wc_tx003871gb_FM10.fm
155
Machines with Aftertreatment Exhaust System
15 Machines with Aftertreatment Exhaust System
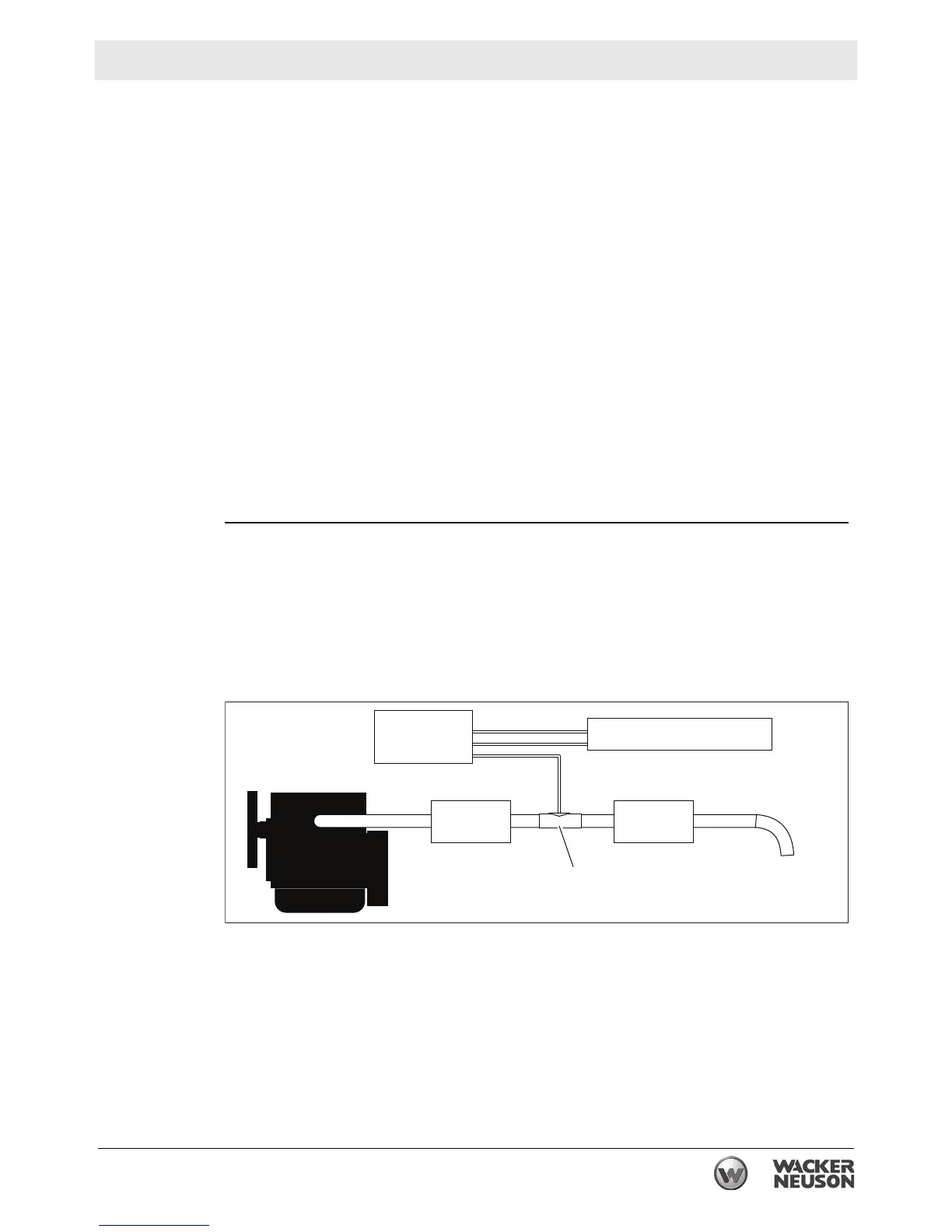
15.1 How the Aftertreatment Exhaust System Works
Background
Many Wacker Neuson Generators with Tier 4 engines use an aftertreatment
exhaust system to reduce emissions. There are five main components to the
system:
■ Heat
■ Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF)
DEF is a urea-based chemical reactant designed specifically for use in SCR
systems to reduce nitrogen oxides (NO
x
) emissions.
■ Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system
An SCR is a catalytic converter which houses a catalyst made of base metal
oxides (such as titanium, vanadium, and tungsten oxides).
■ Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)
A DOC is a catalytic converter that oxides pollutants such as carbon monoxide,
hydrocarbons, and organic diesel particulates.
■ Decomposition Reactor Tube (DRT)
A DRT is a tube between the DOC and the SCR into which the DEF is
introduced (dosed) into the exhaust stream.
How it works
► The exhaust is first treated by the DOC.
► Exhaust (NO
x
) emissions flow through the DOC into the DRT.
► DEF is injected into the DRT.
The amount and frequency is controlled by the DEF supply module.
► The DEF vaporizes and decomposes to form ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Within the SCR catalyst, the NOx are catalytically reduced by the ammonia into
water and nitrogen. These are then released through the exhaust elbow.
Interaction
The system requires very little interaction by the operator. Items that require
attention are:
■ DEF tank—refill as required
■ DEF supply module filter—change every 4500 hours
■ Manual regeneration—a manual regeneration of the system may be necessary
if the engine is unable to complete an automatic regeneration cycle.
DEF Tank
DOC SCR
DRT
DEF Supply
Module
wc_gr012291

 Loading...
Loading...