Appendix
S7-300 Programmable Controller Hardware and Installation
A5E00105492-01
11-15
compatibility (EMC). The table contains information on the general rules governing
clearances to enable you to choose the right cables.
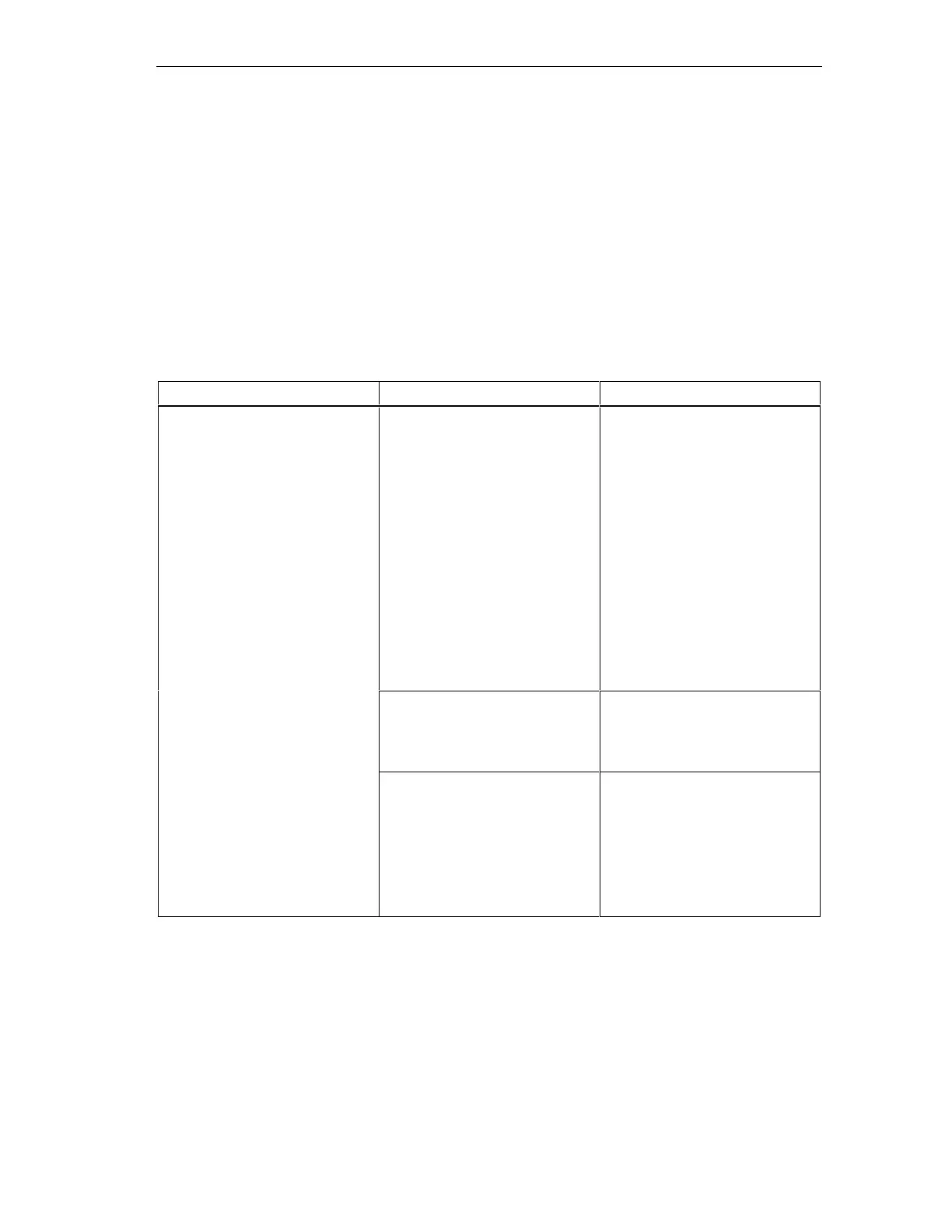
How to Read the Table
To find out how to run two cables of different types, proceed as follows:
1. Look up the type of the first cable in column 1 (Cables for ...).
2. Look up the type of the second cable in the corresponding field in column 2
(and Cables for ...).
3. Read off the guidelines to be observed from column 3 (Run ...).
Table 11-7 Cable routing inside buildings
Cables for ... and cables for ... Run ...
• Bus signals, shielded
(PROFIBUS)
• Data signals, shielded
(programming devices,
operator panels, printers,
counter inputs, etc.)
• Analog signals, shielded
• DC voltage (≤ 60 V),
unshielded
• Process signals (≤ 25 V),
shielded
• AC voltage (≤ 25 V),
unshielded
• Monitors (coaxial cable)
In common bundles or cable
ducts
• DC voltage (> 60 V and
≤ 400 V), unshielded
• AC voltage (> 25 V and
≤ 400 V), unshielded
In separate bundles or cable
ducts (no minimum clearance
necessary)
• Bus signals, shielded
(PROFIBUS)
• Data signals, shielded
(programming devices,
operator panels, printers,
counter inputs, etc.)
• Analog signals, shielded
• DC voltage (≤ 60 V),
unshielded
• Process signals (≤ 25 V),
shielded
• AC voltage (≤ 25 V),
unshielded
• Monitors (coaxial cable)
• DC and AC voltage (> 400 V),
unshielded
inside cabinets:
In separate bundles or cable
ducts (no minimum clearance
necessary)
outside cabinets:
On separate cable racks with a
clearance of at least 10 cm

 Loading...
Loading...