109
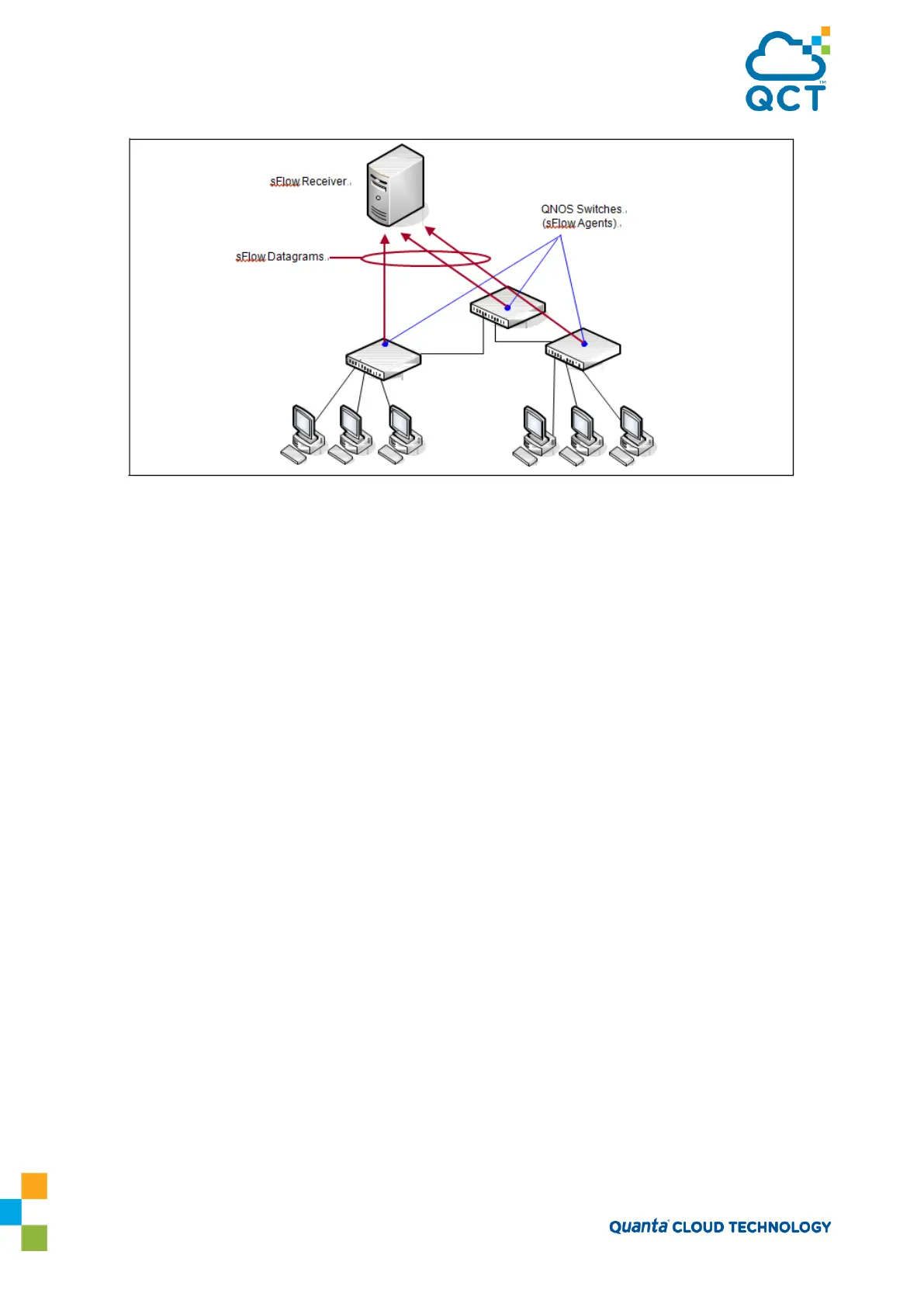
Figure 3-20: sFlow Architecture
The advantages of using sFlow are:
• It is possible to monitor all ports of the switch continuously, with no impact on the distributed
switching performance.
• Minimal memory is required. Samples are not aggregated into a flow-table on the switch; they are
forwarded immediately over the network to the sFlow receiver.
• The sFlow system is tolerant to packet loss in the network because statistical modeling means the loss
is equivalent to a slight change in the sampling rate.
• sFlow receiver can receive data from multiple switches, providing a real-time synchronized view of the
whole network.
• The receiver can analyze traffic patterns based on protocols found in the headers (e.g., TCP/IP, IPX,
Ethernet, AppleTalk…). This alleviates the need for a layer 2 switch to decode and understand all protocols.
3.12.1. sFlow Sampling
The sFlow Agent in the QNOS software uses two forms of sampling:
• Statistical packet-based sampling of switched or routed Packet Flows
• Time-based sampling of counters
Packet Flow Sampling and Counter Sampling are
performed
by sFlow
Instances associated
with individual Data
Sources within an sFlow Agent. Both types of samples are combined in sFlow datagrams. Packet Flow
Sampling creates a steady, but
random,
stream of sFlow
datagrams
that are sent to the sFlow
Collector.
Counter samples may be taken opportunistically to fill these datagrams.

 Loading...
Loading...