Functions
2.6 Circuit-Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
SIPROTEC, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1140-C474-A1, Release date 09.2011
107
End Fault Protection
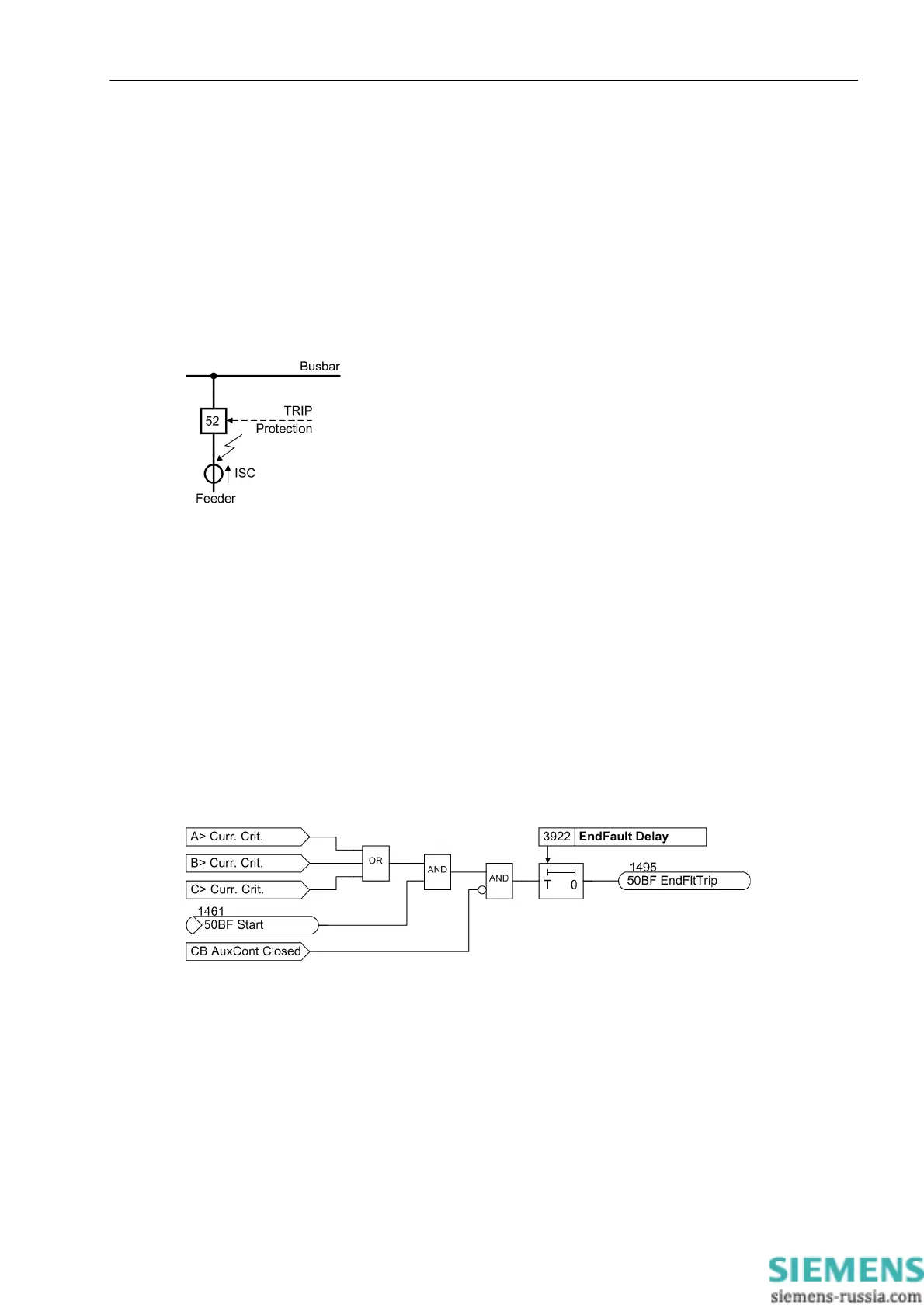
An end fault is defined here as a fault which has occurred at the end of a line or protected object, between the
circuit breaker and the current transformer set.
This situation is shown in Figure 2-41. The fault is located — as seen from the current transformer (= measure-
ment location) — on the busbar side, it will thus not be regarded as a feeder fault by the feeder protection
device. It can only be detected by either a reverse element of the feeder protection or by the busbar protection.
However, a trip command given to the feeder circuit breaker does not clear the fault since the opposite end
continues to feed the fault. Thus, the fault current does not stop flowing even though the feeder circuit breaker
has properly responded to the trip command.
Figure 2-41 End fault between circuit breaker and current transformers
The end fault protection has the task to recognize this situation and to transmit a trip signal to the remote end(s)
of the protected object to clear the fault. For this purpose, the output command „50BF EndFltTrip“ is avail-
able to trigger a signal transmission device (e.g. power line carrier, radio wave, or optical fiber) – if applicable,
together with other commands that need to be transferred or (when using digital signal transmission) as
command via the protection data interface.
The end fault protection detects an end fault because it registers that current is flowing even though the circuit-
breaker auxiliary contacts signal that the circuit breaker is open. An additional criterion is the presence of any
breaker failure protection initiate signal. Figure 2-42 shows the functional principle. If the breaker failure pro-
tection is initiated and current flow is detected (current criteria „L*> current criterion“ according to Figure 2-36),
but no circuit-breaker pole is closed (auxiliary contact criterion „52 closed“), the timer EndFault Delay is
started. At the end of this time, a trip command is sent to the opposite end.
Figure 2-42 Functional diagram of the end fault protection

 Loading...
Loading...











