Appendix B
-
142
-
Appendix B Denition of Communication Data Address and Mod-
bus Communication Protocol
B.1 Denition of Communication Data Address
The drive supports four communication protocols (Modbus-RTU, CANopen, CANlink, and PROFIBUS-DP2).
The user programmable card and point-to-point communication are derivation of CANlink protocol. The host
computer can implement control such as monitoring and parameter viewing and modication on the AC drive
through their protocols.
The drive's communication data is classied into parameter data and non-parameter data. The non-parameter
data includes running commands, running status, running parameters and alarm information.
B.1.1 Parameter Data
The parameter data provides important parameters of the AC drive. In addition to function parameter group F
of MD320, MD500 provides the function parameter group A.
The parameter data is described as below:
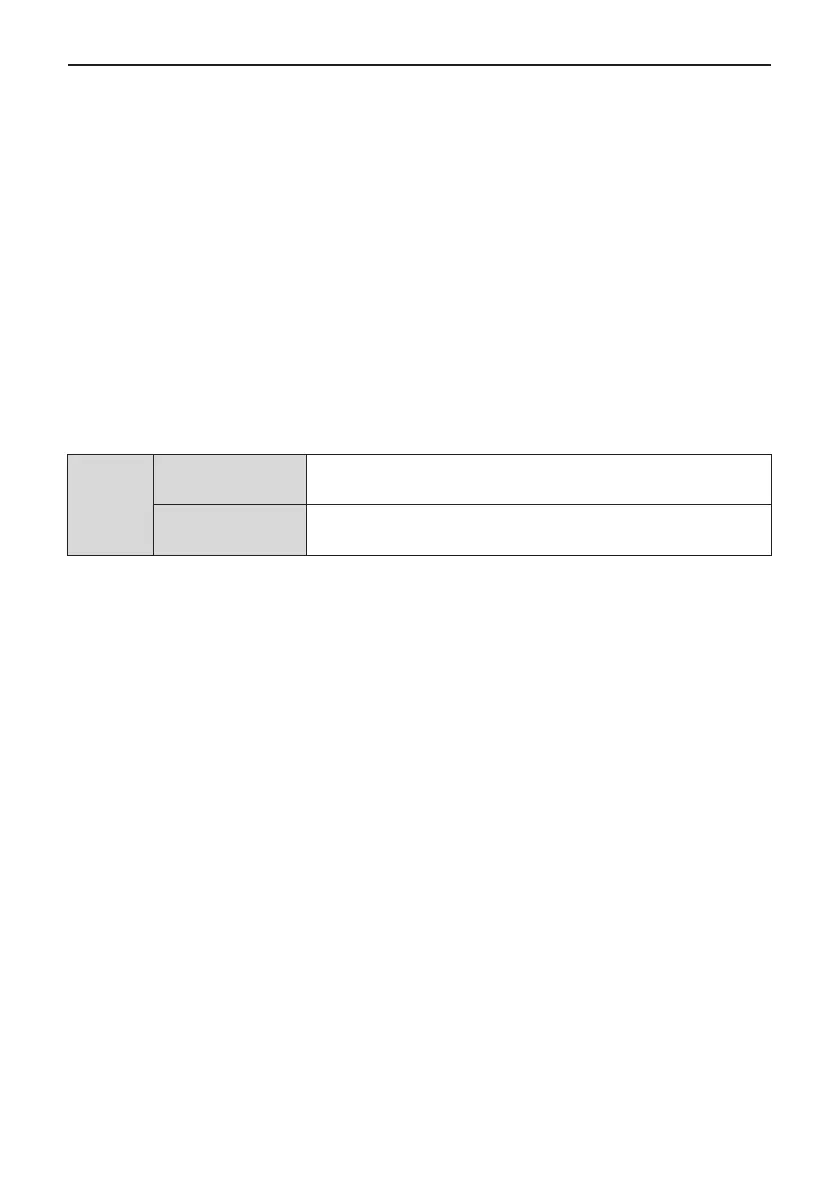
MD500
Parameter
Data
Group F (read-write) F0, F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8, F9, FA, FB, FC, FD, FE, FF
Group A (read-write) A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, AA, AB, AC, AD, AE, AF
Communication addresses of parameter data are dened as follows:
1. Read Function code by communication
For groups F0 to FF and A0 to AF, the high 16 bits of the communication address indicate the group number
and the low 16 bits indicate the parameter number in the group.
Example: Communication address of F0-16 is F010H, where F0H represents group F0 and 10H is the hexa-
decimal data format of serial number 16 in the group.
Communication address of AC-08 is AC08H, where ACH represents group AC and 08H is the hexadecimal data
format of serial number 8 in the group.
2. Write Function code by communication
For groups F0 to FF, whether the high 16 bits in communication address are 00 to 0F or F0 to FF is decided by
whether the high 16 bits are written to EEPROM. The low 16 bits indicate parameter number in the group. Ex-
ample:
F0-16:
If it needs not be written to EEPROM, communication address is 0010H.
If it needs to be written to EEPROM, communication address is F010H.
For groups A0 to AF, whether the high 16 bits in communication address are 40 to 0F or A0 to AF is decided by
whether the high 16 bits are written to EEPROM. The low 16 bits indicate parameter number in the group. Ex-
ample:
AC-08:
If it needs not be written to EEPROM, communication address is 4C08H.
If it needs to be written to EEPROM, communication address is AC08H.

 Loading...
Loading...











