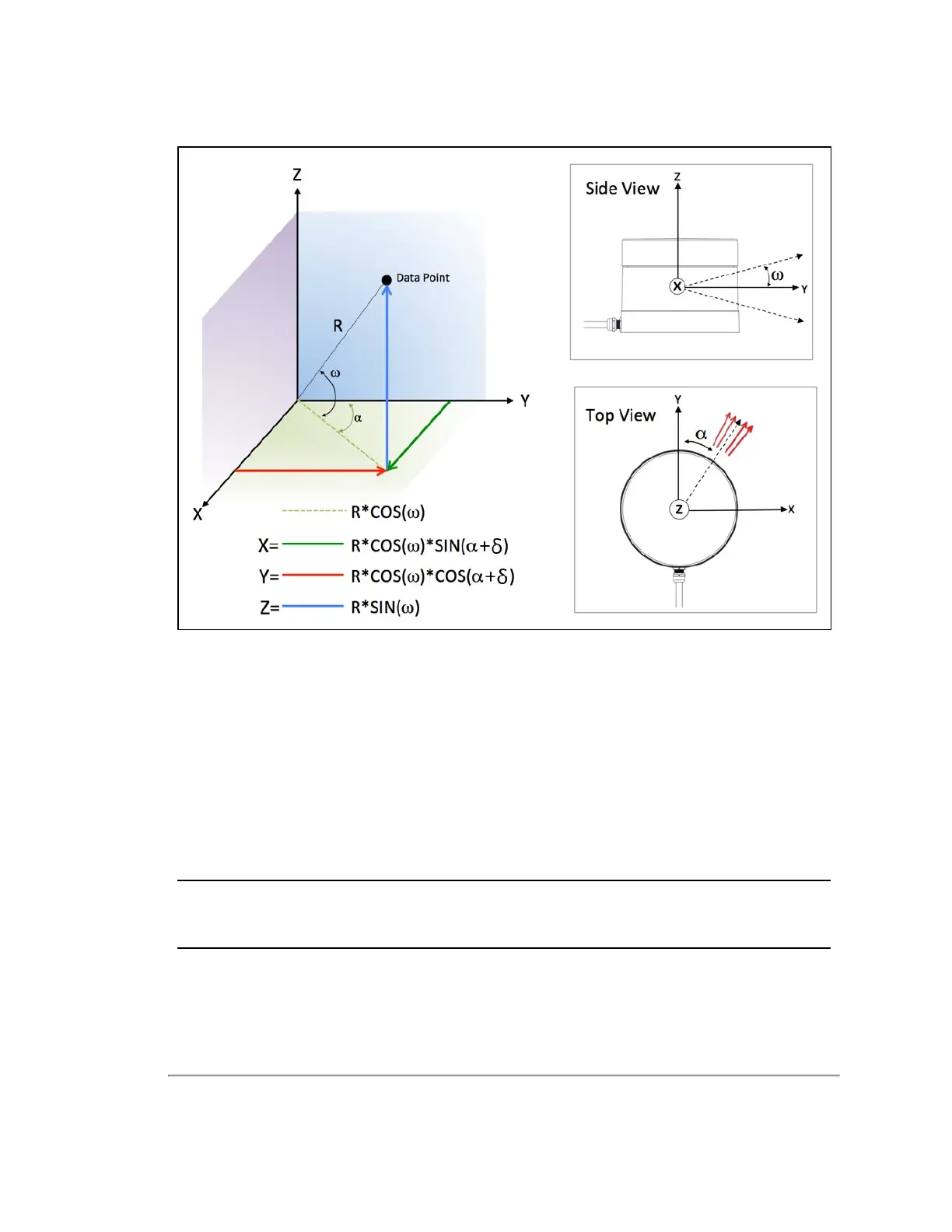
Figure 9-1 VLP-32C Sensor Coordinate System
9.3 Packet Types and Definitions
There are two types of packets generated by the sensor: Data packets and Position packets. Position packets are some-
times referred to as telemetry packets, or GPS packets.
Data packets contain the 3D data measured by the sensor as well as the calibrated reflectivity of the surface from which
the light pulse was returned. Also contained in the data packet is a set of azimuths and a 4-byte timestamp, as well as two
factory bytes identifying the model of sensor and the laser return mode. Knowing the model and return mode provides the
information your software needs to automatically adjust to different data formats.
Position packets provide a copy of the last NMEA message received (either GPRMC or GPGGA) if you've configured your
sensor to synchronize with a GPS time source. See
GPS, Pulse Per Second (PPS) and NMEA Sentence on page 41
for
additional information. Position packets also provide a byte identifying the state of the PPS signal for synchronizing with a
time source. Newer firmware provides even more information.
Note: In both types of packets, multi-byte values (e.g. azimuth, distance, and timestamp) are transmitted with the least
significant byte first (i.e. little-endian).
9.3.1 Definitions
The following sections provide explanations of sensor data packet constructs.
54 VLP-32C User Manual

 Loading...
Loading...