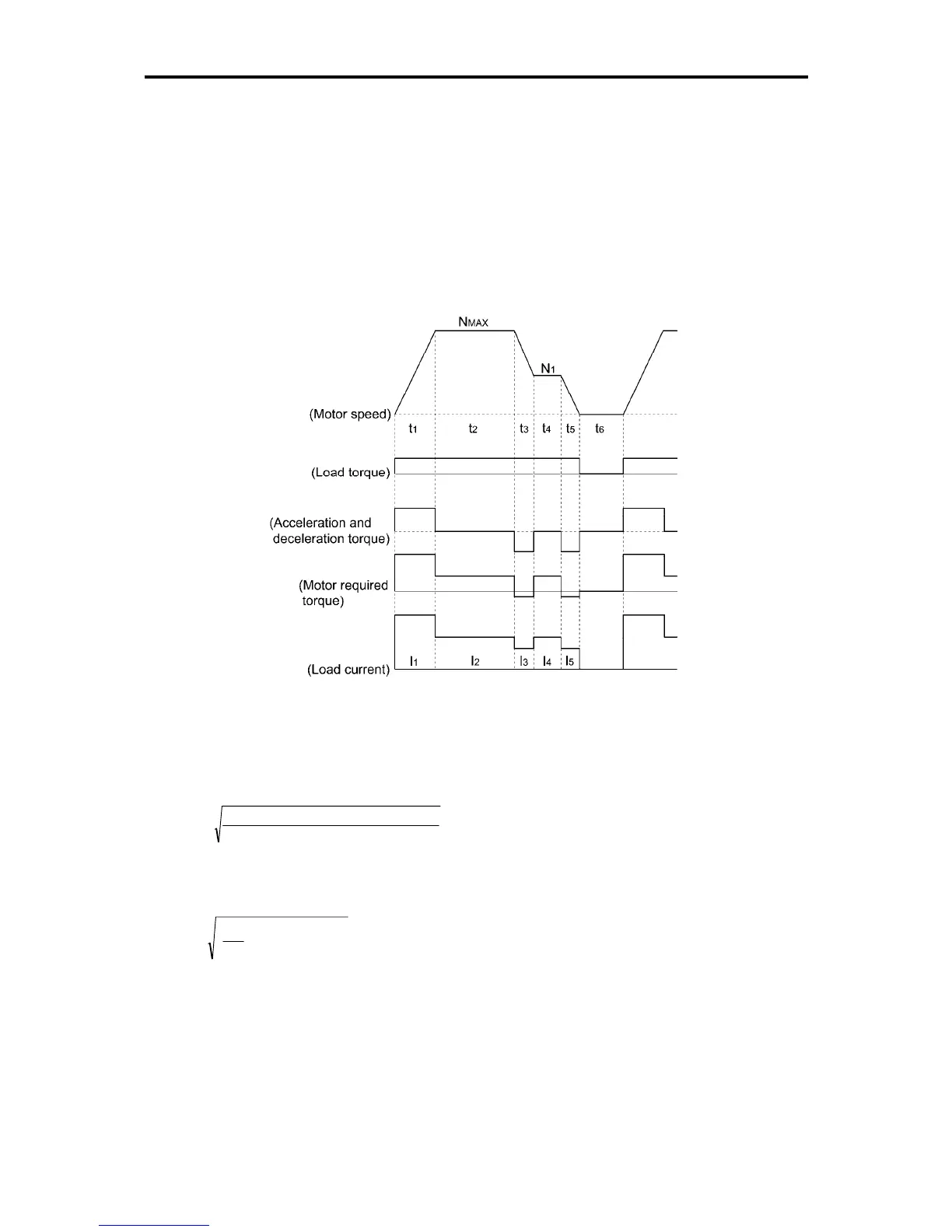
Figure 7.10 Sample of the Repetitive Operation
First, calculate the required torque of each part based on the speed pattern. Then using the
torque-current curve of the motor, convert the torque to the load current. The "equivalent RMS current,
Ieq" can be finally calculated by the following equation:
(A)
t
+
t
+
t
+
t
+
t
+
t
t
I
+
t
I
+
t
I
+
t
I
+
t
I
=
I
654321
5
•
2
5
4
•
2
4
3
•
2
3
2
•
2
2
1
•
2
1
eq
(7.15)
The torque-current curve for the dedicated motor is not available for actual calculation. Therefore,
calculate the load current I from the load torque τ
1
using the following equation (7.16). Then, calculate
the equivalent current I
eq:
(A)
I
m100
I
100
τ
I
2
2
t100
1
+
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
×=
(7.16)
Where, τ
1
is the load torque (%), I
t100
is the torque current, and I
m100
is exciting current.

 Loading...
Loading...











