810
Users Manual
4-26
Sensor Orientation
Consistent Sensor orientation is critical to ensure
repeatable data and consistent diagnoses over time. The
Tester uses a triaxial Sensor that combines three
transducers into a single housing. These three
transducers simultaneously measure the vibration data
from three axes or directions:
• Axial (A)
• Radial (R)
• Tangential (T)
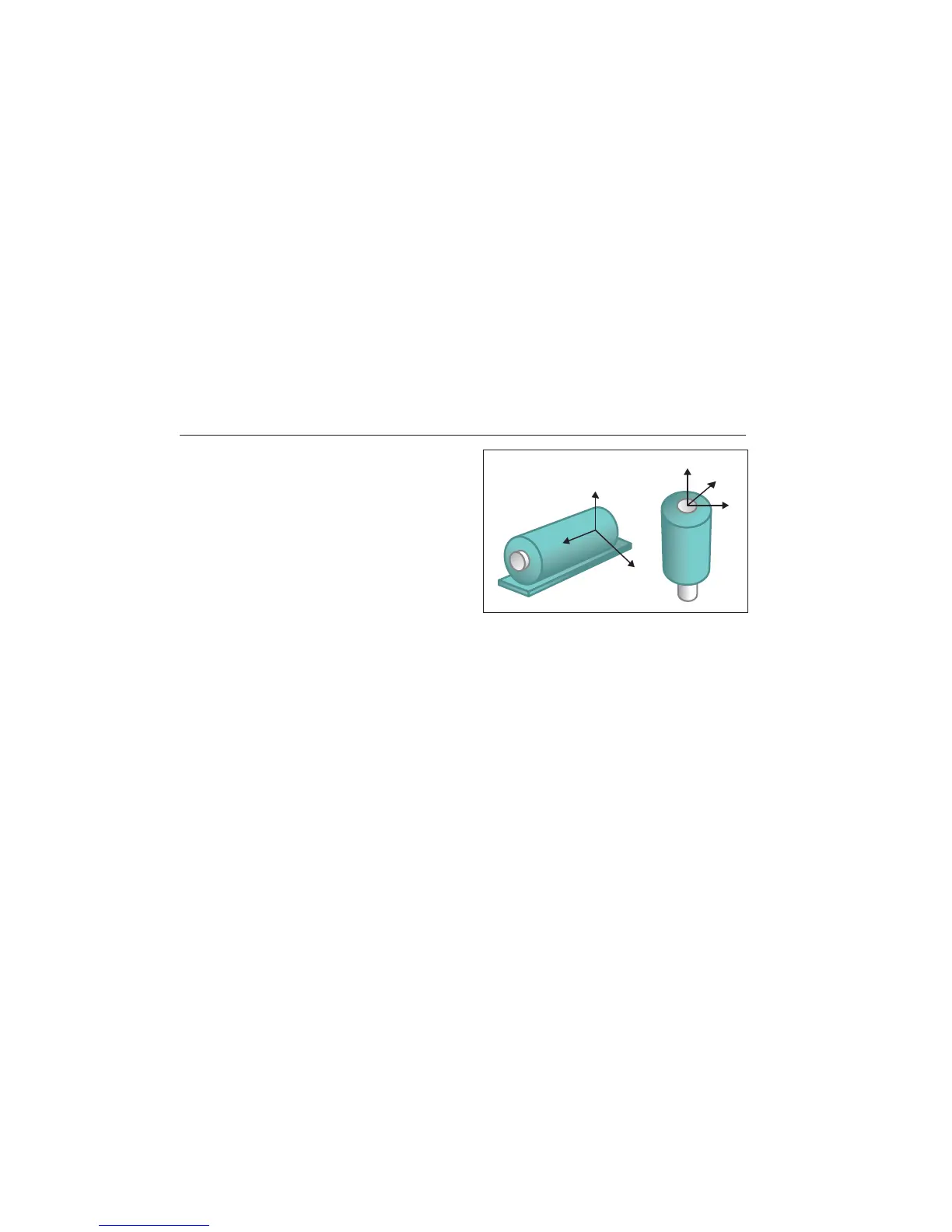
The axes are oriented to the drivetrain shaft and vary
depending on the horizontal or vertical orientation of the
drivetrain. See Figure 4-2.
Note
If you define the Sensor orientation incorrectly in
the user interface, the diagnostic engine is
unable to associate the vibration signals with the
correct axes. The result is a false diagnosis from
the Tester.
R
T
R
T
A
A
A = Axial
R = Radial
T = Tangential
gbk08.eps
Figure 4-2. Axes Orientation
The Tester uses the machine driveshaft as the common
reference point. You must set the orientation of the
Sensor cable as either parallel or perpendicular to the
driveshaft.
 Loading...
Loading...