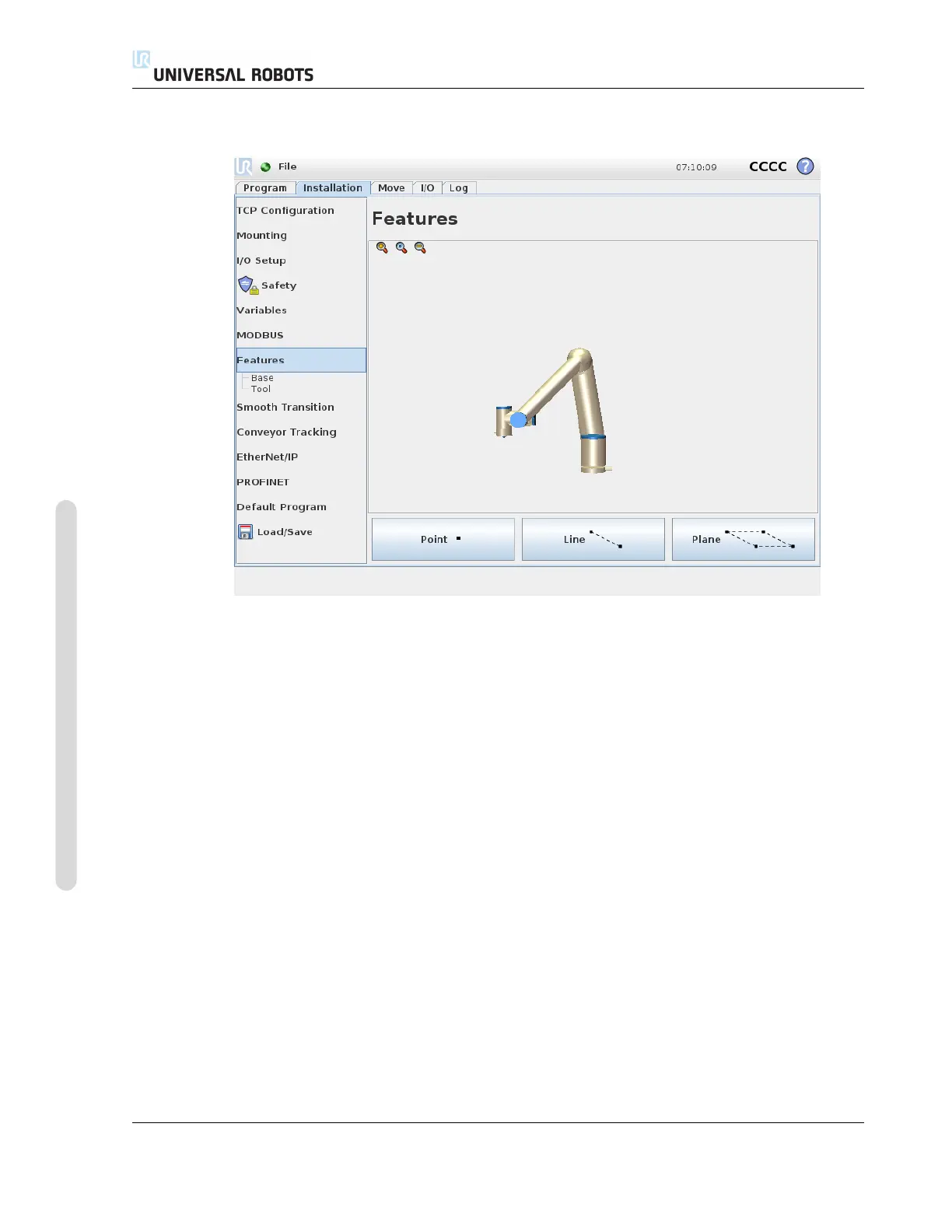
13.12 Installation → Features
13.12 Installation → Features
The Feature, is a representation of an object that is defined with a name for future reference and a
six dimensional pose (position and orientation) relative to the robot base.
Some subparts of a robot program consist of movements executed relative to specific objects other
than the base of the Robot arm. These objects could be tables, other machines, workpieces, con-
veyors, pallets, vision systems, blanks, or boundaries which exist in the surroundings of the Robot
arm. Two predefined features always exist for the robot. Each feature has its pose defined by the
configuration of the Robot arm itself:
• The Base feature is located with origin in the centre of the robot base (see figure 13.1)
• The Tool feature is located with origin in the centre of the current TCP (see figure 13.2)
User-defined features are positioned through a method that uses the current pose of the TCP in the
work area. This means the users can teach feature locations using Freedrive Mode or ”jogging” to
move the robot to the desired pose.
Three different strategies exist (Point, Line and Plane) for defining a feature pose. The best strategy
for a given application depends on the type of object being used and the precision requirements. In
general a feature based on more input points (Line and Plane) is be preferred if applicable to the
specific object.
To accurately define the direction of a linear conveyor, define two points of a Line feature with as
much physical separation as possible. The Point feature can also be used to define a linear conveyor,
CB3 II-54 Version 3.10
Copyright © 2009–2019 by Universal Robots A/S. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...