4.23 Motor Components
4.23.1 Function
Themotortypeemployedisapermanentmagnet,synchronousspeedmotor.Thewindingsectionofthemotoris
similarindesigntoastandard3-phasestar-connectedStator.
4.23.1.1 Stator
TheStatoroperatesastheforcethatdrivestheshaft,utilizingtheHVDCpulsesprovidedtothemotorwindingsby
theInverter.
4.23.1.2 Rotor
Therotorisanintegralpartofthemotorshaftandisapermanentmagnetdesignthatallowsthesynchronous
characteristicrequiredforbroadrangespeedcontrol.
4.23.2 Motor Protection
Conventionalmotorprotectionbasedonincoming3-phasecurrentsandvoltageconditionsareinadequateto
protectthemotorandelectronicsintheeventofmishapduetothetotalseparationofthemotorwindingsfromthe
incoming3-phasecurrentbytheDCconversion.Therefore,thebulkofprotectionisbasedonmeasurementstaken
bytheInverterandcalculationsderivedfromthosemeasurements.
MotorcurrentsandvoltagesdisplayedintheSMTcannotbedirectlycomparedorcorrelatedtoincoming3-phase
ACvalues.
AllStatorsemployoverheatcutoutprotectionutilizingthermistorsineachwinding.
4.23.3 Motor Connections
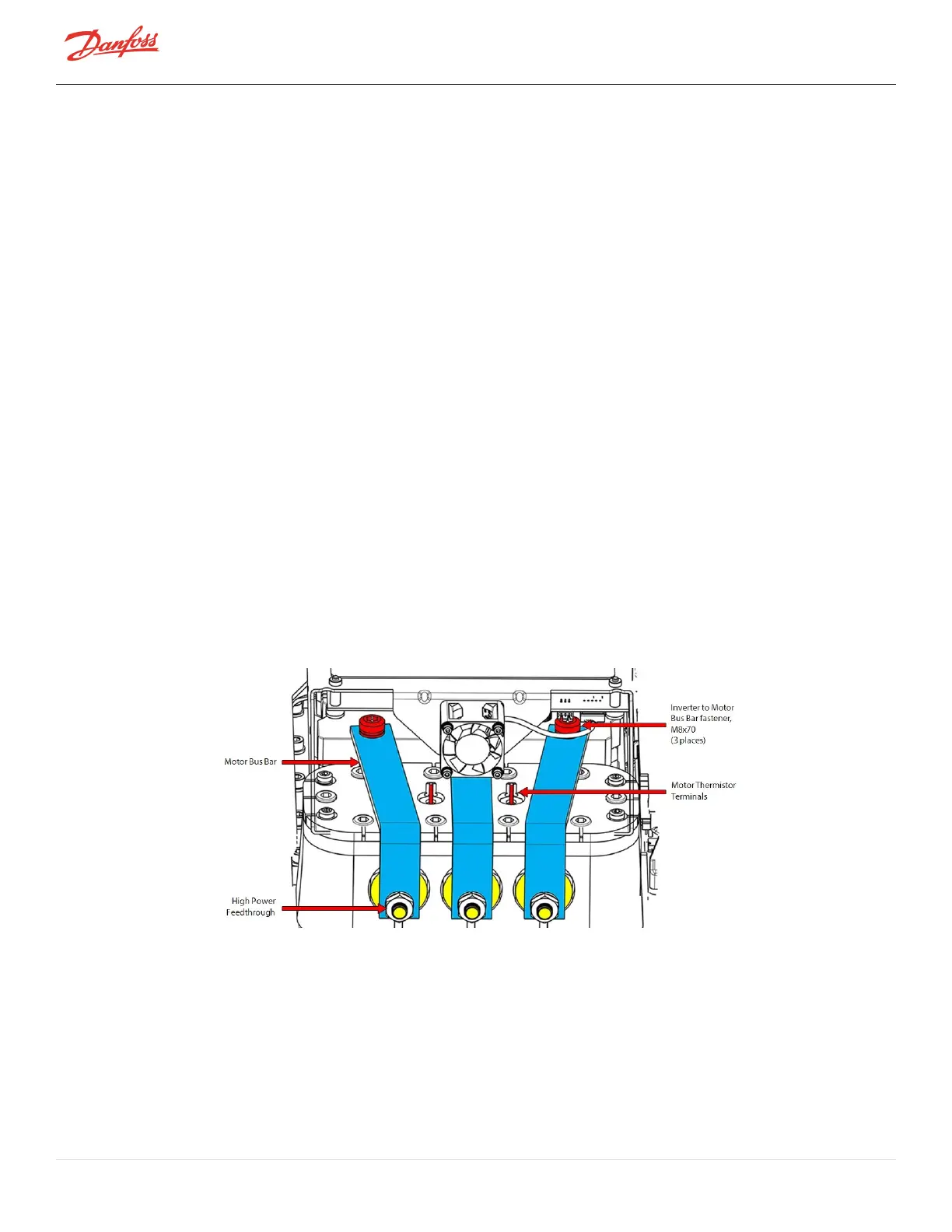
RefertoFigure4-217ConnectiontoStatorfordetailsontheconnectionsandserviceablecomponents.
Figure 4-217 Connection to Stator
Page 194 of 294 - M-SV-001-EN Rev. H 1/23/2023
 Loading...
Loading...











