MPLS Guide MPLS and RSVP-TE
3HE 18686 AAAB TQZZA © 2022 Nokia.
Use subject to Terms available at: www.nokia.com
75
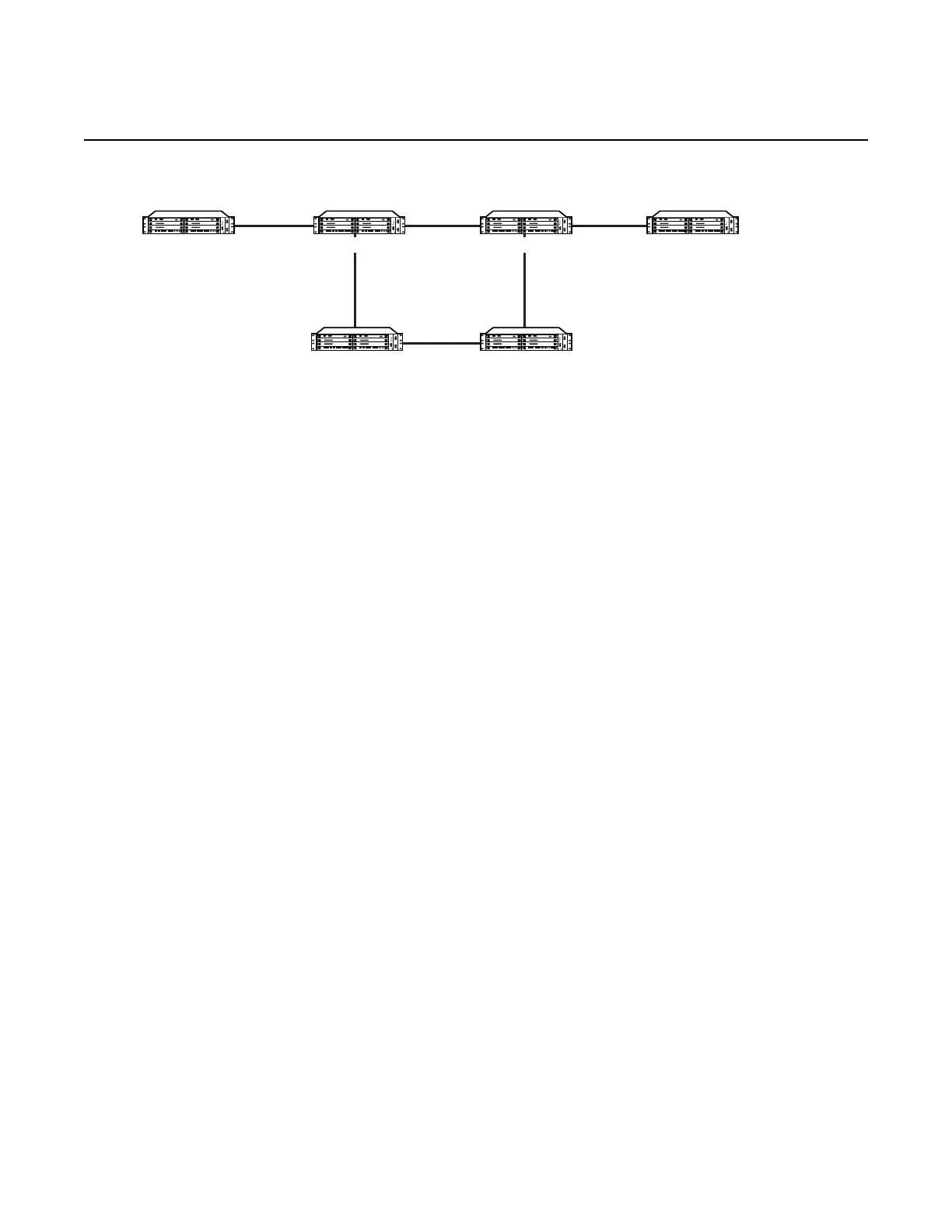
Figure 8 Bypass Tunnel Node Example
The PLR uses the following rules to select a bypass LSP from among multiple
bypass LSPs (manually and dynamically created) when establishing the primary LSP
path or when searching for a bypass for a protected LSP that does not have an
association with a bypass tunnel.
1. The MPLS/RSVP-TE task in the PLR node checks for an existing manual
bypass tunnel that satisfies the constraints. If the PATH message for the primary
LSP path indicated that node protection is desired, which is the default LSP FRR
setting at the head-end node, then the MPLS/RSVP-TE task searches for a
node-protect bypass LSP. If the PATH message for the primary LSP path
indicated that link protection is desired, then it searches for a link-protect bypass
LSP.
2. If multiple manual bypass LSPs satisfying the path constraints exist, the PLR will
prefer a manual bypass LSP terminating closer to the PLR over a manual
bypass LSP terminating further away. If multiple manual bypass LSPs satisfying
the path constraints terminate on the same downstream node, the PLR selects
the one with the lowest IGP path cost, or if there is a tie, it picks the first one
available.
3. If none of the manual bypass LSPs satisfy the constraints and dynamic bypass
tunnels have not been disabled on the PLR node, then the MPLS/RSVP-TE task
in the PLR node checks to determine if any of the already established dynamic
bypass LSPs of the requested type satisfy the constraints.
4. If none of the dynamic bypass LSPs satisfy the constraints, then the MPLS/
RSVP-TE task will ask CSPF to check if a new dynamic bypass of the requested
type, node-protect or link-protect, can be established.
5. If the PATH message for the primary LSP path indicated node protection is
desired, and no manual bypass was found after Step 1, and/or no dynamic
bypass LSP was found after three attempts to perform Step 3, the MPLS/RSVP-
TE task will repeat Steps 1 to 3 looking for a suitable link-protect bypass LSP. If
none are found, the primary LSP will have no protection and the PLR node must
clear the Local Protection Available flag in the IPv4 address sub-object of the
RRO, starting in the next RESV refresh message it sends upstream.
Node A
Node E Node F
Node DNode B Node C
20123

 Loading...
Loading...