DC Voltage Measurement
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7-2
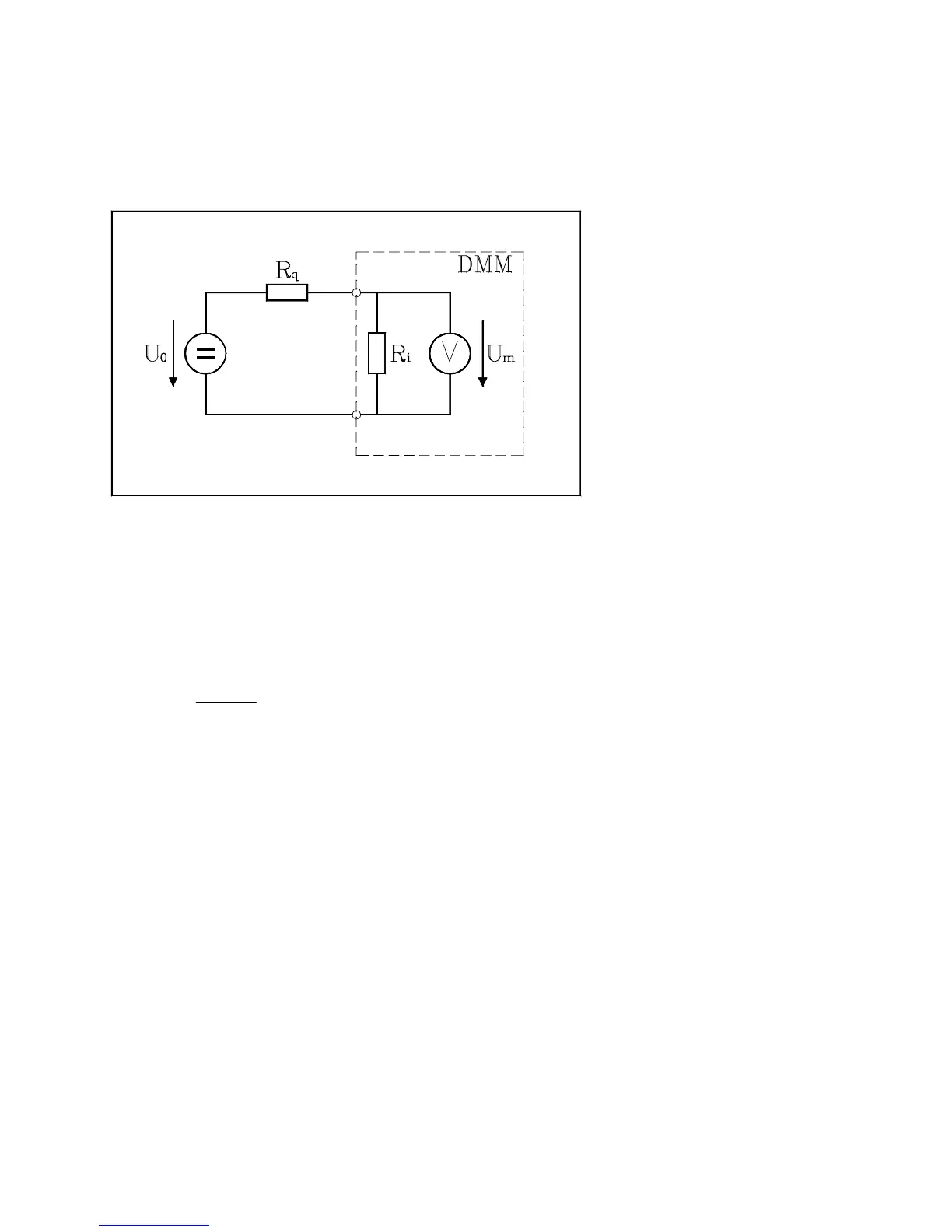
The influence of the source resistance is visualized in the following diagram:
Figure: Influence of source resistance on the measurement unit
R
i
= Input Resistance of the Multimeter ( 10MΩ or >1GΩ )
R
q
= Source Resistance of the Measurement Object
U
o
= Voltage of the Measurement Object
The error, in %, of a measurement, is calculated as follows:
Example: R
i
>= 1GΩ; R
q
= 10kΩ
Error = 0.0001% (1 ppm)
The error rating, in ppm (parts per million), often used in measurement technology, is
derived from: Error(%) x 10,000.
Series Mode Suppression
One of the main advantages of the integrating measurement process lies in the high
suppression of series AC voltage components (e.g. main line scatter), which are
overlaid on the actual signal voltage. For frequencies, where the measurement time is
an integer multiple of the period length, an infinitely high noise suppression level
theoretically results.
Short-term fluctuations of the mains frequency would lead to measurement errors in
case of fixed measurement times.
Error(%)
R
RR
=
×
+
100
q
qi
 Loading...
Loading...