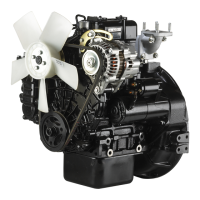
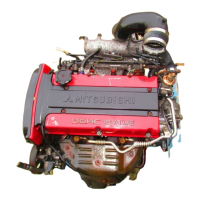
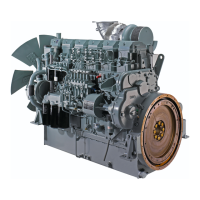
11
11-11
• As the Powertard cam further rotates
and the cam lobe top leaves the mas-
ter piston, the oil pressure in the oil
passage is reduced.
• As a result, the exhaust valve is
closed by its spring force, which allows
the valve to open and close according
to ordinary valve timing. At the same
time, the check valve in the control
valve opens to let engine oil (oil pres-
sure produced by ordinary engine oil
pump) work through the oil passages
and, allowing the exhaust valve to be
forced open again through the move-
ment of the Powertard cam.
• When the Powertard release condi-
tions are met, the following sequence
of operation is followed.
• When the solenoid valve is de-ener-
gized, the control valve shuts the in-
coming path (A) for engine oil from
the rocker case and opens the out-
going path (B) to the cylinder head.
• Engine oil in the oil passage is let
out through B, relieving the control
valve of oil pressure.
• The control valve opens the path
(C)
th
at has been closed by oil pres-
sure to let out engine oil in the
chamber of the slave piston and oil
passage.
• As the oil pressure is removed, the
master piston is lowered to leave
the Powertard cam.
• At the same time, the slave piston is
forced up by the spring force. As a
result, the exhaust valve is closed
and the Powertard is turned off.
(3) Powertard brake control (Power-
tard: Switch is placed in the sec-
ond stage)
• The turbocharger magnetic valve
feeds air A to the air cylinder, narrow-
ing turbine vane B.
• The number of revolutions of the tur-
bocharger increases, taking more air
into the combustion chamber.
• Compressed air C increases and the
braking force of the Powertard be-
comes stronger.

 Loading...
Loading...