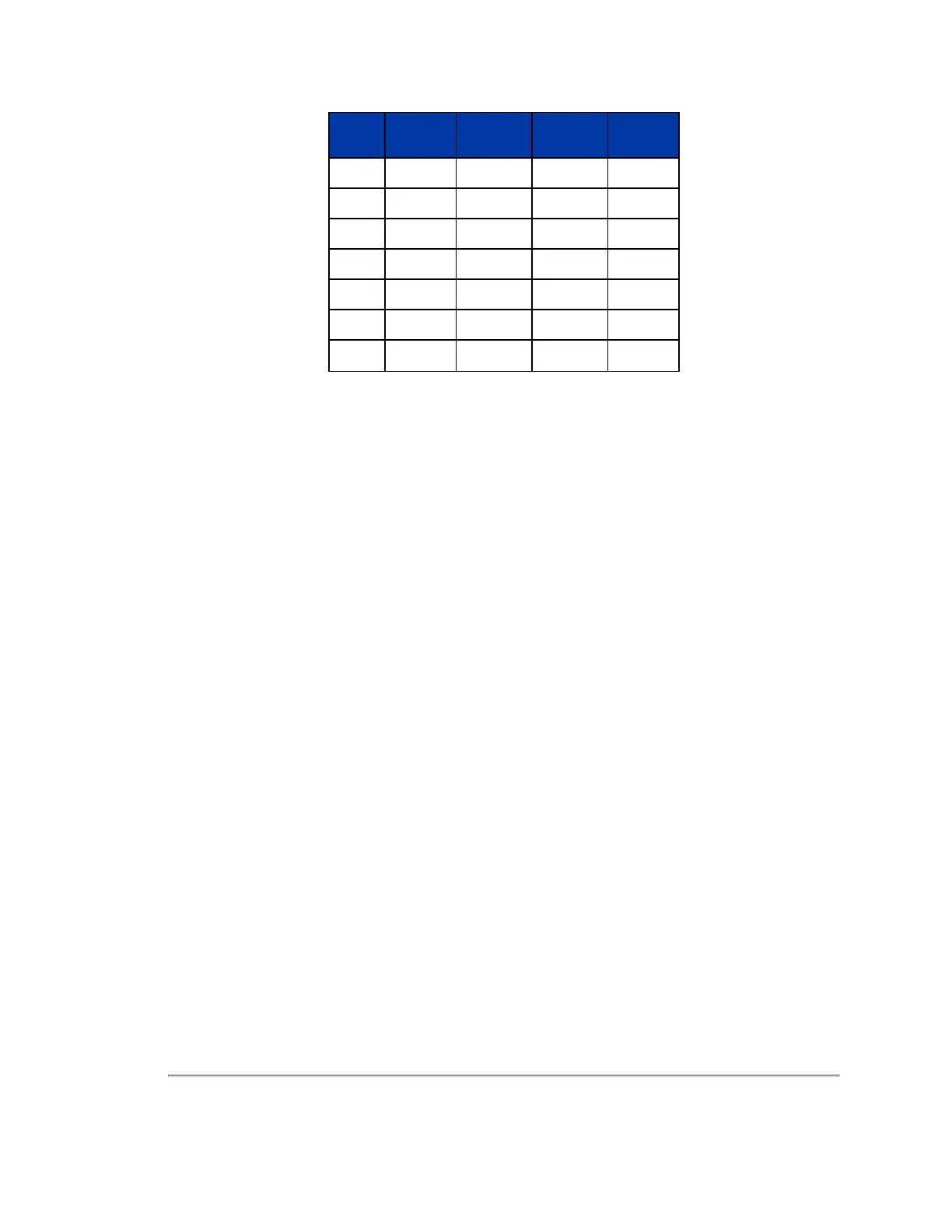
Firing
Order
Laser ID
Elevation
Angle (°)
Elevation
Angle (°)
Laser ID
9 18 1 -3.667 19
10 20 -3.333 3.333 21
11 22 2.333 -2.667 23
12 24 -3 7 25
13 26 4.667 -2.333 27
14 28 -2 15 29
15 30 10.333 -1.333 31
To calculate the exact time, in microseconds, of each data point in a packet, first number the points in the firing sequence
from 0 to 31. This becomes the data point index (aka Laser ID) for your calculations. Next, number the firing sequences 0
to 11. This becomes your sequence index.
The timestamp in the packet indicates the time of the first data point in the packet. You’ll need to calculate a time offset for
each data point and then add that offset to the timestamp. See
Figure 9-7 on page 65
for specific Data Point Timing Off-
sets (Single Return Mode) and
Figure 9-8 on page 66
for specific Data Point Timing Offsets (Dual Return Mode).
The offset equation is given by:
TimeOffset = (55.296 µs * SequenceIndex) + (2.304 µs * DataPointIndex)
To calculate the exact point time, add the TimeOffset to the timestamp.
ExactPointTime = Timestamp + TimeOffset
Example: Calculate the timing offsets of every point in a packet, in single or dual return mode. The following is working
Python code:
def make_table(dual_mode):
timing_offsets = [[0.0 for x in range(12)] for y in range(32)] # Init matrix
# constants
full_firing_cycle = 55.296 # µs
single_firing = 2.304 # µs
# compute timing offsets
for x in range(12):
for y in range(32):
dataBlockIndex = x / 2 if dual_mode else x
dataPointIndex = y / 2
timing_offsets[y][x] = \
(full_firing_cycle * dataBlockIndex) + (single_firing * dataPointIndex)
return timing_offsets
To verify the values are correct, you can print them out and compare them with values in
Figure 9-7 on page 65
and
Figure
9-8 on page 66
.
timing_offsets = make_table(False) # False : single return mode
print('\n'.join([', '.join(['{:8.3f}'.format(value) for value in row])
for row in timing_offsets]))
Example: Calculate the exact firing time of the last firing in a packet if the timestamp value is 45,231,878 µs.
Chapter 9 • Sensor Data 63

 Loading...
Loading...