Calculation of motor-shaft conversion torque and effective torque
Calculate the acceleration torque from the motor-shaft conversion load inertia, the motor-rotor iner-
tia and the acceleration. Then, calculate the load torque from the external force (gravity and ten-
sion) and friction force applied to the load. Finally, combine these calculation results to calculate
the torque required for the motor.
•
Calculation of acceleration torque (T
A
)
JL
JM
η
N
tA
TA:Acceleration torque [N·m]
JL:Motor-shaft conversion load inertia [kg·m
2
]
J
M:Motor-rotor inertia [kg·m
2
]
η:Efficiency of transfer part (η≦1)
tA:Acceleration time [s]
N:Motor rotation speed [r/min]
Motor
Speed (rotation speed)
Time
+JM
60・tA
2π・N
η
JL
=
TA[N·m
]
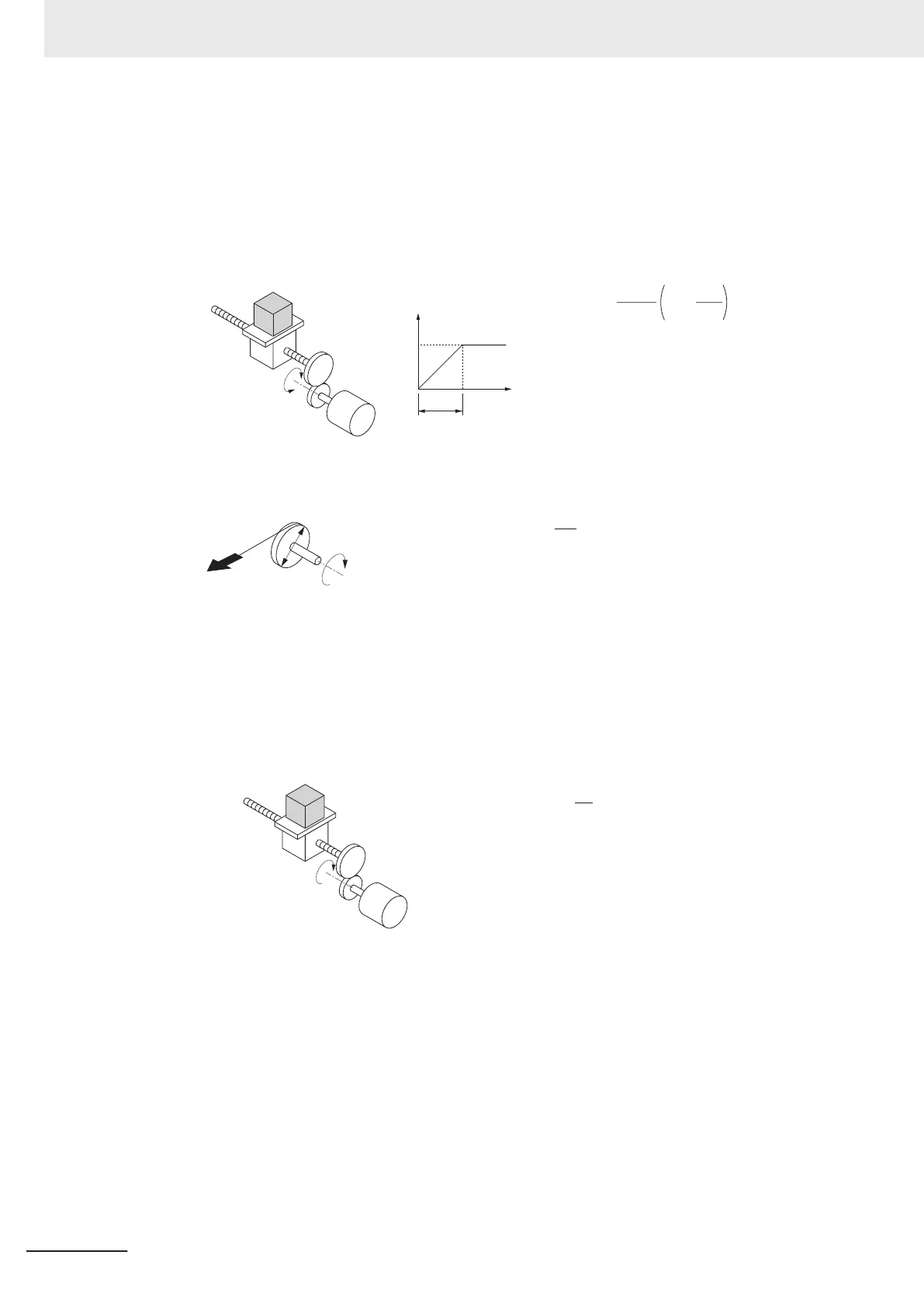
• Calculation of motor-shaft conversion load torque (T
L
)
F
D
TW
TW [N·m]=F· ×10
-3
D
2
(Generally, the friction force can be calculated as below:)
F=
μ
Mg [N]
μ: Coefficient of friction
M: Mass of motion part [kg]
g: Acceleration of gravity (g≈9.8 [m/s
2
])
TW: Load torque (Load-shaft conversion) [N·m]
F: External force [N]
D: Diameter of cylinder [mm]
T
: Motor-shaft conversion load torque [N·m]
T
: Load torque (Load-shaft conversion) [N·m]
Z
: Number of motor-side gear teeth
Z
: Number of load-side gear teeth
G : Gear ratio (Speed reduction ratio) = Z / Z
G
η
T
[N·m] = T
·
Z
T
Z
Motor
T
• Calculation of combined torque and effective torque
Appendix
A-12
M1 Series Standard Type User's Manual (I669)
 Loading...
Loading...