2B-4 - ELECTRICAL 90-826148R2 MARCH 1997
Battery Charging System
(14 or 18 Ampere Alternator)
Description
The battery charging system components are the
stator, voltage regulator and battery. Alternating cur-
rent (generated in stator alternator coils) flows to the
voltage regulator, which changes the alternating cur-
rent to direct current for charging the battery.
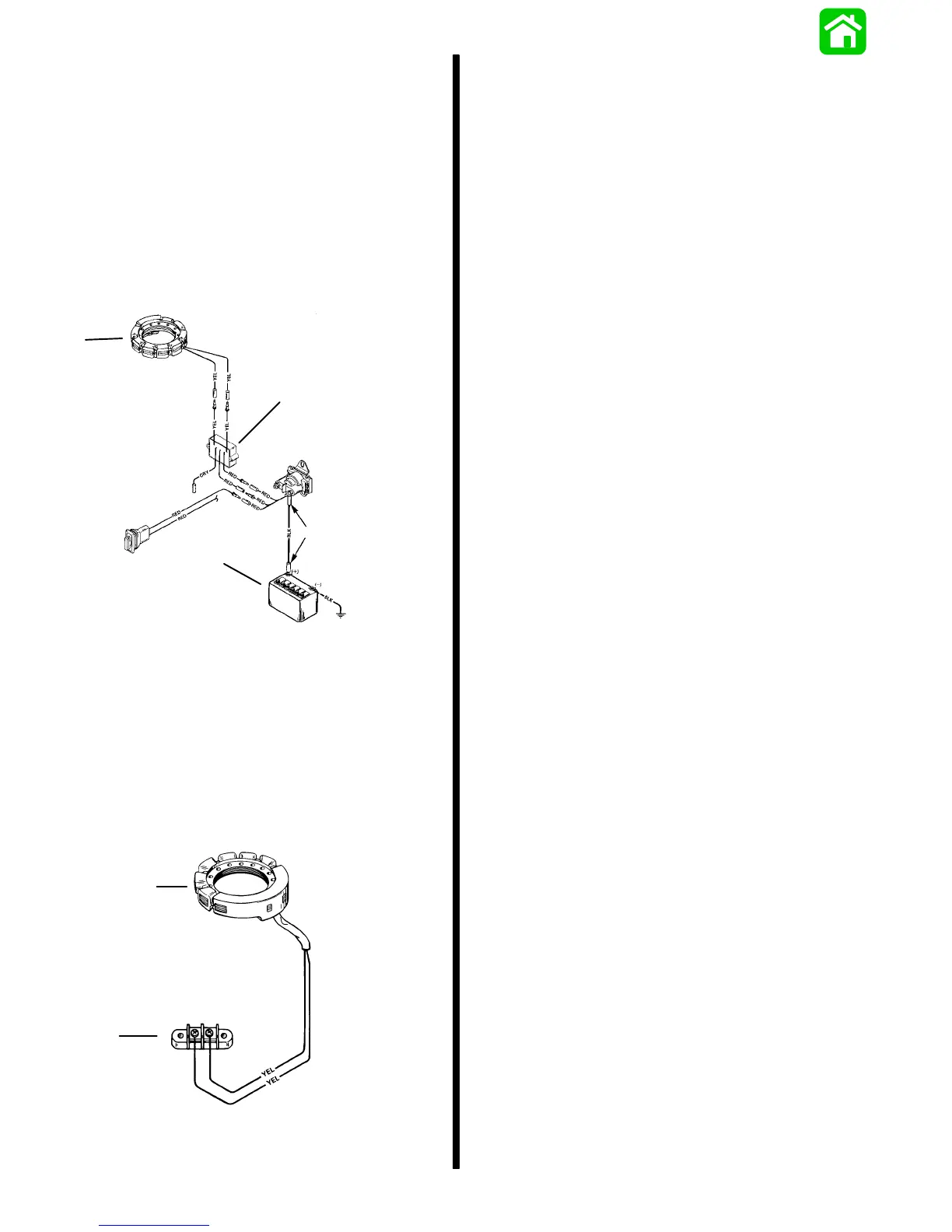
ELECTRIC START MODELS
RED SLEEVE
52684
a
b
c
a - Stator
b - Regulator
c - Battery
The charging system may be damaged by: 1) re-
versed battery cables, 2) running the engine with bat-
tery cables disconnected and stator leads connected
to rectifier, and 3) an open circuit, such as a broken
wire or loose connection.
MANUAL START MODELS
52657
a
b
a - 9 Ampere Stator
b - Terminal Block
Battery Charging System
Troubleshooting
A fault in the battery charging system usually will
cause the battery to become undercharged. Check
battery electrolyte level, and charge battery. See
“Electrolyte Level”, and “Charging a Discharged
Battery”.
If battery will NOT accept a satisfactory charge, re-
place battery.
If battery accepts a satisfactory charge, determine
the cause of the charging system problem as follows.
1. Check for correct battery polarity [RED cable to
POSITIVE (+) battery terminal]. If polarity was in-
correct, check for damaged rectifier. See “REC-
TIFIER TEST”.
2. Check for loose or corroded battery connections.
3. Visually inspect wiring between stator and bat-
tery for cuts, chafing; and disconnected, loose or
corroded connection.
4. Excessive electrical load (from too many acces-
sories) will cause battery to run down.
If visual inspection determines that battery connec-
tions and wiring are OK, perform the following stator
and rectifier tests.

 Loading...
Loading...