Description
102
SIMV
Synchronised Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation
Combination of mandatory ventilation and spontaneous
breathing.
SIMV enables the patient to breathe spontaneously in regular
prescribed intervals between mandatory ventilation strokes
that ensure a minimum ventilation.
This minimum ventilation is defined by two set values, tidal
volume (VT) and ventilation frequency (f). The minimum
ventilation is the product of VT x f.
The ventilation pattern is set by the ventilation parameters
tidal volume VT, frequency f, inspiration time Tinsp and flow
acceleration FlowAcc.
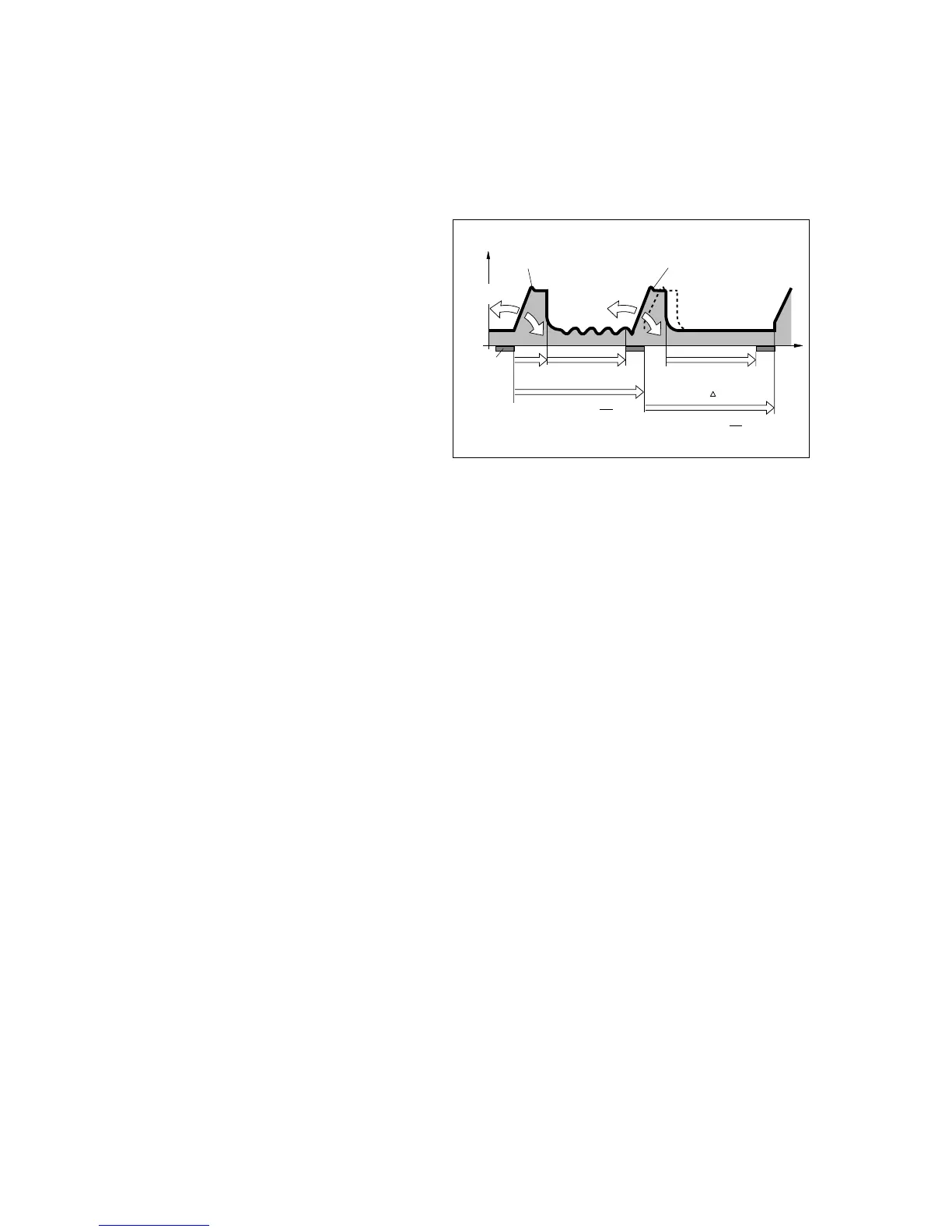
To prevent the mandatory ventilation stroke being applied
during spontaneous expiration, the Flowtrigger of the machine
ensures that the ventilation stroke is triggered within a "trigger
window" and synchronised with the patient's spontaneous
inspiration.
The "trigger window" is no longer than 5 seconds. If the
expiration times are less than 5 seconds, the trigger window
covers the entire expiration time, less a minimum expiration
time of 500 ms.
Since the synchronisation of the mandatory ventilation stroke
reduces the effective SIMV time and therefore would normally
result in an undesirable increase in the effective IMV
frequency, Savina adds in the reduced SIMV time by
prolonging the subsequent spontaneous breathing phase by
the SIMV time difference ∆ T – thus preventing an increase in
SIMV frequency. The frequency parameter f remains constant.
This parameter, in combination with the tidal volume VT, sets
the minimum ventilation. If the patient has breathed in a
considerable inspiratory volume at the beginning of the trigger
window, the machine reduces the subsequent mandatory
ventilation stroke by shortening the time for the inspiratory flow
phase and the inspiration time. In this way, the tidal volume VT
remains constant, and over-inflation of the lungs is avoided.
During the spontaneous breathing phases, the patient can be
assisted by ASB pressure support.
In the course of progressively weaning the patient from
artificial ventilation, the ventilation frequency f is further
reduced while the spontaneous breathing time is increased,
so that the required total minute volume is supplied more and
more by spontaneous breathing.
The ventilation frequency can be reduced to 2/min.
041 37388
Paw
PEEP
t
spontaneous
breathing time
spontaneous
breathing time
+ T
set IMV time
Trigger
window
synchronised
mandatory
ventilation stroke
unsynchronised
mandatory
ventilation stroke
Tinsp
f
1
f
1
set IMV time
FlowAcc FlowAcc

 Loading...
Loading...