166
configuration file does not contain the switch's IP address, the switch attempts a reverse DNS lookup to
resolve its host name.
A sample
fp-net.cfg
file follows:
config
...
ip host switch1 192.168.1.10 ip host switch2 192.168.1.11
... <other hostname definitions>
exit
Once a host name has been determined, the switch issues a TFTP request for a file named hostname.cfg,
where hostname is the first thirty-two characters of the switch's host name.
If the switch is unable to map its IP address to a host name, Auto Install sends TFTP requests for the default
configuration file host.cfg.
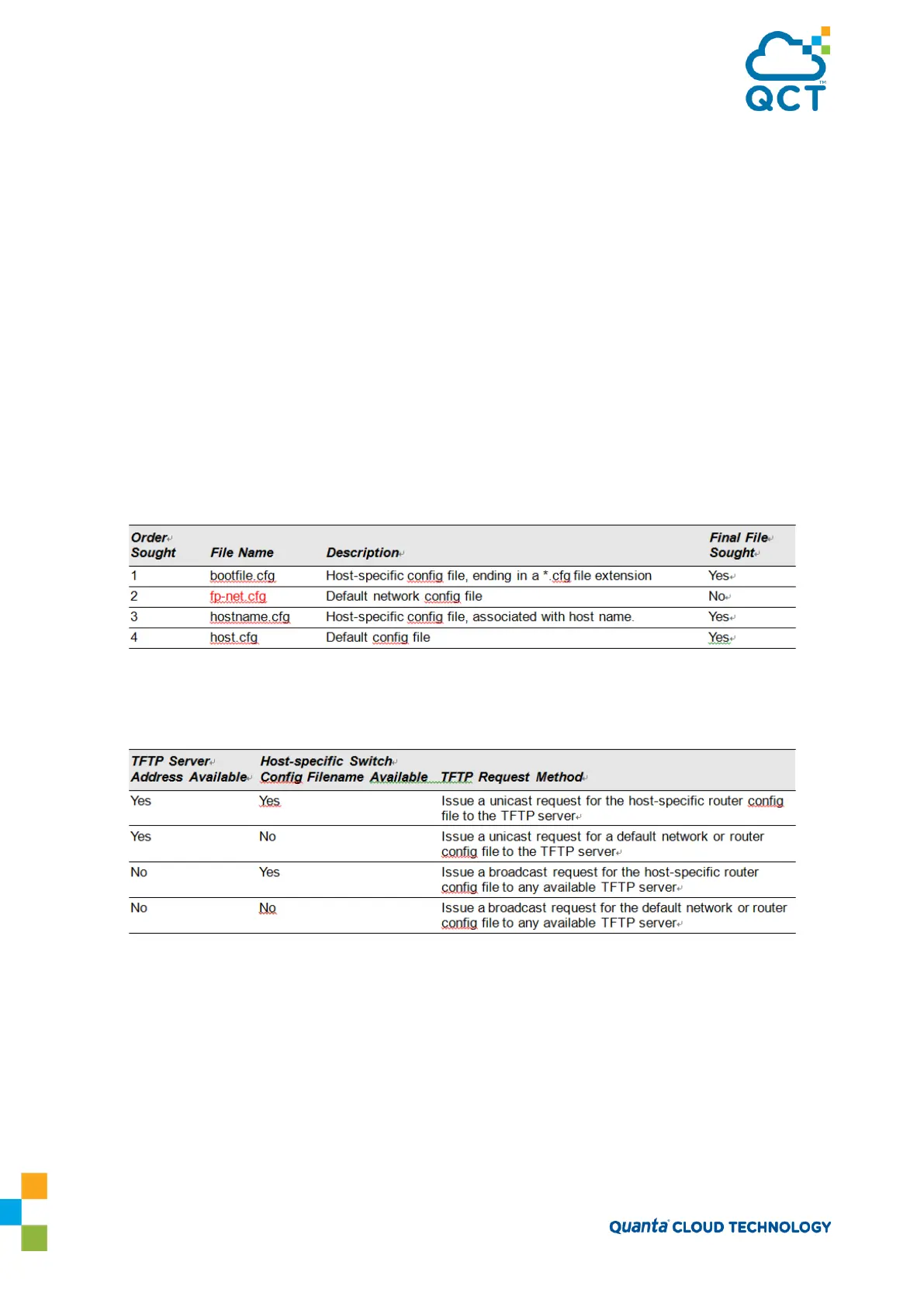
Table 9 summarizes the config files that may be downloaded and the order in which they are sought.
Table 6-2: Configuration File Possibilities
Table 10 displays the determining factors for issuing unicast or broadcast TFTP requests.
Table 6-3: TFTP Request Types
6.2.2. Monitoring and Completing the DHCP Auto Install Process
When the switch boots and triggers an Auto Install, a message is written to the buffered log. After the
process completes, the Auto Install process writes a log message. You can use the show logging
buffered
command to view information about the process. The following log message indicates that the switch has
broadcast a request to download the fp-net.cfg file from any TFTP server on the network.
<14> Jan 1 00:00:42 10.27.22.157-1 AUTO_INST[310234388]: auto_install_control.c(2427) 202 %%
AutoInstall<->TFTP : Downloading tftp://255.255.255.255/fp-net.cfg (via eth0)

 Loading...
Loading...