Description Gas Monitoring (optional)
11 - 2 0070- 0-0704-02 Passport V Operating Instructions
The Minimum Alveolar Concentration (MAC) is also displayed in the Gas tile. MAC is a
calculated value defined in ISO 21647:2004(E) as follows:
MAC - alveolar concentration of an inhaled anesthetic agent that, in the
absence of other anesthetic agents and at equilibrium, prevents 50% of
subjects from moving in response to a standard surgical stimulus.
The MAC value is calculated using the following formula:
where AA is the anesthetic agent in use, ET AA is the end-tidal agent concentration, x(AA) is
a clinically-derived coefficient based on anesthetic agent (known as 1MAC values), ET N
2
O
is the end-tidal N
2
O concentration and x(N
2
O) is a clinically-derived coefficient for N
2
O
(also known as the 1MAC value). From ISO 21647:2004(E), the 1MAC values used in the
calculation are:
NOTE: The calculated MAC value is not corrected for ambient
pressure (altitude & barometric effects), patient age, patient
core temperature or any other individual factors influencing
the effect of volatile anesthetic agents.
NOTE: If mixed agents are detected, the MAC value is invalidated
(displayed as dashes).
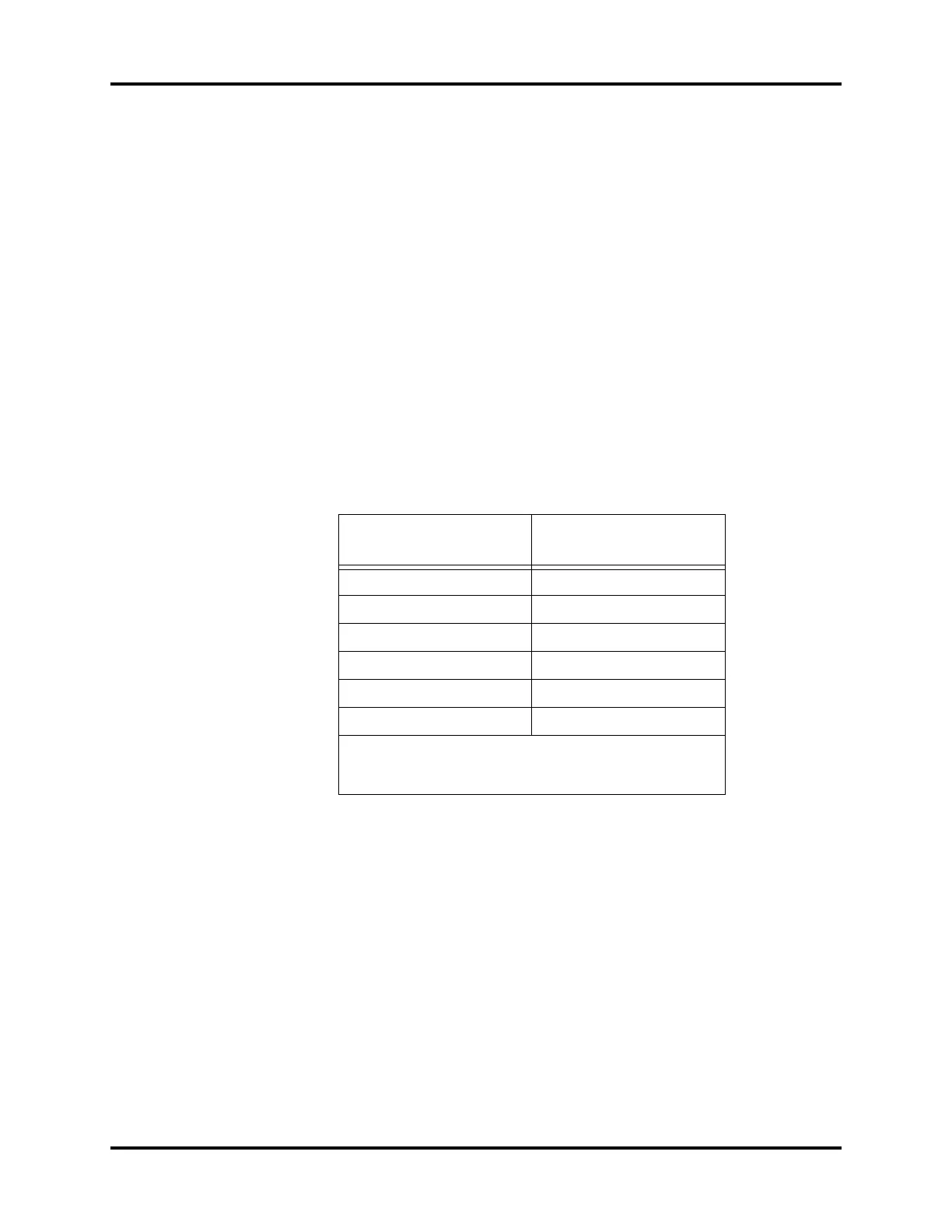
HALOGENATED AGENT
1MAC
(IN OXYGEN)
% VOLUME FRACTION
Halothane 0.77
Enflurane 1.7
Isoflurane 1.15
Desflurane 7.3
Sevoflurane 2.1
N
2
O 105
With the exception of Desflurane, the 1MAC values shown in this
table apply to an age sample of 40-years-old. The Desflurane 1MAC
value applies to an age sample of 25-years-old.
MAC (AA) =
% (ET AA)
x(AA)
---------------------------------------------
% (ET N2O)
x(N2O)
-----------------------------------------------------+
0
 Loading...
Loading...