9. Navigation and control system
MiR1000 User Guide (en) 12/2020 - v.1.4 ©Copyright 2019-2020: Mobile Industrial Robots A/S. 63
9.2 User input
To enable the robot to navigate autonomously, you must provide the following:
• A map of the area, either from a .png file or created with the robot using the mapping
function—see Creating and configuring maps on page 102.
• A goal destination on that map—see Markers on page 114.
• The current position of the robot on the map. This usually only needs to be provided when
a new map is activated.
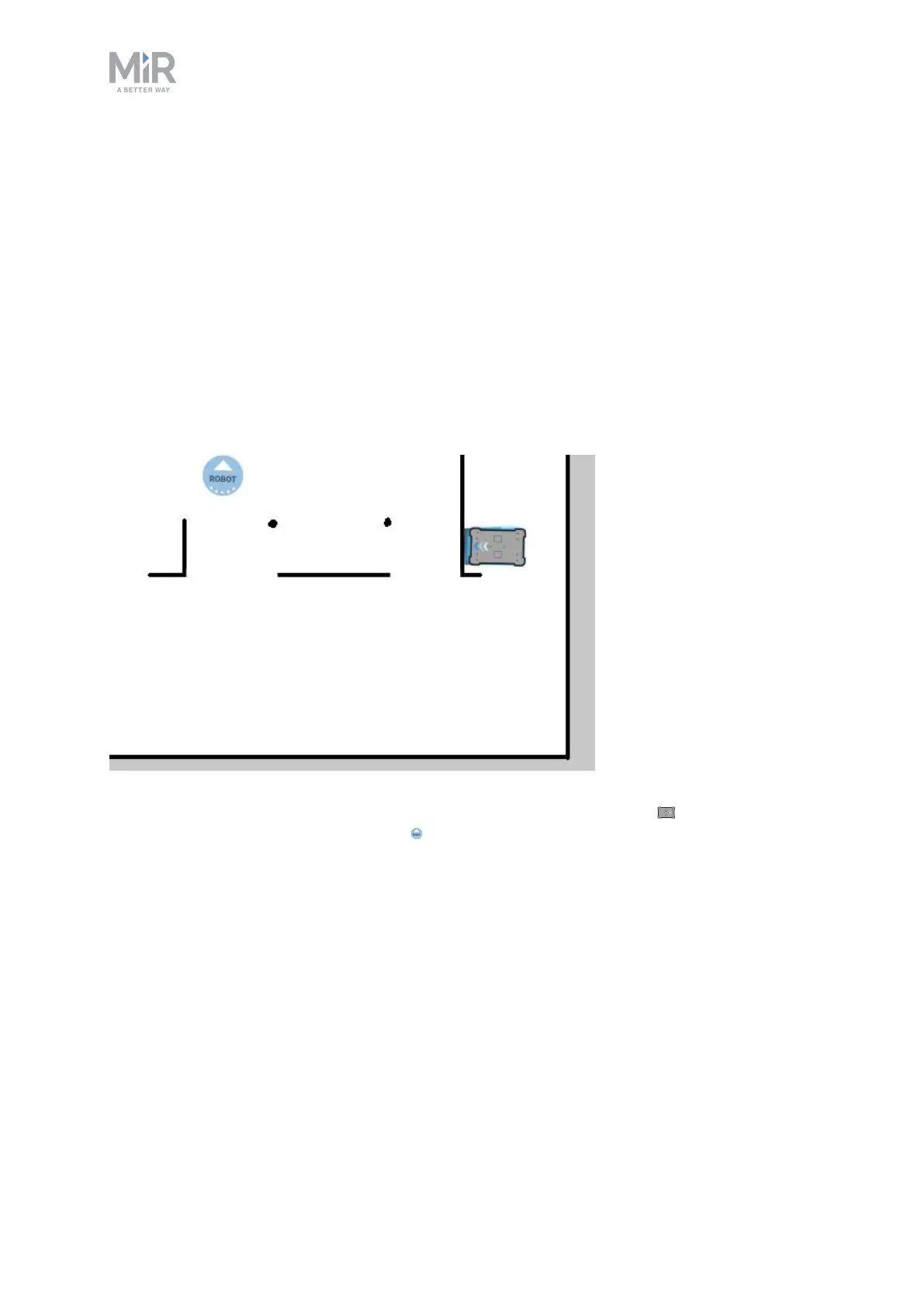
Figure 9.2. On the map, the current position of the robot is identified by the robot icon , and the goal
destination in this example is the robot position . The robot computer now determines a path from the
current position to the goal position.
Once the robot computer has a map with the robot's current position and a goal destination,
it begins planning a route between the two positions on the map using the global planner.
9.3 Global planner
The global planner is an algorithm in the robot computer that generates a path to the goal
position.This path is known as the global path.
 Loading...
Loading...