Aligna
®
4D User Manual
25 / 84
5 Some Typical Configurations
In the following, some typical 2D and 4D configurations are discussed. In particular, we think
about rather long beam paths between the laser and the target.
In the examples, we will mostly use beam sampling mirrors (BSM). Alternatively, we can use
wedged beam sampling plates (WBSP). (The advantages of the different beam sampling
methods are described in a separate chapter.)
Following actuated mirrors can be used:
PiA: Piezo Actuators High resolution, high speed
MoA: Motorized Actuators Large Stroke, Auto-Alignment
MoPiA: Combination of MoA and PiA High resolution, high speed, large stroke, auto-align
Following detectors are used::
PSD 2D: Position Sensitive Detector for measuring the Beam Position, OR (in combination
with a detector lens) measuring the Beam Angle
PSD 4D: Simultaneous and independent measurement of Beam Angle AND Beam Position
AimPD: One or several photo detectors, located along the beam path at important optical
components, for example at entrance of a beam line tube, before an amplifier
stage, before mirrors, delay lines, SHG, …
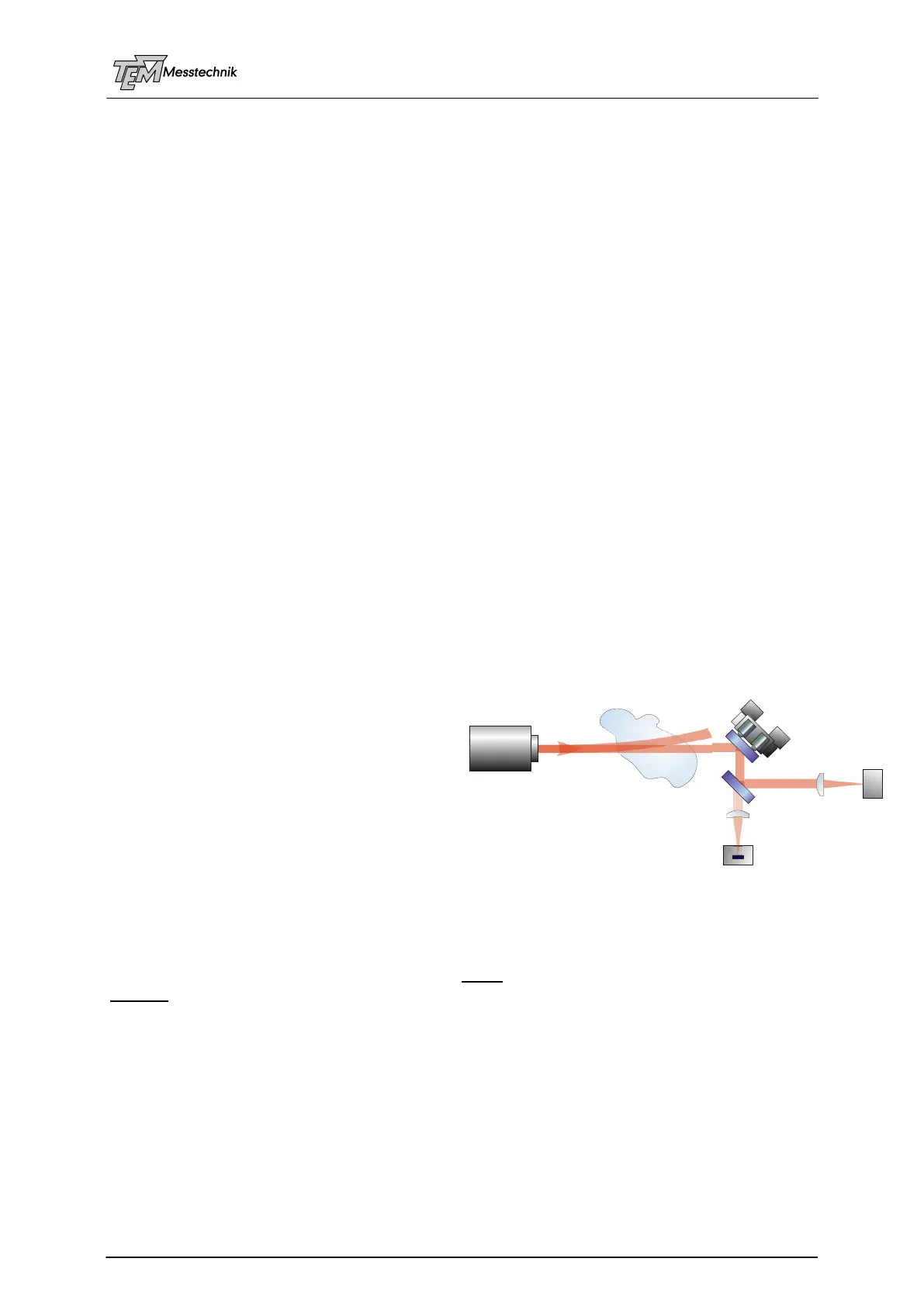
5.1 2D System (Angle Stabilization)
The 2D angle stabilization system is the
simplest of systems discussed here. A laser
is focused to a target by means of a lens (or
objective). The spot position in the target
plane has to be held stable. However, the
target spot position is influenced by laser
drifts, by thermal effects of mechanical and
optical components, as well as air fluctua-
tions, etc. These effects have to be compen-
sated by the stabilization system, controlling
the active mirror M1.
In this case, the laser beam is sampled by the leak of the beam sampler mirror BSM. The
"PSD lens" is focusing the sampled beam onto a position sensitive detector (PSD 2D). If the
spot position at the PSD2D is stabilized by movement of active mirror M1, also the spot posi-
tion at the target will be stabilized.
(As explained before, in most cases the beam angle is much more sensitive, than the beam
position: The angle represents the position of the spot at the target, while the beam position
just influences the angle of incidence at the target, which is by far less sensitive in most cases,
of course not in all.)
5.2 2D System (Long Path)
If the laser beam has to be guided over a more or less long beam path, in a simple 2D system
the active mirror should be located near the laser, while the detector should be located close
to the target.
M1
2D System
Angle Stabilization
MoPiA
PSD 2D
Laser
(or PSD 4D)
BSM
Target
Lens
PSD Lens
 Loading...
Loading...