Number of
discrete
reectances
greater than –55
dB
QSFP28 50G-FR
(Maximum value
of each discrete
reectance)
QSFP28 50G-LR
(Maximum value
of each discrete
reectance)
QSFP28 50G-ER
(Maximum value
of each discrete
reectance)
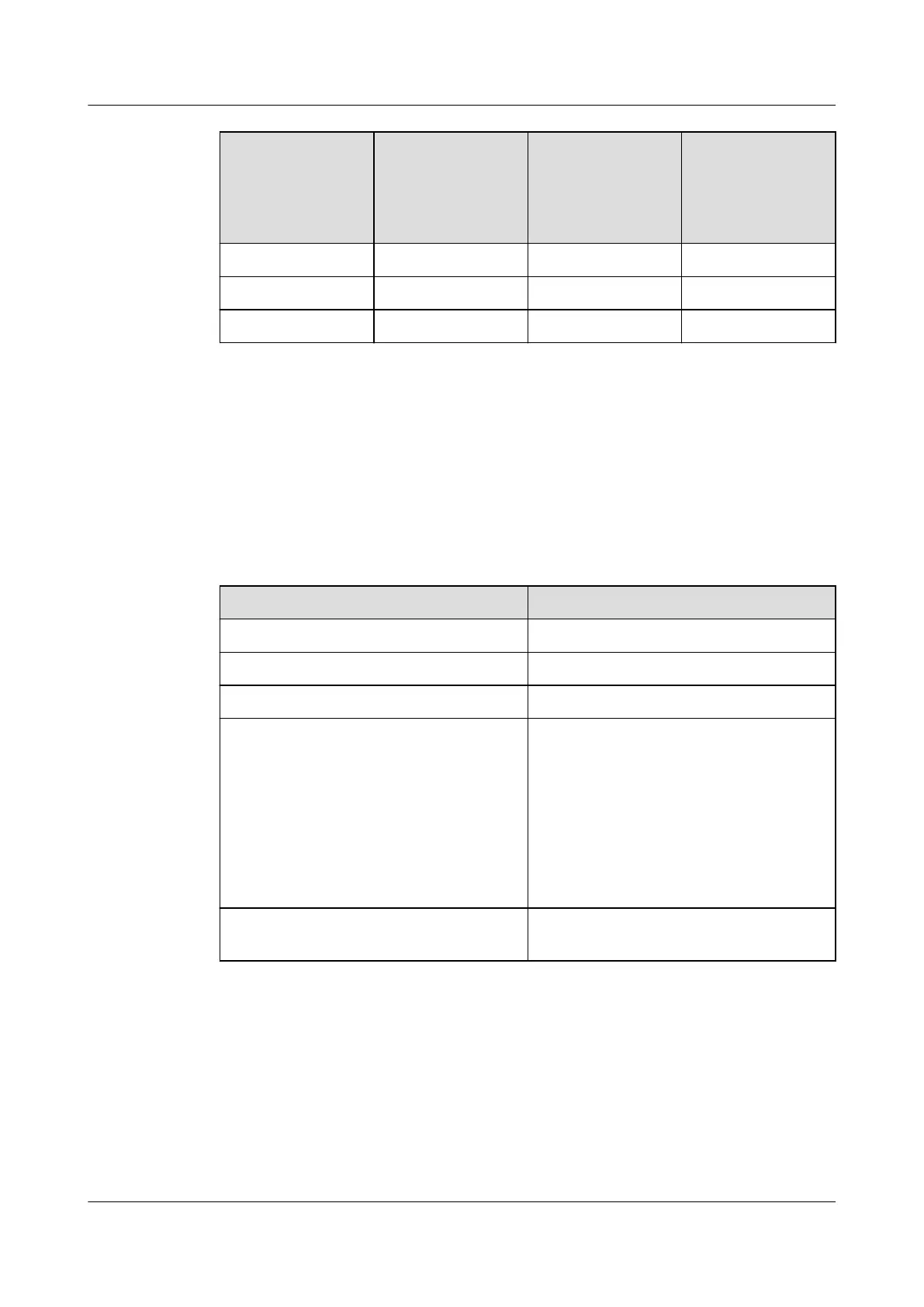
6 -38 dB -35 dB -35 dB
8 -40 dB -37 dB -37 dB
10 -41 dB -39 dB -39 dB
3.4.1.5
Conguring an Optical Attenuator
This section describes how to congure an optical attenuator.
Calculating the Optical Attenuation
You can calculate the optical attenuation based on the actual optical power.
Table 3-91 Description of the Paramater
Name
Description
P(in)min maximum transmit optical power.
P(out)max transmission distance.
S transmission distance.
A attenuation coecient. Note that the
attenuation coecient is related to
optical ber types and wavelengths. By
default, the attenuation coecient of
a 1310-nm wavelength in a G.652
ber is 0.45 dBm/km or 0.4 dBm/km;
the attenuation coecient of a 1550-
nm wavelength in a G.652 ber is
0.235 dBm/km or 0.25 dBm/km.
P(in)max maximum receive optical power, that
is, minimum overload point.
The principle for determining whether an attenuator needs to be congured at a
transmission point is as follows:
If P(out)max – S x Attenuation
coecient > P(in)max, an attenuator needs to be
congured. The optical attenuation is calculated in the following formula: T=
P(out)max - S x Attenuation
coecient - P(in)max.
HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F
Hardware Guide 3 Hardware Description
Issue 05 (2023-03-31) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 117

 Loading...
Loading...











