11. Module reference: Sequencer group NORD MODULAR G2 V1.1
Page 186
S
SS
S
E
EE
ER
RR
RI
II
IA
AA
AL
LL
L
C
CC
CO
OO
ON
NN
NN
NN
NE
EE
EC
CC
CT
TT
TI
II
IO
OO
ON
NN
N
1
1 1
1
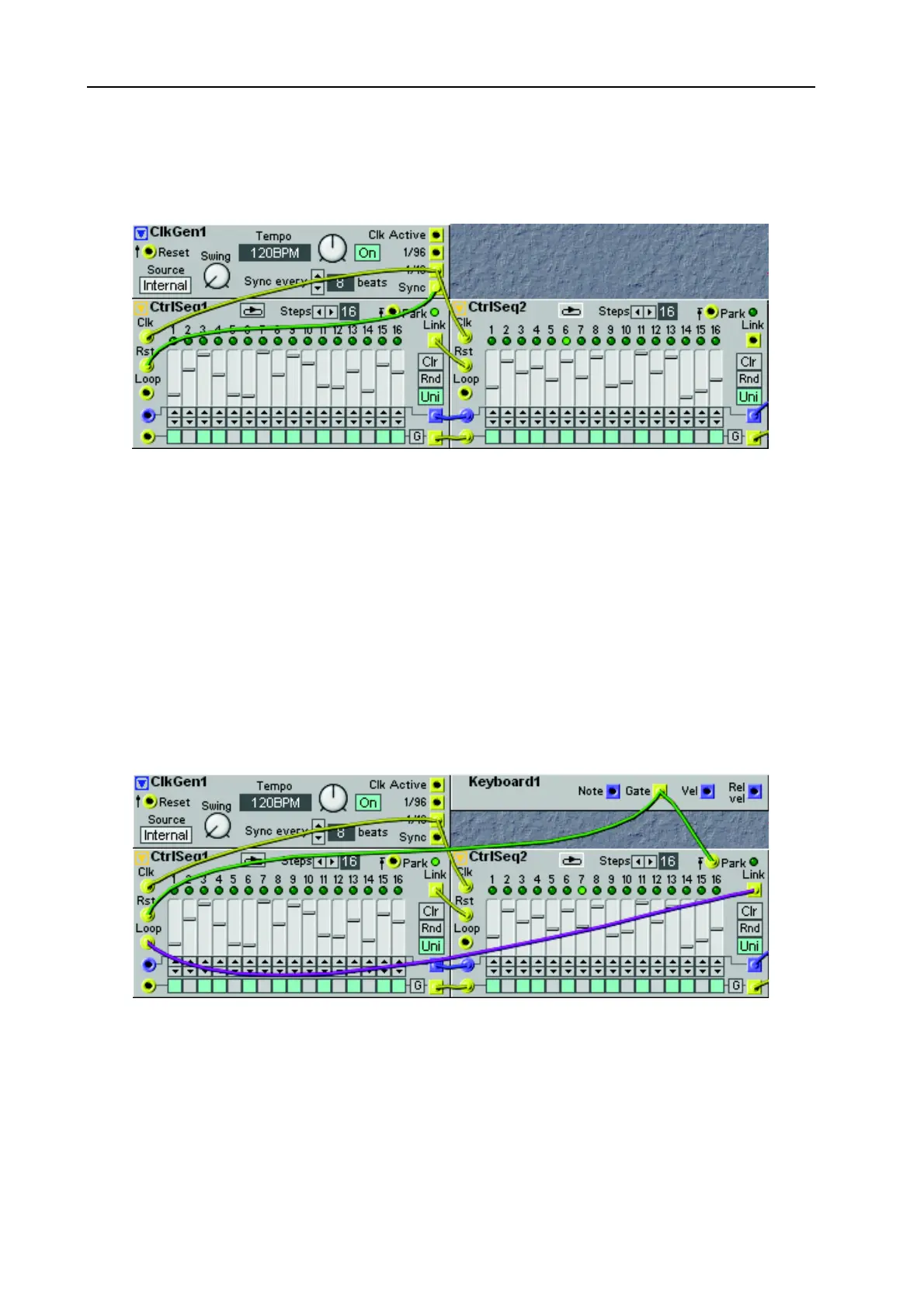
In this example we have created a 32 step sequence based on two “serially connected” Ctrl Sequencer
modules.
The Loop mode of the sequencers in this example must be set to off, otherwise they will continue to loop
after their last steps and this is not what we want. When the signal from the first sequencer’s Link output
resets the second sequencer, the second sequencer will start sequencing its 16 steps. The first sequencer
will be inactive until it receives a Sync signal on its Rst input from the Clock Generator. Note that the
Sync parameter of the Clock Generator is set to 8 beats. If set to the default 4 beats, the first sequencer
will automatically restart after 16 steps even though Loop mode is off.
To be able to route the control signals from both sequencers to a common destination without needing
to use a mixer module, connect the Control signal Out from the first sequencer to the Control signal In
of the second sequencer. This way, the control signal from the first sequencer will be throughput via the
second sequencer’s Control signal Out even when it’s not running.
S
SS
S
E
EE
ER
RR
RI
II
IA
AA
AL
LL
L
C
CC
CO
OO
ON
NN
NN
NN
NE
EE
EC
CC
CT
TT
TI
II
IO
OO
ON
NN
N
2 -
2 - 2 -
2 -
W
WW
WI
II
IT
TT
TH
HH
H
K
KK
KE
EE
EY
YY
YB
BB
BO
OO
OA
AA
AR
RR
RD
DD
D
R
RR
RE
EE
ES
SS
ST
TT
TA
AA
AR
RR
RT
TT
T
In some situations you may want to restart a sequencer by pressing a new key on the keyboard, for exam-
ple when sequencing a bass line. In a serial connection you can do like this to make it work:
Connect the Gate output of the Keyboard module to the first sequencer’s Rst input (green cable). We
don’t use the Clock Generator’s Sync output because we want to manually restart the sequence. To make
the first sequencer start over again after the second sequencer’s last step, we patch the second sequencer’s
Link output to the first sequencer’s Loop input (purple cable). This way the whole sequence will loop
automatically. Now, if we press a new key when the sequence is somewhere between steps 17 and 32 we
 Loading...
Loading...