Representation of analog values at a resolution of 16 bits
The digitized analog value applies to input and output values of the same nominal range.
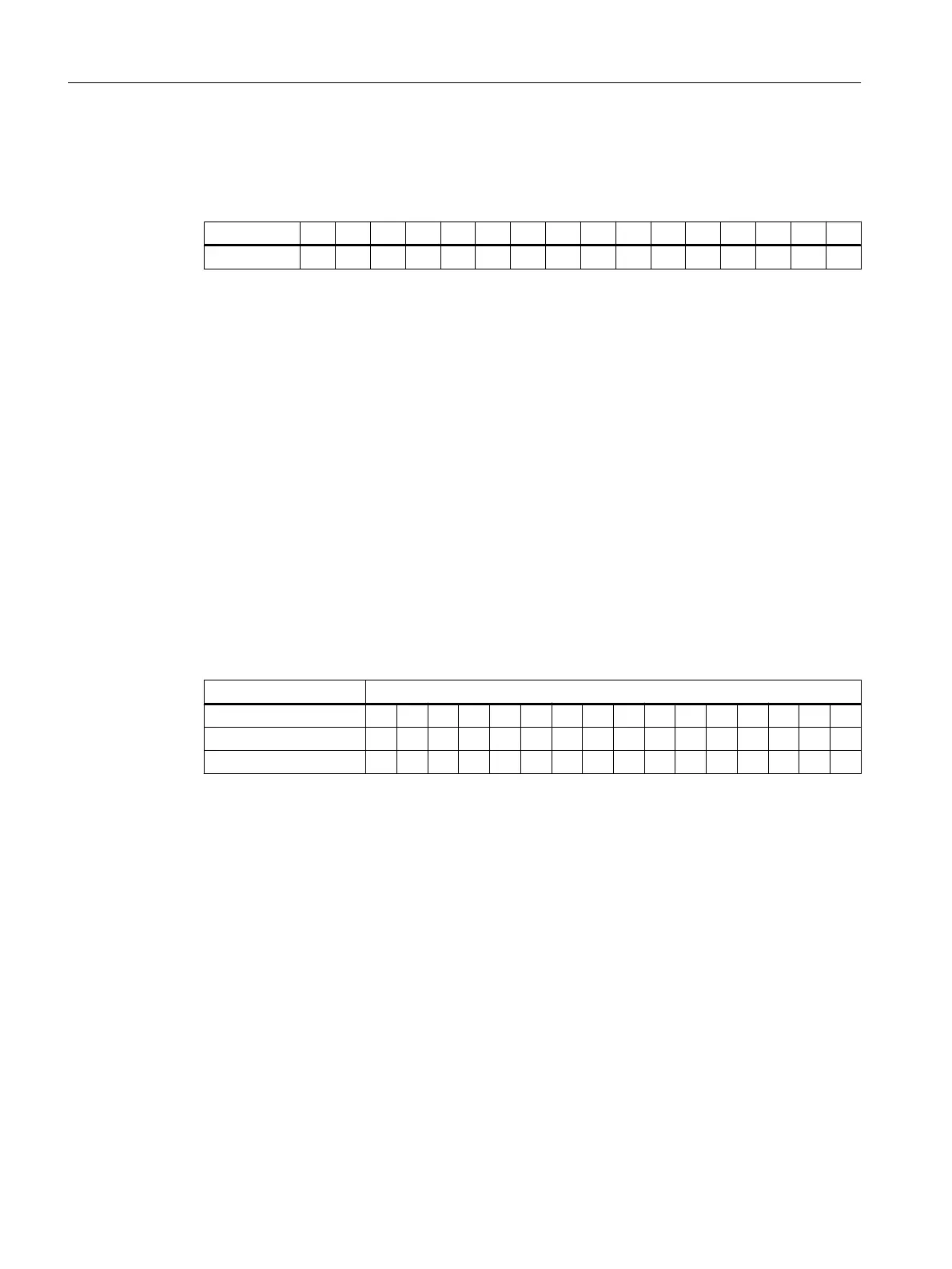
Analog values are output as real numbers in two's complement. The resulting assignment:
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit values 2
15
2
14
2
13
2
12
2
11
2
10
2
9
2
8
2
7
2
6
2
5
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
Bit 15 can be interpreted as a sign
The sign of the analog value is always set at bit 15:
● "0" → +
● "1" → -
Resolution less than 16 bits
On analog modules with a resolution of less than 16 bits, the analog value is stored left-justified.
The unused least significant bit positions are padded with "0".
Example
The example below demonstrates the "0" padding of unused bit positions for low resolution
values.
Table 5-4 Example: Bit pattern of a 16-bit and 13-bit analog value
Resolution Analog value
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
16-bit analog value 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1
13-bit analog value 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
Analog modules
5.4 Representation of analog values
S7-400 Automation System Module Data
168 Reference Manual, Ausgabe 11/2016, A5E00850736-08

 Loading...
Loading...




















