133
KMHA 500-000099
Revision D
KDR
TM
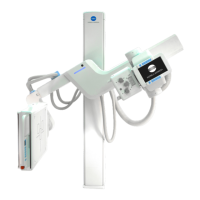
AU-DDR Advanced U-Arm System with
Dynamic Digital Radiography (KDR AU DDR)
VIII. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
31.0 EXPOSURE INDEX
The Exposure Index ( hereafter, EI) complies with IEC62494-1 (issued in 2008) to show the exposure dose received by
the detector. Using EI means the exposure dose received by detector can be compared to a common scale for different
manufacturers. The KDR AU DDR calculates and displays the Exposure Index (hereafter, EI) and Deviation Index (hereafter,
DI) for each exposure, displays the TI (hereafter, TI or EIT) for each exposure, and can send in a DICOM tag. EI is used as a
measure for image quality versus the dose, but it is not used to manage patient exposure doses.
31.1 Exposure Index Calculation Flow
The calculation ow stipulated by IEC62494-1 is as follows:
1. Select the Relevant Image Region for the exposure image Raw Data.
2. Calculate the Value of Interest from the data within the Relevant Image Region.
3. Convert the Value of Interest to a detector exposure.
4. Calculate the EI (ensure that EI=100 in advance when image receptor AIR KERMA at radiation quality RQA5 is
1μGy).
IEC62494-1 does not specify (1) the selection method for Relevant Image Region, or (2) calculation method for Value of In-
terest above, and these have been specied by each individual manufacturer. As Konica Minolta considers that the "region
of image quality to be managed with EI (Relevant Image Region), and region to display as the ideal diagnostic image using
image processing (Region of Interest)" should be the same, the Region of Interest (hereafter, ROI) that uses automatic
grayscale processing is used as the Relevant Image Region. The Value of Interest is also based on the standard signal value
calculated using histogram analysis after setting ROI using the same automatic grayscale processing.
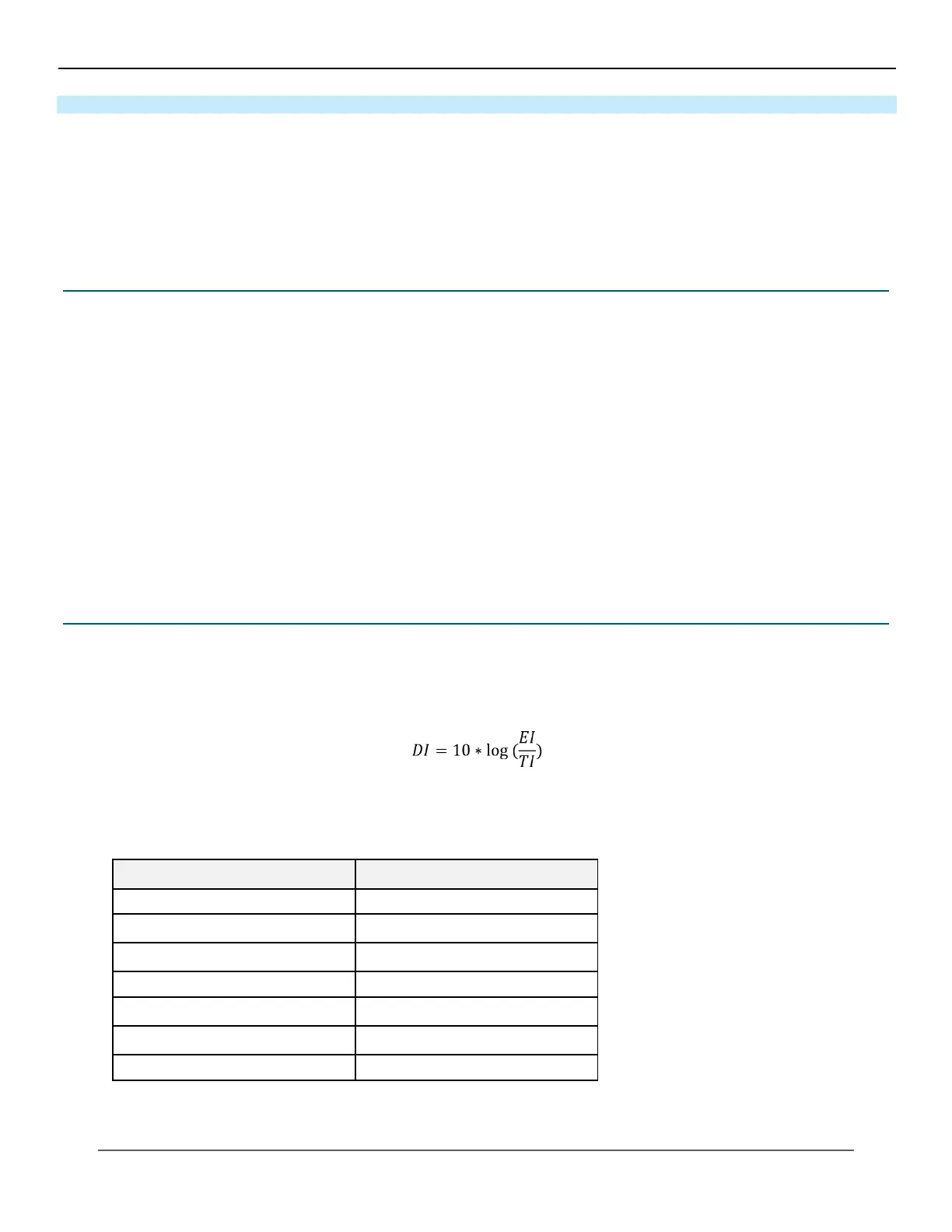
31.2 Calculation of Deviation Index
According to IEC62494-1, image quality should be managed by viewing the amount of deviation (DI) from the target value
(TI), rather than the EI value itself. DI is calculated using the following formula if the TI of each part set in advance, and the
EI acquired from the actual exposed image are granted.
When there is a difference between EI and TI (as shown in the table below), DI=0 when EI is equal to TI, a negative value
when it is smaller than TI, and a positive value if it is larger than TI.
DI Dierence between EI and TI
-3 -50 % (1/2 dose)
-2 -37 %
-1 -21 %
0 0 % (target dose)
1 26%
2 58%
3 100% (double dose)
 Loading...
Loading...