67
Severit
y value
Level Description
3 Error Error condition. For example, the link state changes.
4 Warning
Warning condition. For example, an interface is disconnected, or the memory
resources are used up.
5 Notification
Normal but significant condition. For example, a terminal logs in to the device,
or the device reboots.
6 Informational
Informational message. For example, a command or a ping operation is
executed.
7 Debugging Debug message.
Log destinations
The system outputs logs to the following destinations: console, monitor terminal, log buffer, log host,
and log file. Log output destinations are independent and you can configure them after enabling the
information center.
Default output rules for logs
A log output rule specifies the source modules and severity level of logs that can be output to a
destination. Logs matching the output rule are output to the destination. Table 7
shows the default log
output rules.
Table 7 Default output rules
Destination Log source modules Output switch Severity
Console All supported modules Enabled Debug
Monitor terminal All supported modules Disabled Debug
Log host All supported modules Enabled Informational
Log buffer All supported modules Enabled Informational
Log file All supported modules Enabled Informational
Default output rules for diagnostic logs
Diagnostic logs can only be output to the diagnostic log file, and cannot be filtered by source
modules and severity levels. Table 8 sh
ows the default output rule for diagnostic logs.
Table 8 Default output rule for diagnostic logs
Destination Log source modules Output switch Severity
Diagnostic log file All supported modules Enabled Debug
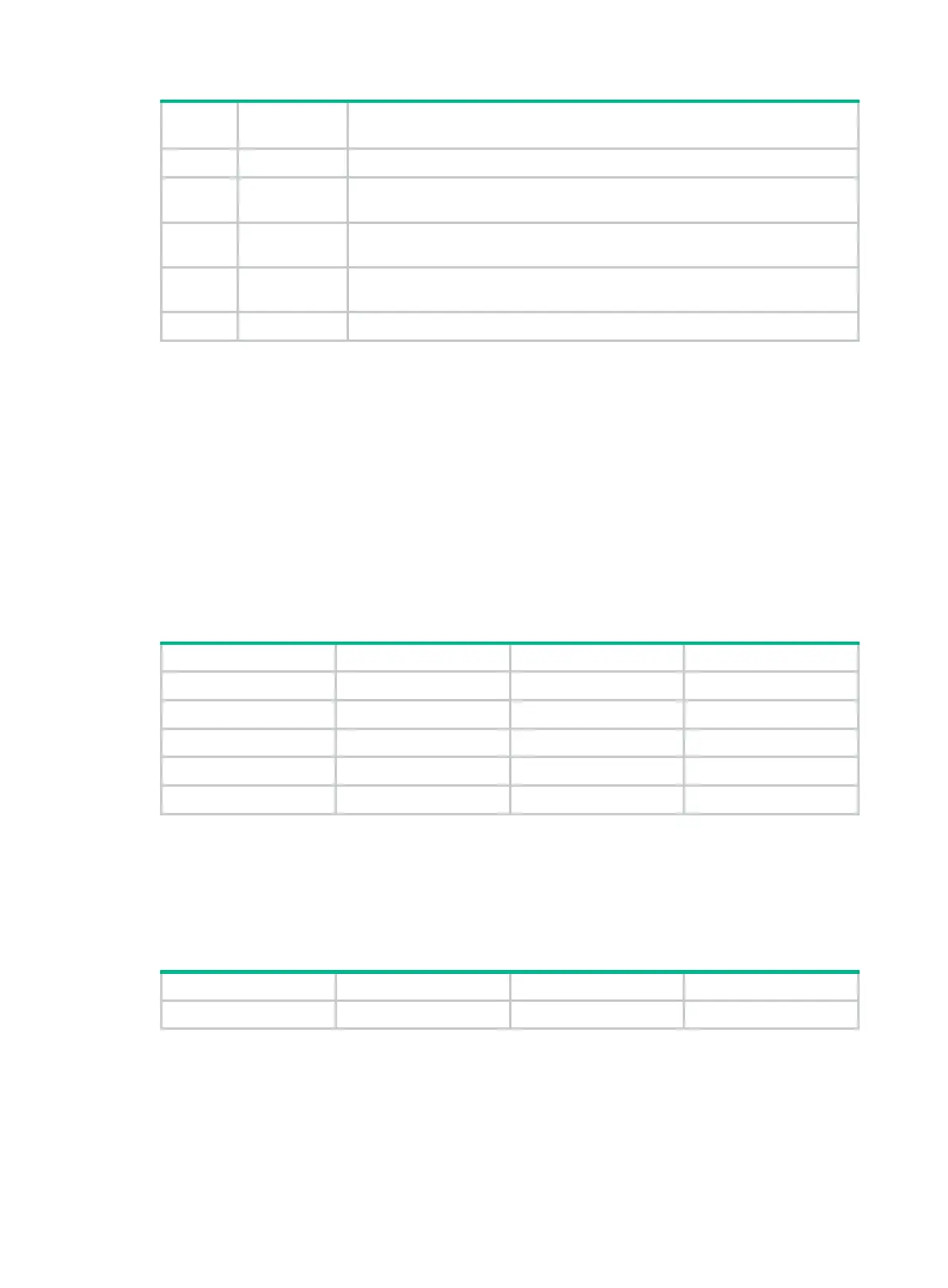
Default output rules for security logs
Security logs can only be output to the security log file, and cannot be filtered by source modules and
severity levels. Table 9 sh
ows the default output rule for security logs.

 Loading...
Loading...











