110
FEEDBACK MODE:
During normal driving, sequential control, which performs injection in the order 1–3–2 for each cylinder, is used. Injection
is performed in the exhaust sequence of each cylinder. The fuel injection amount is calculated by adding following
correction to the basic fuel injection time, which is determined according to the engine rpm and air intake amount.
Volume efficiency correction: The fuel injection time is adjusted according to the engine rpm and intake air pressure.
Feedback correction: The air–fuel ratio is corrected from the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas according
to the O
2
sensor to the theoretical air–fuel ratio.
Amount increase correction immediately after starting: The fuel injection time is corrected according to cooling
water temperature when starting. The correction amount is gradually reduced after starting.
Idle A/F learning function correction: The fuel injection time is corrected during idling. If the basic air–fuel ratio to
which the air–fuel ratio feedback correction is added is significantly deviated from the theoretical air–fuel ratio due
to the passage of years, etc., problems occur in driving which prevent feedback correction from being performed
when the engine is cold, etc. For this reason, a learning function is added to the ECM, and the changing basic
air–fuel ratio can be maintained close to the theoretical air–fuel ratio.
A/F correction: Corrects for deviation in air–fuel ratio in all driving regions.
Atmospheric pressure correction: Predicts atmospheric pressure from engine running status and corrects for
deviation in air–fuel ratio occurring due to changes in atmospheric pressure.
Acceleration amount increase correction: Detects acceleration status from changes in air intake pressure amount,
cooling water temperature, and engine rpm, and extends fuel injection time.
Deceleration amount increase correction: Detects acceleration status from changes in air intake pressure amount,
cooling water temperature, and engine rpm, and extends fuel injection time.
Acceleration asynchronous injection control: Detects changes in throttle sensor amount as acceleration status,
causes fuel injection in an injection timing determined according to cooling water temperature outside of the
aforementioned injection timing.
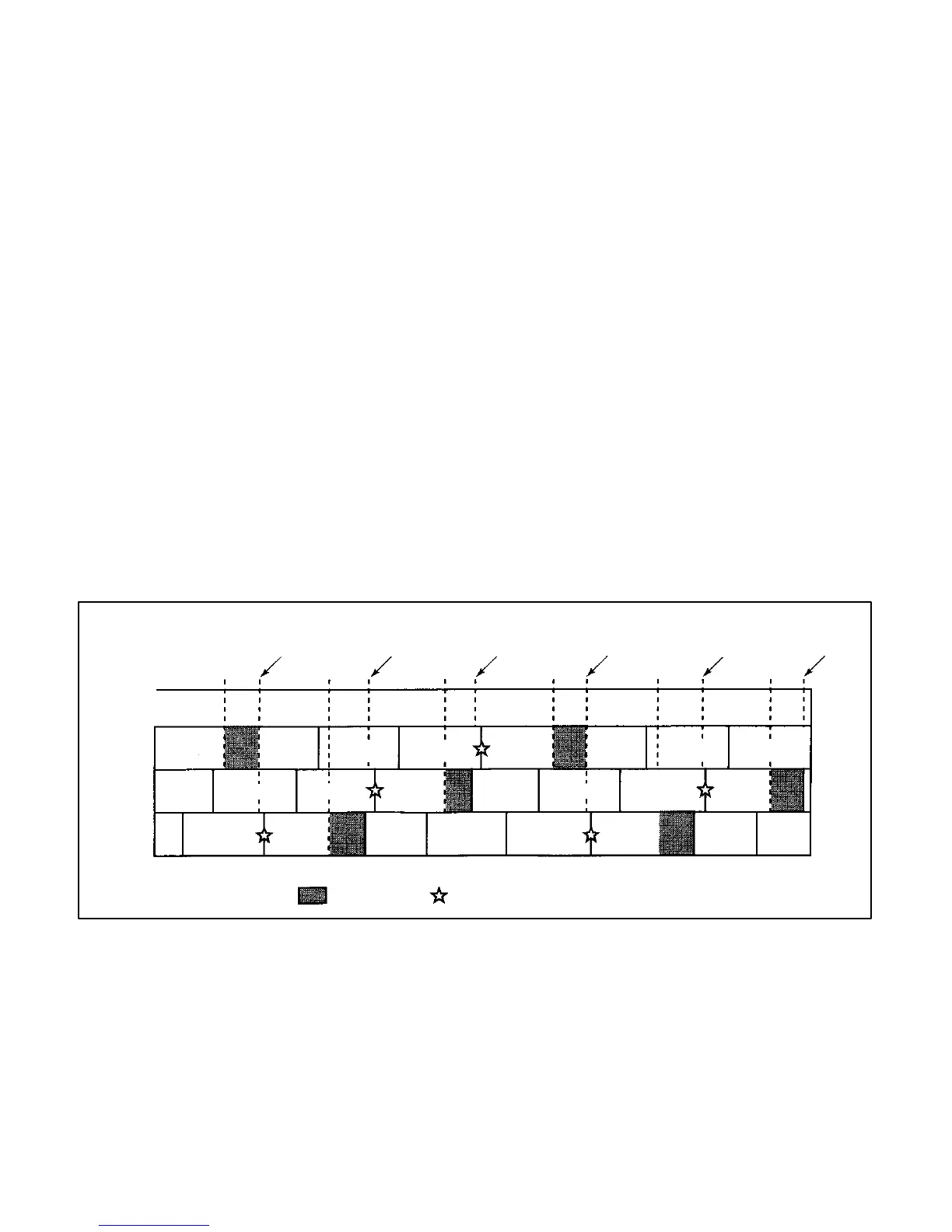
CRANK
ANGLE
SENSOR
CYLINDER NO.
NO. 1
NO. 2
NO. 3
EXPLOSION EXHAUST INTAKE
NO. 3
BTDC5°
NO. 2
BTDC5°
NO. 1
BTDC5°
NO. 3
BTDC5°
NO. 2
BTDC5°
NO. 1
BTDC5°
EXPLOSION EXHAUST INTAKE COMPRESSION
EXHAUST INTAKE COMPRESSION EXPLOSION INTAKE COMPRESSION EXPLOSION
COMPRESSION EXPLOSION INTAKE COMPRESSION EXPLOSION EXHAUST INTAKE
INJECTION
IGNITION
COMPRESSION
EXHAUST
EXHAUST
FUEL CUT MODE:
Under the following conditions, fuel injection is stopped.
Fuel cut at high engine rpm: In order to prevent the engine from running at excessively high rpm, fuel injection is
halted when the engine speed reaches 7800 rpm or above.
Fuel cut upon deceleration:
When the throttle valve opening is small and engine rpm is high, injection is halted
in order to prevent emission of HC.
When the engine rpm falls below a specified level, the fuel cut is released.
The specified rpm for fuel cut upon deceleration is determined based on the cooling
water temperature.
 Loading...
Loading...