• The execution timing of an event task depends on how the condition expression is met. The
match can be triggered by I/O refreshing in the primary periodic task, or by execution of a pro-
gram that is assigned to the primary periodic task. This difference is described in the following
table. This difference occurs because the condition expression is evaluated for a match by sys-
tem common processing 1 inside the primary periodic task. Processing in the primary periodic
task takes place in this order: I/O refreshing, system common processing 1, and user program
execution.
• In order for an event task to be executed, the condition expression must be met in the evalua-
tion after the previous evaluation where the condition expression was not met. This means that
even if the status of the condition expression changes from not met to met, if the condition
returns to not met before the next evaluation, the event task will not be executed.
You can also set the same execution priority for more than one event task. If the execution conditions
are met for more than one event task that has the same execution priority, the event tasks will be exe-
cuted in the order that their execution conditions are met.
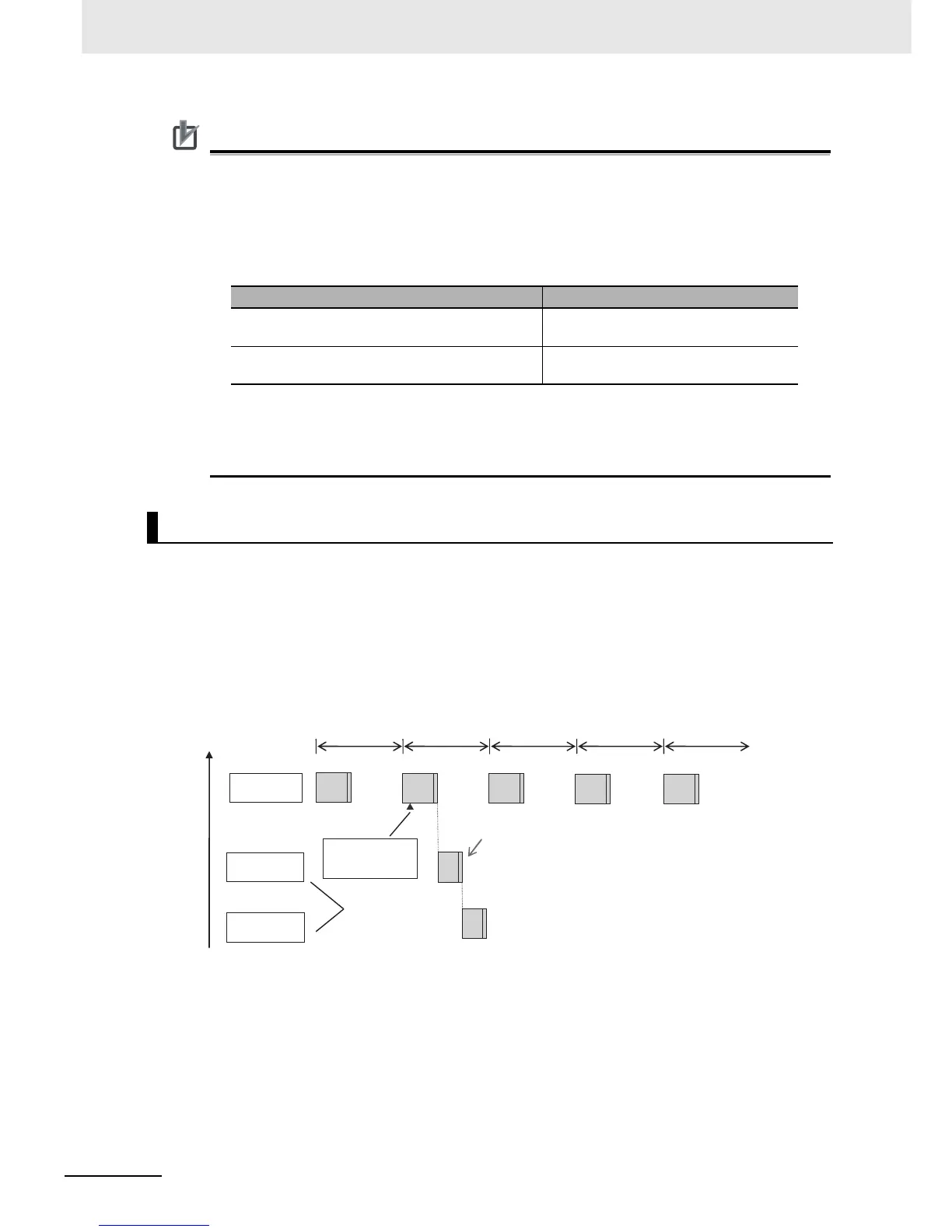
Example 1: When Two ActEventTask instructions Are Executed
In the example given below, two ActEventTask instructions are used to execute two event tasks. The T1
event task is executed before the T2 event task because the ActEventTask instruction that triggered T1
was executed first.
Trigger for condition expression to match Event task execution timing
I/O refreshing in the primary periodic task After completion of the primary periodic
task
Execution of the programs in the primary periodic
task
After completion of the next execution of
the primary periodic task
Execution Timing for Event Tasks with the Same Execution Priority

 Loading...
Loading...





