140
4.3.10. ACL Configuration Process
To configure ACLs, follow these steps:
1. Create a MAC ACL by specifying a name.
2. Create an IP ACL by specifying a number.
3. Add new rules to the ACL.
4. Configure the match criteria for the rules.
5. Apply the ACL to one or more interfaces.
4.3.11. Preventing False ACL Matches
Be sure to specify ACL
access-list,
permit, and deny rule criteria as fully as possible to avoid false matches. This
is especially important in networks with protocols such as FCoE that have newly-introduced EtherType values.
For example, rules that specify a TCP or UDP port value should also specify the TCP or UDP protocol and the
IPv4 or IPv6 EtherType. Rules that specify an IP protocol should also specify the EtherType value for the frame.
In general, any rule that specifies matching on an upper-layer protocol field should also include matching
constraints for each of the lower-layer protocols. For example, a rule to match packets directed to the well-
known UDP port number 22 (SSH) should also include matching constraints on the IP protocol field
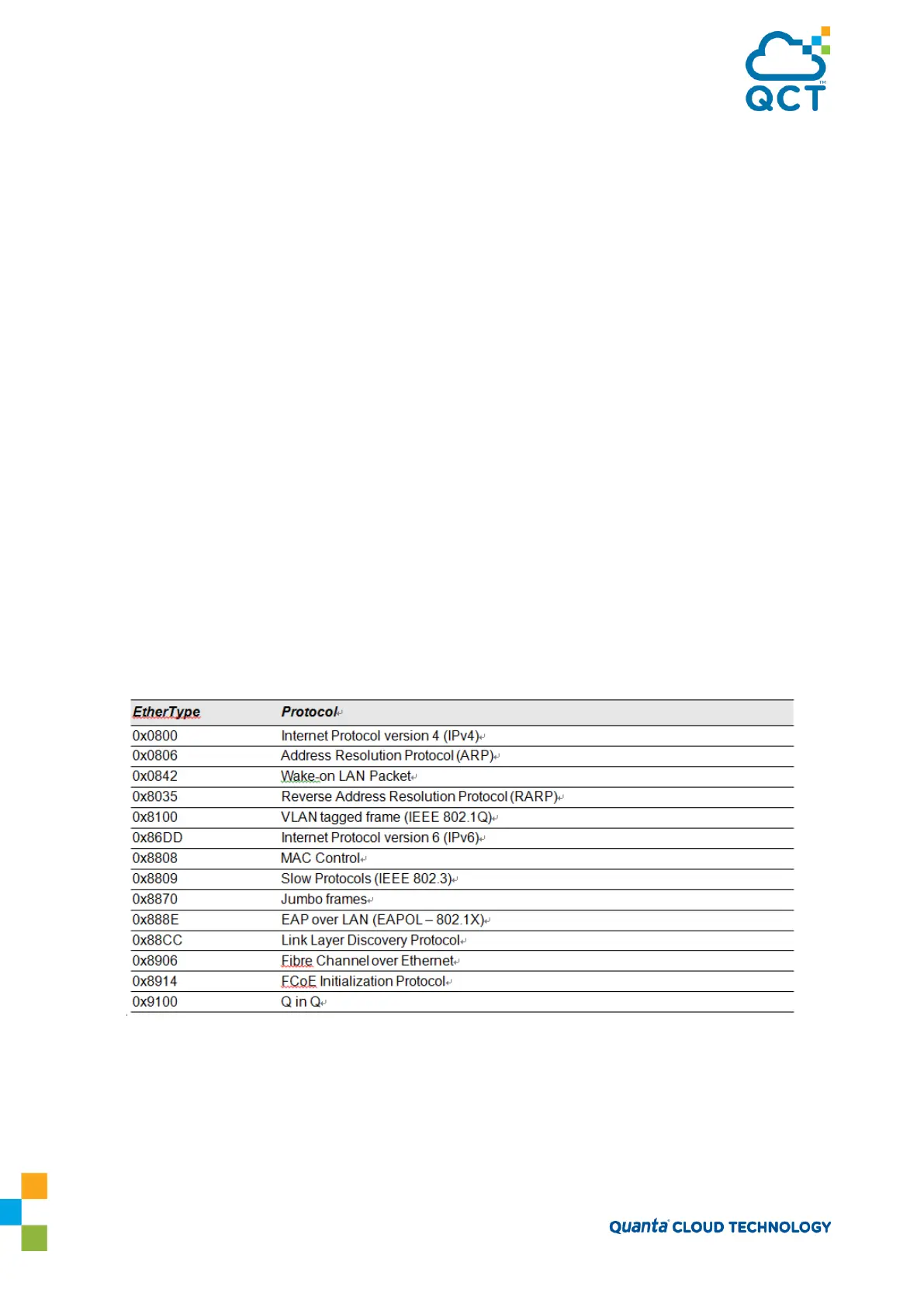
(protocol=0x11 or UDP) and the EtherType field (EtherType=0x0800 or IPv4). Table 6 lists commonly-used
EtherTypes numbers:
Table 4-2: Common EtherType Numbers
Table 7 lists commonly-used IP protocol numbers:

 Loading...
Loading...