4MELFA-BASIC IV
Detailed explanation of command words 4-172
[Explanation]
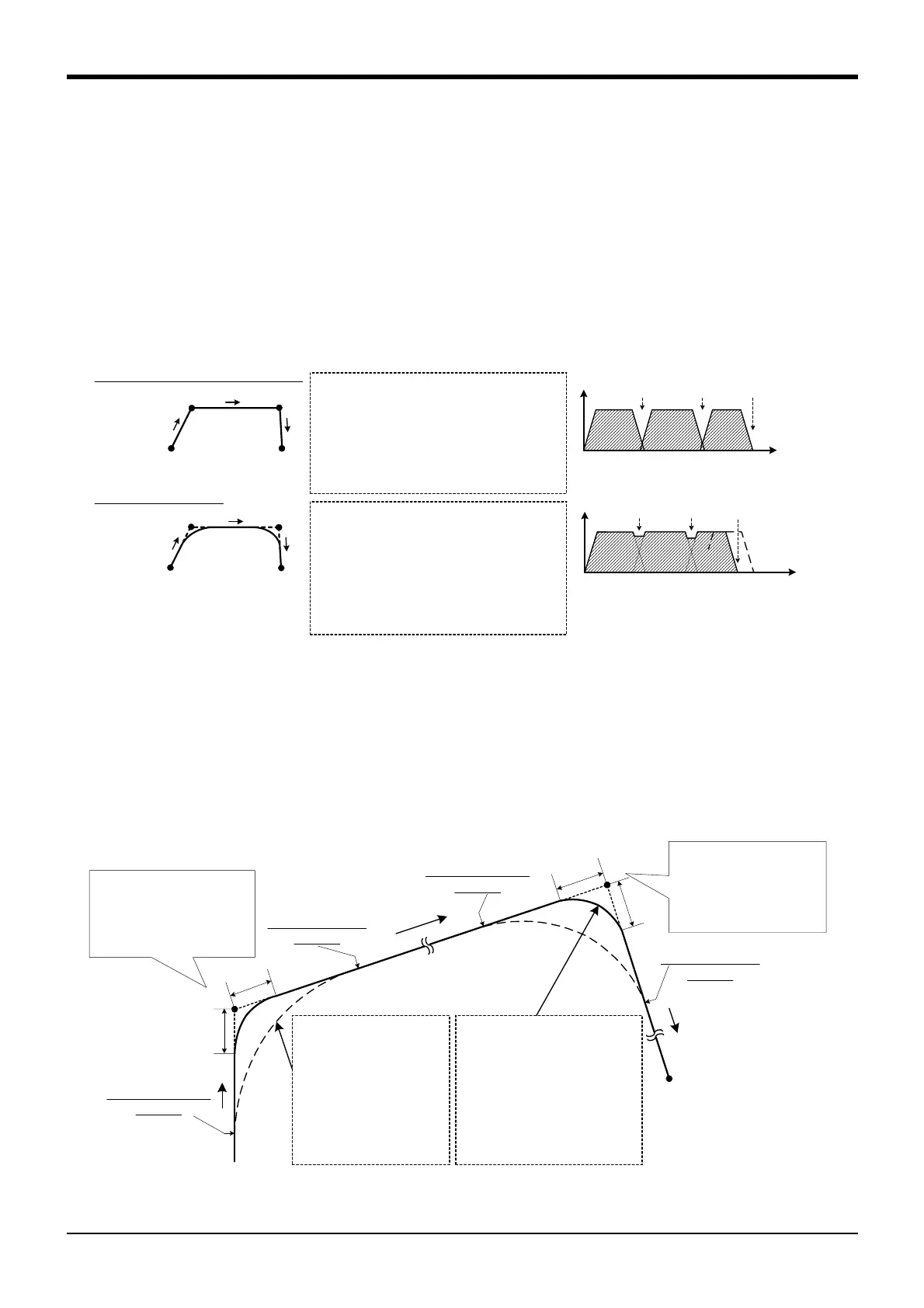
(1) The interpolation (40 step to 80 step of the example) surrounded by Cnt 1 - Cnt 0 is set as the target of
continuous action.
(2) The system default value is Cnt 0 (Acceleration/deceleration movement).
(3) If values 1 and 2 are omitted, the connection with the next path segment is started from the time the
deceleration is started.
(4) As shown in Fig. 4-7, in the acceleration and deceleration operating mode, the speed is reduced in front
of the target position. After moving to the target position, the speed for moving to the next target position
starts to be accelerated. On the other hand, in the continuous operating mode, the speed is reduced in
front of the target position, but it does not stop completely. The speed for moving to the next target posi-
tion starts to be accelerated at that point. Therefore, it does not pass through each target position, but it
passes through the neighborhood position.
Fig.4-7:Acceleration/deceleration movement and continuous movement
(5) The neighborhood distance denotes the changing distance to the interpolation operation at the next tar-
get position. If this neighborhood distance (numerical value 1, numerical value 2) is omitted, the accel-
erate and deceleration starting position will be the changing position to the next interpolation. In this
case, it passes through a location away from the target position, but the operating time will be the short-
est. To pass through a location closer to the target position, set this neighborhood distance (numerical
value 1, numerical value 2).
Fig.4-8:Setting Up the Neighborhood Distance
10 MOV P1
20 MVS P2
30 MOV P3
It decelerates and accelerates to P1, P2
and P3. After moving to the target position,
it moves to the next target position.
10 CNT 1
20 MOV P1
30 MVS P2
40 MOV P3
50 CNT 0
It passes through the neighborhood of P1
and P2, and then moves to P3.
P1
P2
P3
Start position of
movement
Acceleration/deceleration movement
P1 P2
P3
Continuous movement
P3
P2
t (Time)
P1
v (Speed)
P3P2
P1
*The above graph shown an example.
Depending on the moving distance and/or
speed, acceleration and deceleration may
occur during interpolation connection.
Start position of
movement
v (Speed)
t (Time)
P1
P2
P3
If the neighborhood
distance is not specified,
dotted line operation will
be performed.
10 CNT 1
20 MOV P1
30 MVS P2
40 MOV P3
50 CNT 0
If the neighborhood distance
is specified, solid line
operation will be performed.
10 CNT 1, MA, MB
20 MOV P1
30 CNT 1, MC, MD
40 MVS P2
50 MOV P3
60 CNT 0
Deceleration start
position
Acceleration end
position
MB
MC
MC
MD
If the MB and MC values
are different, connection
is made using a value
lower than the smaller of
these two values.
*If "30 CNT 1, MC, MD" are
not described, the value of
MC in the figure will be MA,
and the value of MD will be
MB.
Acceleration end
position
Deceleration start
position
If the MB and MC values
are different, connection
is made using a value
lower than the smaller of
these two values.

 Loading...
Loading...











