FX Series Programmable Controllers Devices in Detail 4
4-44
4.15.1 Scientific Notation
This format could be called the step between the ‘integer’ formats and the full floating point
formats. In basic terms Scientific Notation use two devices to store information about a number
or value. One device contains a data string of the actual characters in the number (called the
mantissa), while the second device contains information about the number of decimal places
used in the number (called the exponent). Hence, Scientific Notation can accommodate values
greater/smaller than the normal 32 bit limits, i.e. -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 where
Scientific Notation limits are;
Maximums Minimums
9999 5 10
35
9999 5 10
-41
-9999 5 10
35
-9999 5 10
-41
Scientific Notation can be obtained by using the BCD, or EBCD in FX2N, instruction (FNC 18 or
FNC 118) with the float flag M8023 set ON. In this situation floating point format numbers are
converted by the BCD instruction into Scientific Notation - see page 5-22 for details. When
using the FX2N the INT instruction (FNC 129) can be used.
Scientific Notation can be converted back to floating point format by using the BIN instruction
(FNC 19) with the float flag M8023 set ON - see page 5-22 for details.
The following points should be remembered about the use of Scientific Notation within
appropriate FX units;
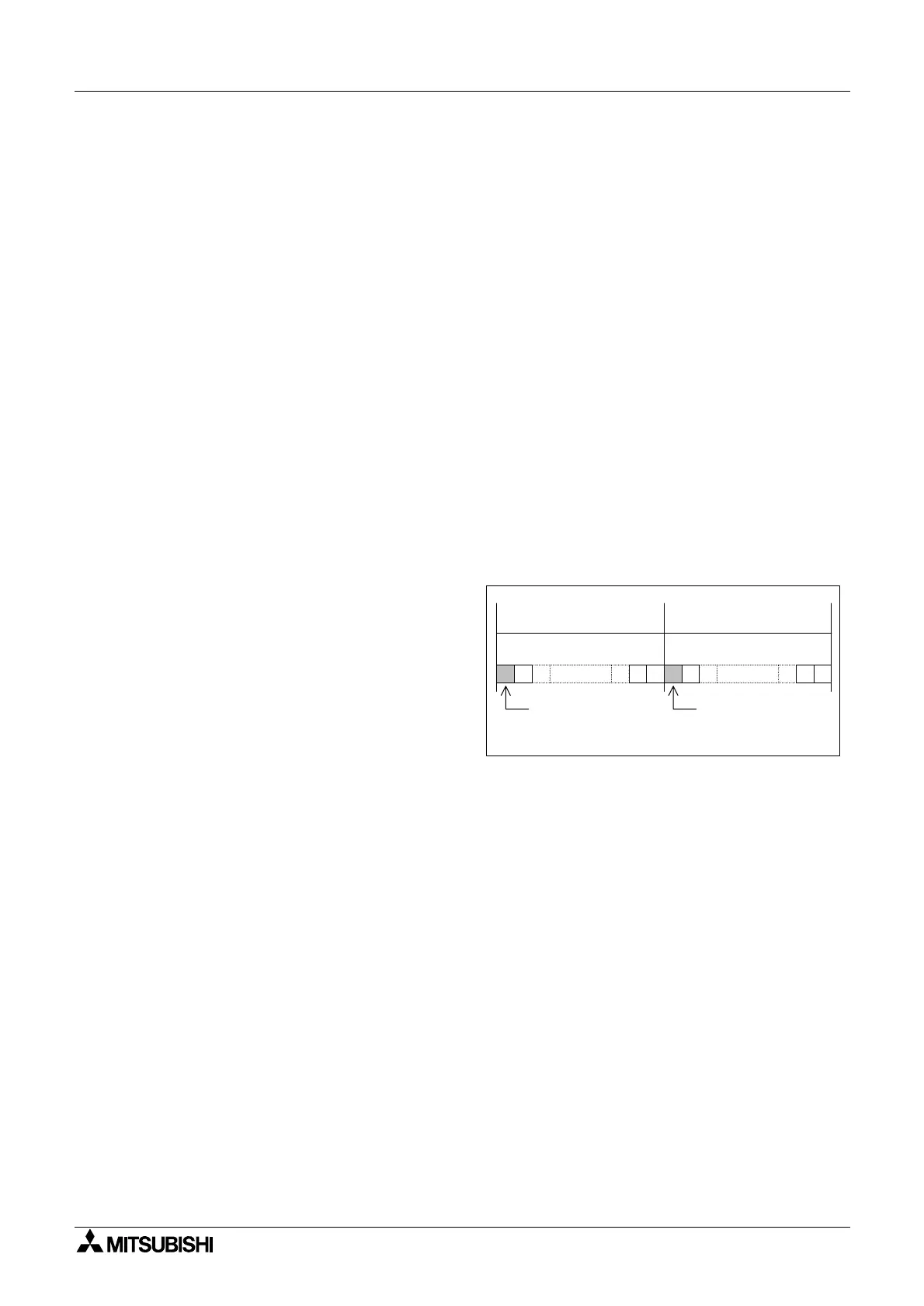
• The mantissa and exponent are stored
in consecutive data registers.
Each part is made up of 16 bits and can
be assigned a positive or negative value
indicated by the value of the most
significant bit (MSB, or bit 15 of the data
register) for each number.
• The mantissa is stored as the first 4
significant figures without any rounding
of the number, i.e. a floating point number of value 2.34567 5 10
3
wouldbestoredasa
mantissa of 2345 at data register D and an exponent of 0 (zero) at data register D+1.
• The range of available mantissa values is 0, 1000 to 9999 and -1000 to -9999.
• The range of available exponent values is +35 through to -41.
• Scientific format cannot be used directly in calculations, but it does provide an ideal method
of displaying the data on a monitoring interface.
b0b15 b15 b0
EXPONENT MANTISSA
Sign bit (MSB)
1= Negative
0 = Positive
Sign bit (MSB)
1= Negative
0= Positive
Data Register D+1 Data Register D

 Loading...
Loading...











