Aligna
®
4D User Manual
7 / 84
1 Introduction
Laser beams, used in an experiment or in industrial applications, can move in space by many
reasons:
1. Thermal properties of the laser itself
2. Thermal movement by the laser cooling system
3. Drifts of alignment and folding mirrors
4. Air turbulences and temperature gradients in the air
5. Thermal effects of optical elements
6. Mechanically moved optical elements (delay lines, switching mirrors, motorized tele-
scopes, …)
7. Movement of the experimental (optical) tables or vacuum chambers
(In the chapter “Reasons of Pointing Instabilities” these topics will be discussed in more detail.)
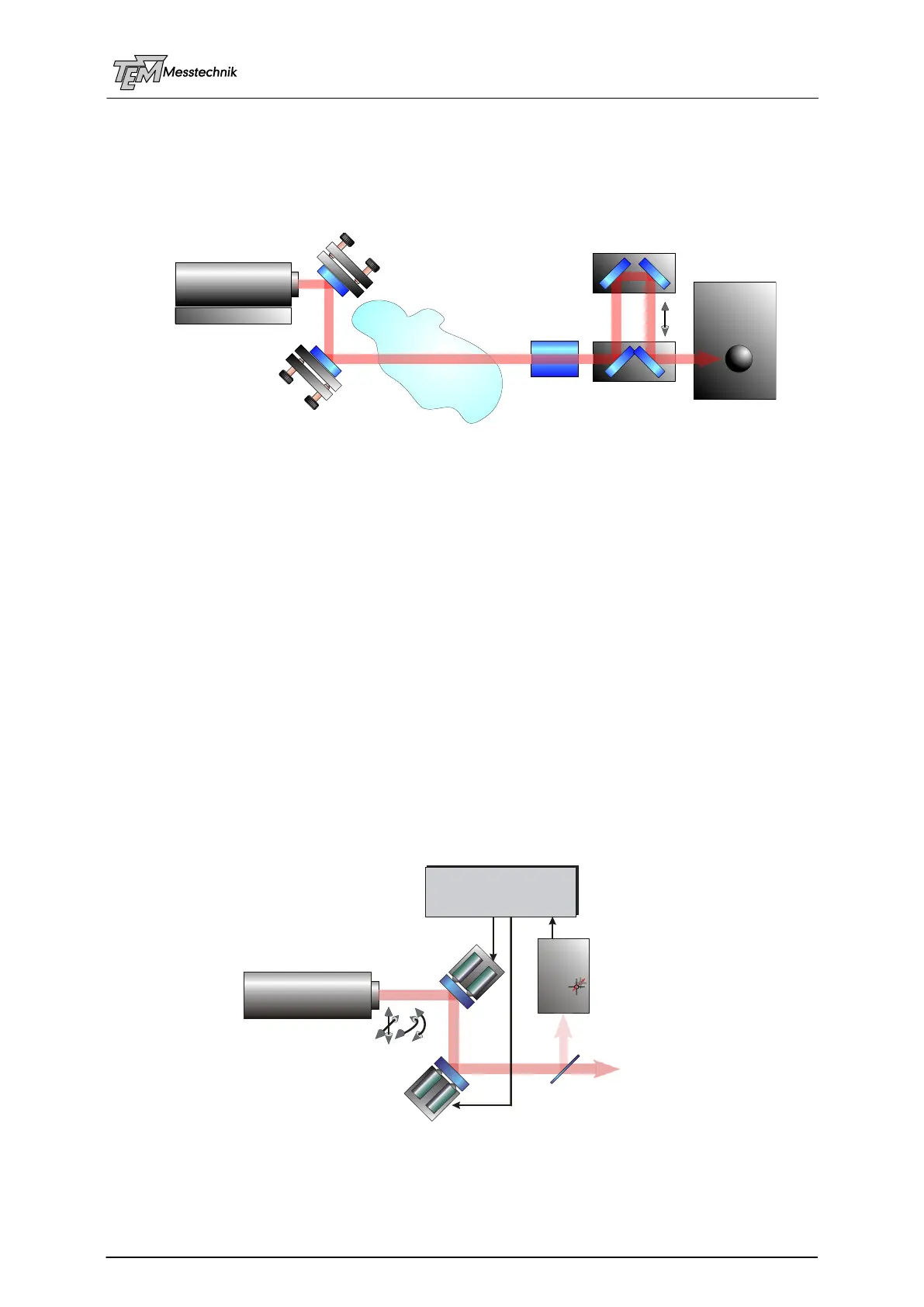
The laser beam pointing stabilization system Aligna
®
compensates for all of these disturb-
ances. The laser beam position and its angle are measured by the 4D position sensitive detec-
tor PSD 4D in four degrees of freedom (two beam positions “X” and “Y”, and two angles “”
and “”). The position of a (collimated) laser beam is characterized by these four values, like a
line in space. The measured deviation signals of the laser axis with respect to the reference
axis are processed continuously by the Aligna
®
electronics. Herein control signals for four
piezo actuators of the BeamScan mirrors and/or motorized mirror mounts (Aligna60, e.g.) are
generated. Two 2D movable mirrors, which control these four degrees of freedom in four fast
closed lock loops keep the laser beam exactly at the reference axis.
Aligna
®
is a modular system, consisting of different elements, which can be adapted to the
individual application: Different types of scanners (with various values of displacement, beam
diameters, mirror types, movement speeds) and different types of PSDs (Position Sensitive
Laser
Cooling System
1: thermal drifts
inside the laser,
movements by
frequency detuning,
by power variation
2: thermal drifts
of cooling system
and mechanical mounts
3: drifts of alignment
and folding mirror
holders
4: air fluctuations and
temperature gradients
6: moved optical elements
(delay lines, switching mirrors,
motorized telescopes,...)
7: Movement of the experimental
(optical) tables or vacuum chambers
5: thermal effects in
optical elements and
mirrors
Target
Laser
BeamScan 2D
1
PSD 4D
BeamLock®
electronics
BeamScan 2D
2
X
Y
Beam Splitter
to Experiment
 Loading...
Loading...