9. Others
MKC-710 113
Principle of measurement 9-4.
In the Karl Fisher moisture content measurement, water reacts with iodine and
sulfur dioxide in the presence of base and alcohol.
H
2
O + I
2
+ SO
2
+ CH
3
OH + 3RN o [RNH]SO
4
CH
3
+ 2[RNH]I ................. (1)
In the volumetric titration, iodine is added as a titrant. In the coulometric
technique, iodine is electrolytically generated in the anolyte, which contains
iodide.
2I
-
o I2 + 2e
-
..................................................................................... (2)
As long as water is present in the titration cell the generated iodine reacts
according to (1).
As soon as all the water reacts, excess of iodine appears in the anolyte. This
iodine is detected by the platinum electrode and the iodine production is stopped.
According to Faraday's law, the quantity of iodine produced is proportional to the
current generated. In equation (1), I
2
and H
2
O react with each other in
proportion 1:1.
Therefore a mole of water (18 g) is equivalent to 2 u 96500 coulombs, or 10.72
coulombs/ 1 mg H
2
O. The total amount of moisture can thus be determined by
measuring the total consumption of electricity.
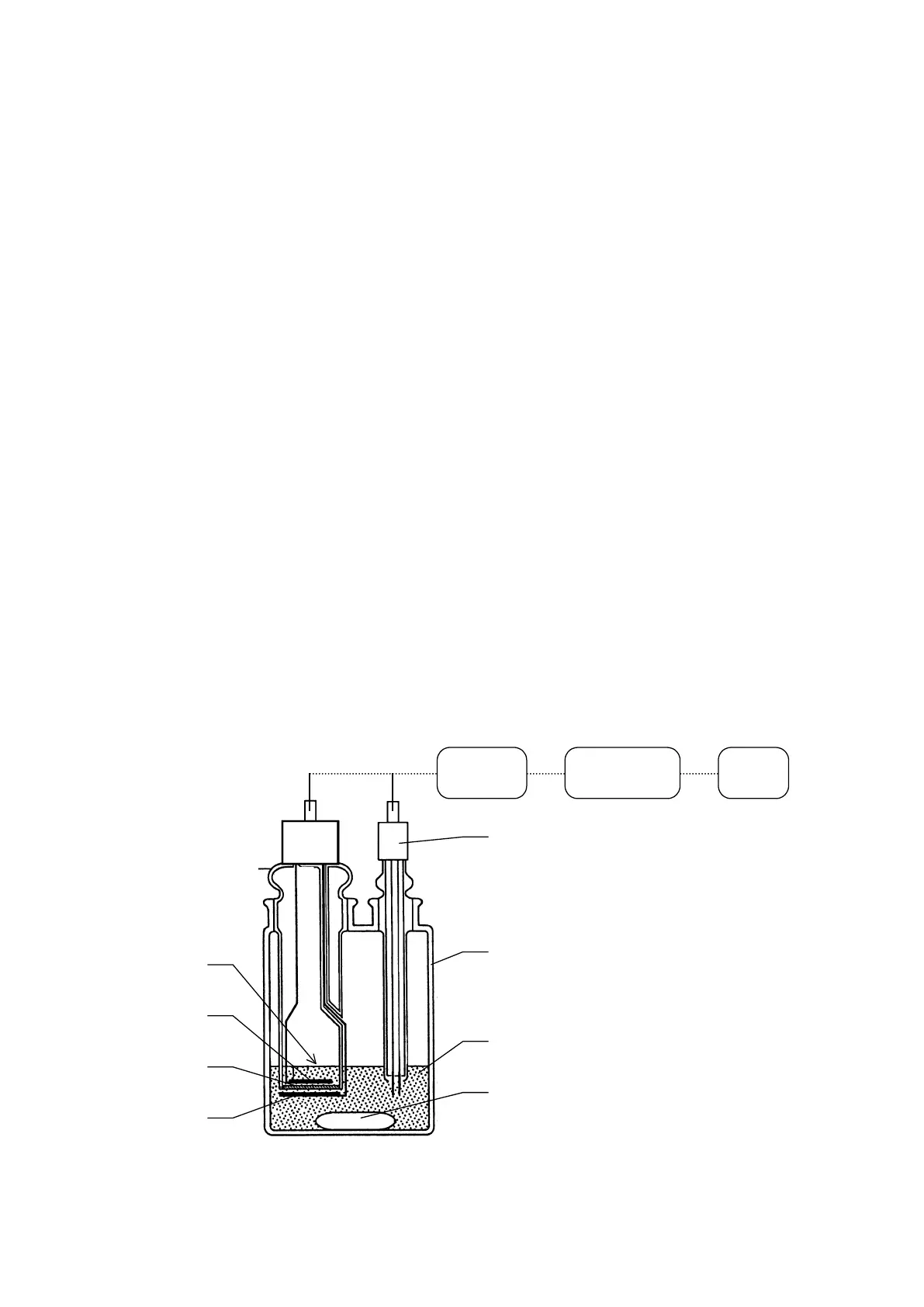
Detection/
control
Microcomputer Display
Detection electrode
(twin platinum electrode)
Titration cell
Anolyte
Rotor
Anode
Membrane
Cathode
Catholyte
 Loading...
Loading...