82 Keysight InfiniiVision 2000 X-Series Oscilloscopes User's Guide
4 Math Waveforms
Aliasing happens when there are frequency components in the signal higher than
half the sample rate. Because the FFT spectrum is limited by this frequency, any
higher components are displayed at a lower (aliased) frequency.
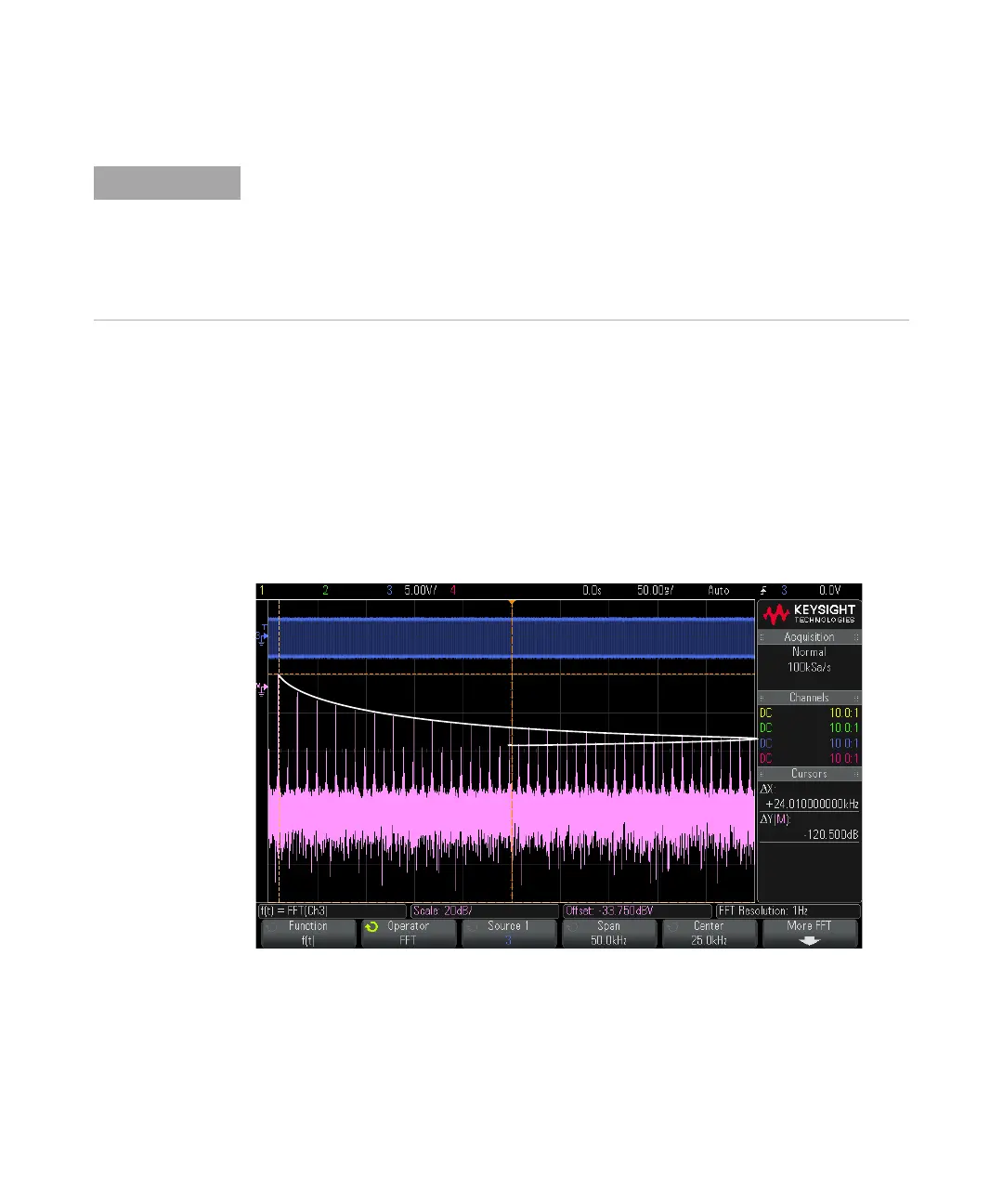
The following figure illustrates aliasing. This is the spectrum of a 990 Hz square
wave, which has many harmonics. The sample rate is set to 100 kSa/s, and the
oscilloscope displays the spectrum. The displayed waveform shows the
components of the input signal above the Nyquist frequency to be mirrored
(aliased) on the display and reflected off the right edge.
Nyquist Frequency and Aliasing in the Frequency Domain
The Nyquist frequency is the highest frequency that any real-time digitizing oscilloscope can
acquire without aliasing. This frequency is half of the sample rate. Frequencies above the
Nyquist frequency will be under sampled, which causes aliasing. The Nyquist frequency is also
called the folding frequency because aliased frequency components fold back from that
frequency when viewing the frequency domain.
Figure 7 Aliasing
 Loading...
Loading...











