Cooling
System
DODGE
Turbo Diesel
Cooling
System
Malfunctions -
Diagnosis
Page
7-3
Cooling
System
Malfunctions - Diagnosis
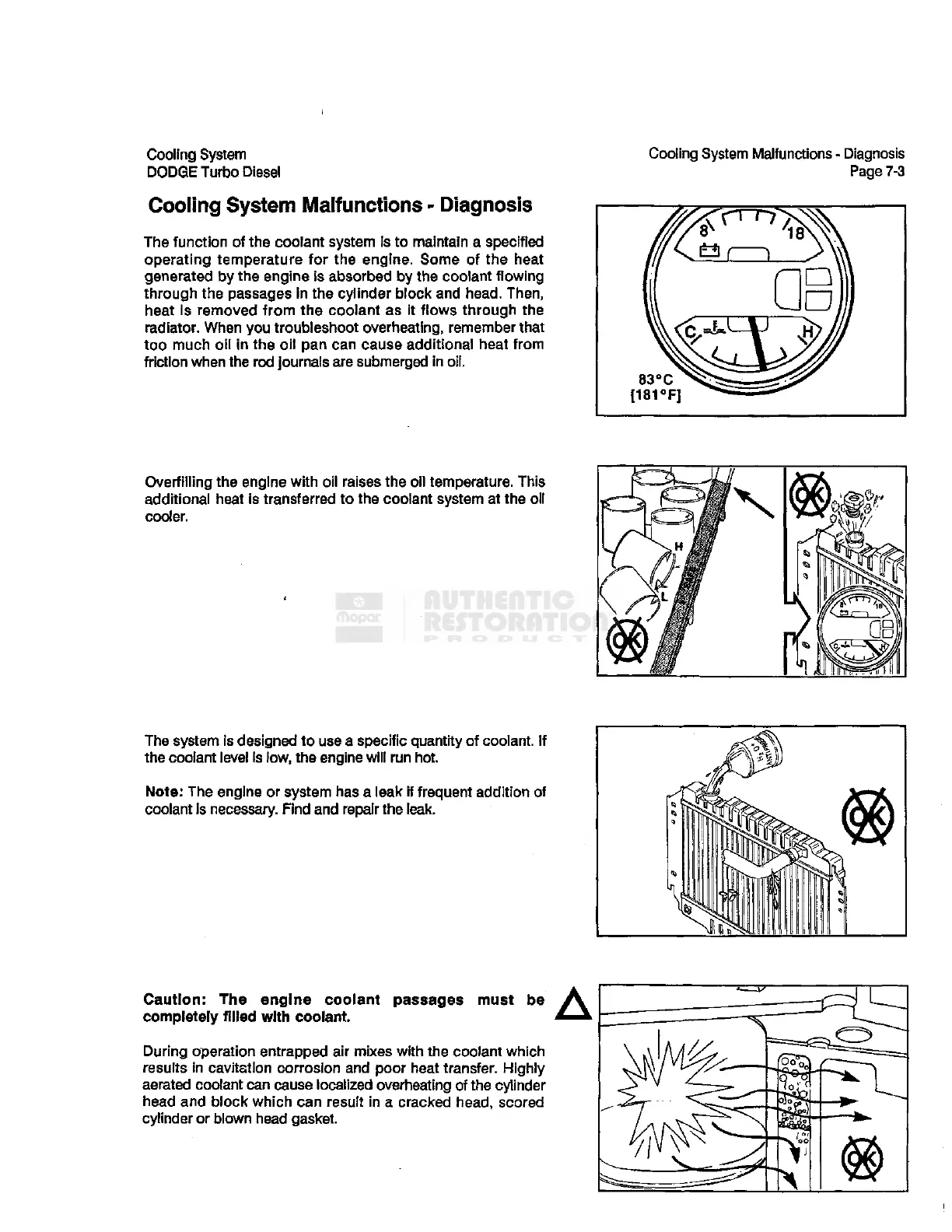
The
function of the coolant
system
is to maintain a specified
operating temperature for the engine. Some of the heat
generated by the engine is absorbed by the coolant flowing
through the
passages
in the cylinder block and head. Then,
heat Is removed
from
the coolant as it flows through the
radiator. When you troubleshoot overheating, remember
that
too much oil in the oil pan can
cause
additional heat
from
friction when the rod
journals
are submerged in oil.
Overfilling the engine
with
oil
raises
the oil temperature. This
additional heat is transferred to the coolant system at the oil
cooler.
The
system
is
designed
to
use
a
specific
quantity
of coolant. If
the coolant level Is low, the engine
will
run hot.
Note:
The engine or
system
has a leak if frequent addition of
coolant
is
necessary.
Find and repair the leak.
Caution:
The engine coolant
passages
must be
completely
filled
with
coolant.
During operation entrapped air mixes
with
the coolant which
results
in cavitation corrosion and poor heat transfer. Highly
aerated coolant can
cause
localized overheating of the cylinder
head
and block which can result in a cracked head, scored
cylinder
or blown head gasket.
 Loading...
Loading...











