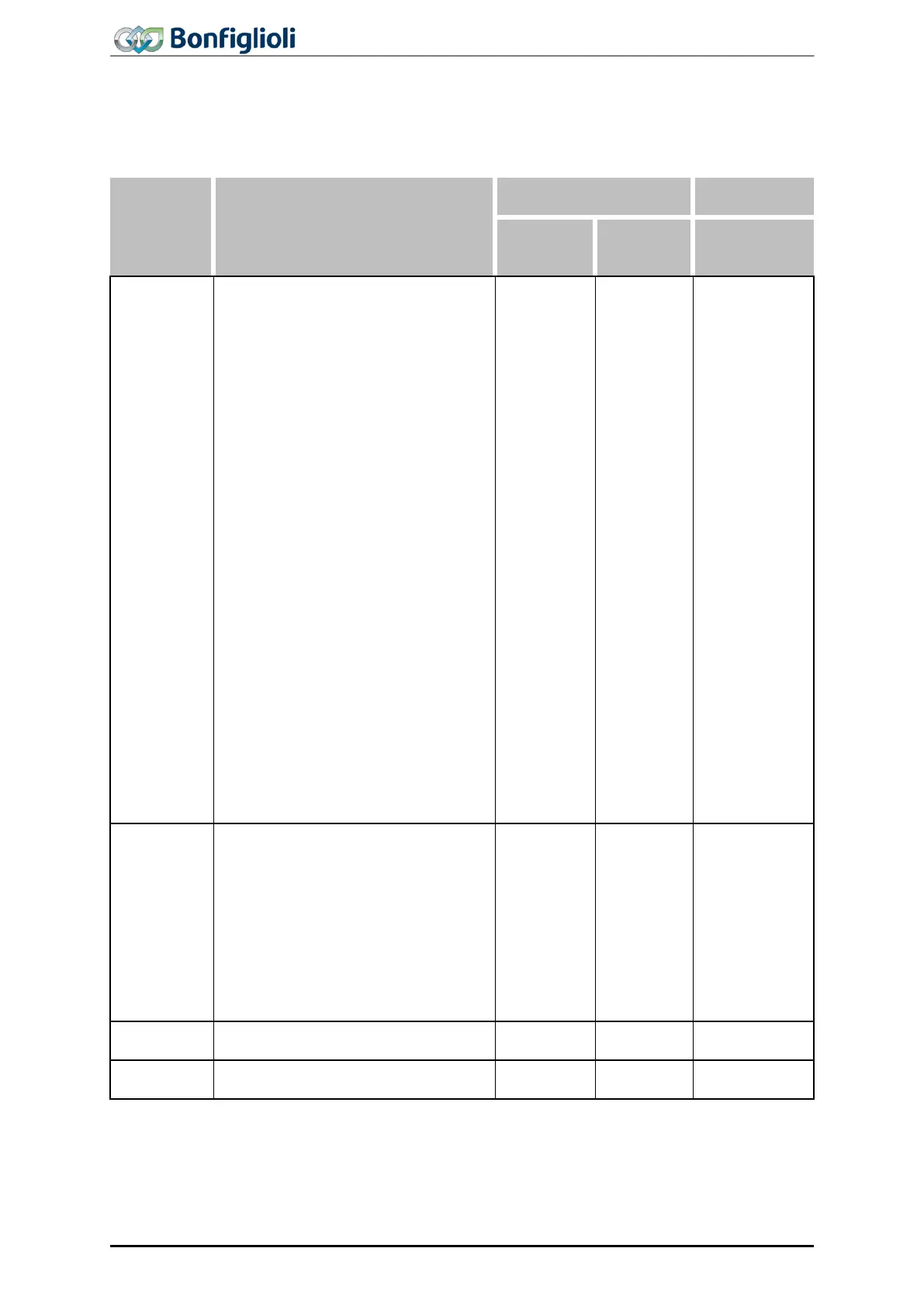
8.2 Handling of index parameters / cyclic writing
Index parameters are used for various ACU functions. Here, 16 or 32 indexes are used instead of the
4 data sets. For each function, the individual indexes are addressed separately via an index access
parameter. Via the indexing parameter, you can select if the data is to be written to EEPROM or RAM.
EEPROM
RAM
1202 Target position / distance
1203 Speed
1204
Acceleration
1205
Ramp Rise time
1206
Deceleration
1207
Ramp Fall time
1208
Motion mode
1209
Touch-Probe Window
1210 Touch-Probe-Error: Next Mo-
tion Block
1211
No. of Repetitions
1212 Delay
1213
Delay: Next Motion Block
1214 Event 1
1215 Event 1: Next Motion Block
1216 Event 2
1217 Event 2: Next motion block
1218 Digital signal 1
1219 Digital signal 2
1247 Digital signal 3
1248 Digital signal 4
1260 Interrupt-Event 1
1261 Int.-Event 1: Eval.-Mode
1262 Int. event 1: Next motion block
1263 Interrupt-Event 2
1264 Int.-Event 2: Eval.-Mode
1265 Int. event 2: Next motion block
0
1)
;
1…32
33
1)
;
34…65
1200 Write
1201 Read
(Function
Table)
1344 FT-Input 1
1345 FT-Input 2
1346 FT-Input 3
1347 FT-Input 4
1348 FT-Parameter 1
1349 FT-Parameter 2
1350 FT-Target Output 1
1351 FT-Target Output 2
1352
0
1)
;
1…32
33
1)
;
34…65
1341 Write
1342 Read
1) When the indexing parameter = 0, all indexes will be written upon parameter
access in EEPROM. 17 (for 16 indexes) or 33 (for 32 indexes) will write all indexes in
42
ACU
Modbus/TCP 10/13
 Loading...
Loading...











