Settings
37
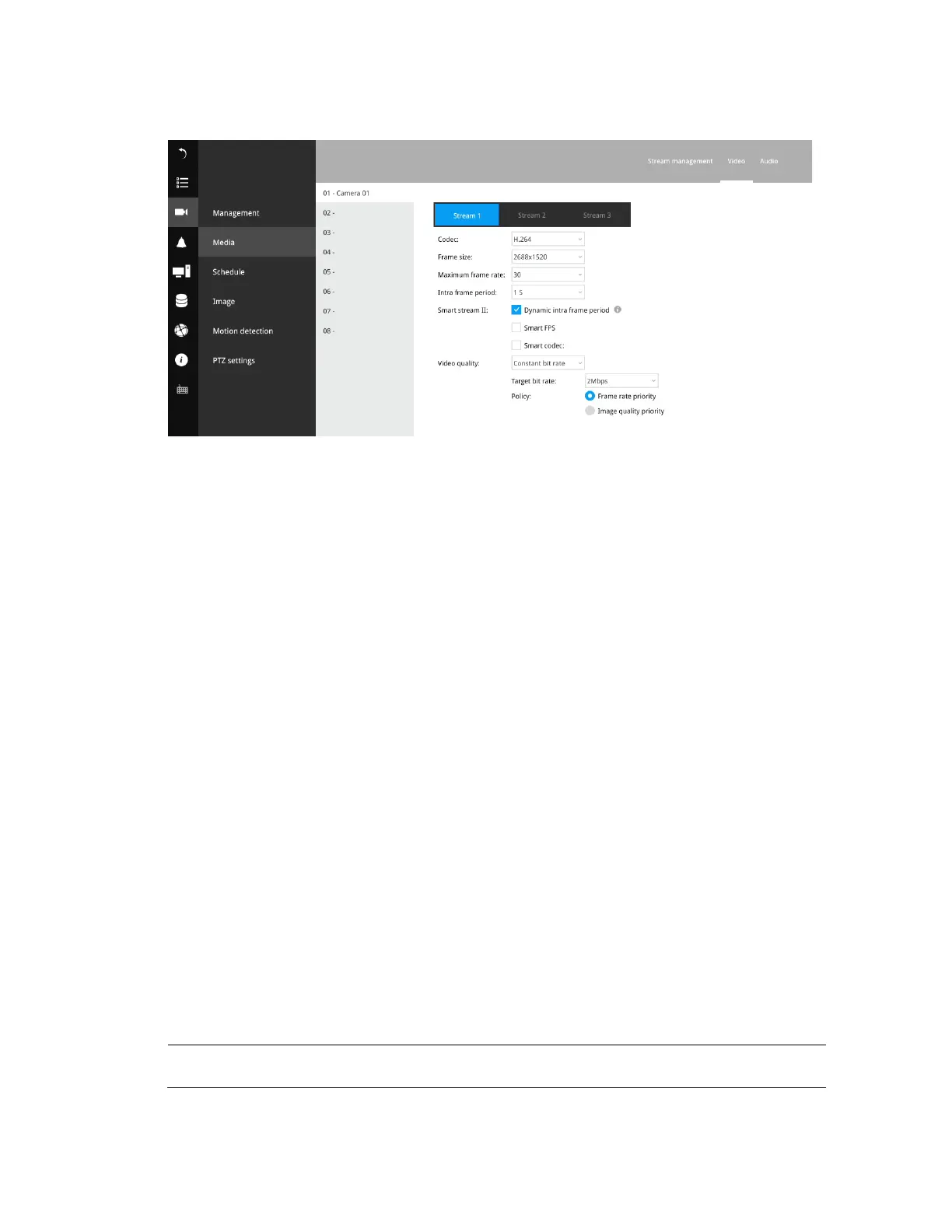
Figure 6-11 Media-Video
The Video window allows you to configure all video streams (the no. of stream available can be
different for different models). You can configure the following:
Codec: video compression codec in H.264, H265 or MJPEG.
Frame size: video resolution.
Maximum frame rate: the highest frame rate.
Intra frame period: how often an I-frame will be inserted into the video stream.
Smart Stream II: some newer camera models come with Smart Stream features.
•
Dynamic intra frame period: High quality motion codecs, such as H.265, utilize the
redundancies between video frames to deliver video streams at a balance of quality and
bit rate. The encoding parameters are summarized and illustrated below. The I-frames are
completely self-referential and they are largest in size. The P-frames are predicted
frames. The encoder refers to the previous I- or P-frames for redundant image
information.
•
Smart FPS: In a static scene, the algorithm puts old frames in queue when no motions
occur in scene. When motions occur, the encoding returns to normal to deliver real-time
streaming.
By queuing the old frames from a static scene, both the computing efforts and the size of
P frames are reduced. It is beneficial for keeping up with the frame rate requirements.
A default frame difference threshold, 1%, is embedded in firmware for returning from
Smart FPS to normal encoding when motions occur.
•
Smart Codec: Smart codec effectively reduces the quality of the whole or the non-
interested areas on a screen and therefore reduces the bandwidth consumed.
Video quality: you may either select Constant bit rate or Fixed quality as the defining rules
for video transmission:
Table 6-2 Video Quality
Constant bit rate
Places a packet size threshold on video frames; This
guarantees the frame rate per second performance, yet

 Loading...
Loading...











