6-93
6 Programming
NJ-series CPU Unit Software User’s Manual (W501)
6-5 Programming Languages
6
6-5-3 Structured Text Language
• Example for an Integer Expression
• Example of an Integer Enumeration Function Return Value
Data Types That You Can Use in CASE Constructs
FOR
Overview:
This construct repeatedly executes the same statements until a variable (called the FOR variable)
changes from one value to another value.
The following expressions are used to specify whether the condition is met.
TRUE: The condition is met.
FALSE: The condition is not met.
Reserved Words:
FOR, TO, (BY), DO, END_FOR
Note You can omit BY.
Construct Structure:
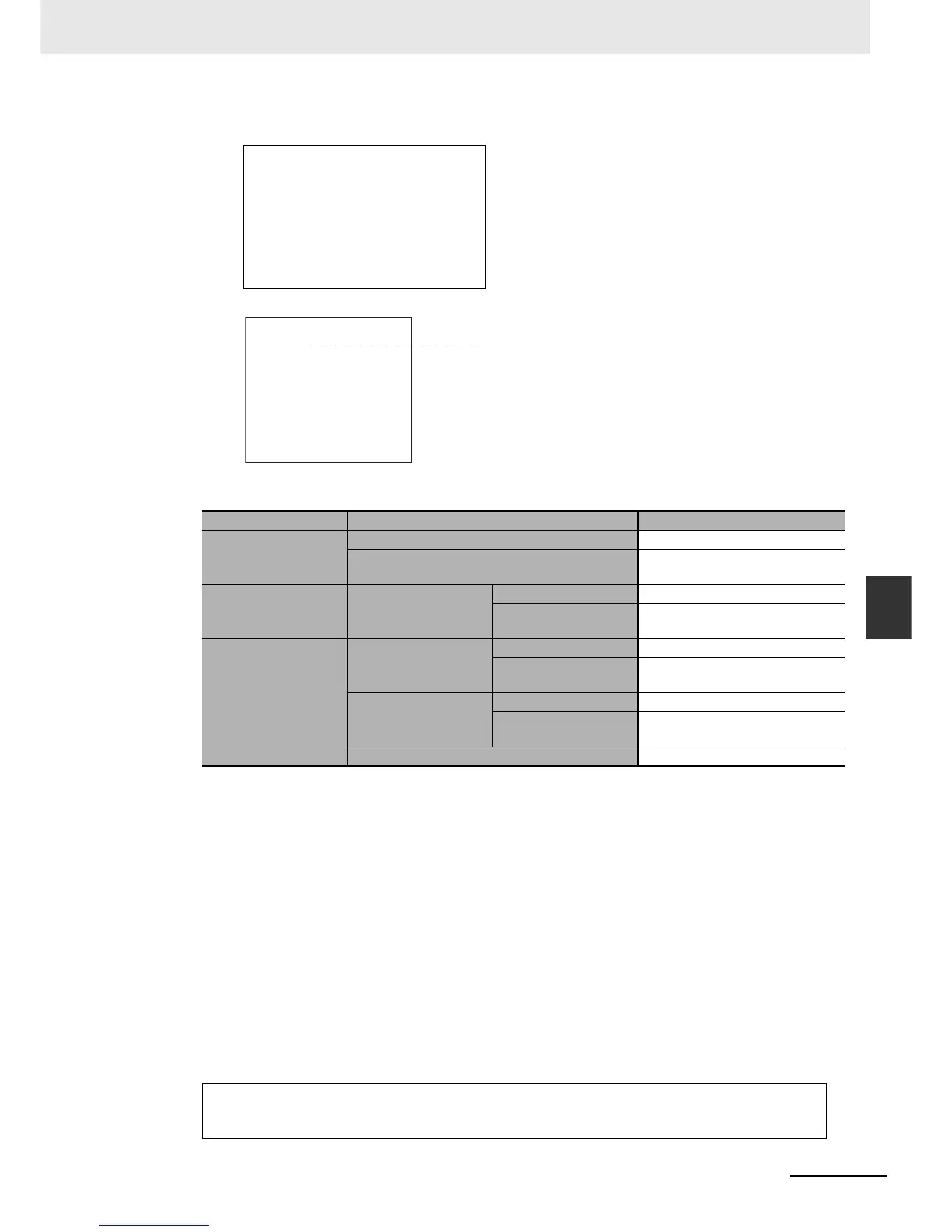
CASE (a1 + a2) OF
0:
X := 0;
1:
X := 1;
ELSE
X := 2;
END_CASE;
Classification Data type <integer_expression>
Basic data types
Integers Supported.
Boolean, bit string, real, duration, date, time
of day, date and time, or text string data
Not supported.
Data type specifica-
tions
Array specifications
Arrays Not supported.
Elements
Supported for integers and enu-
merations only.
Derivative data types
Structures
Structures Not supported.
Members
Supported for integers and enu-
merations only.
Unions
Unions Not supported.
Members
Supported for integers and enu-
merations only.
Enumerations Supported.
FOR <FOR_variable>:= <initial_value> TO <end_value> BY <increment/decrement> DO
<statement>;
END_FOR;

 Loading...
Loading...





