7
7.2 Fault Recorders
89Digital Fault Recorder, SIMEAS R-PMU, Manual
E50417-H1076-C360-A5, Release 10.2012
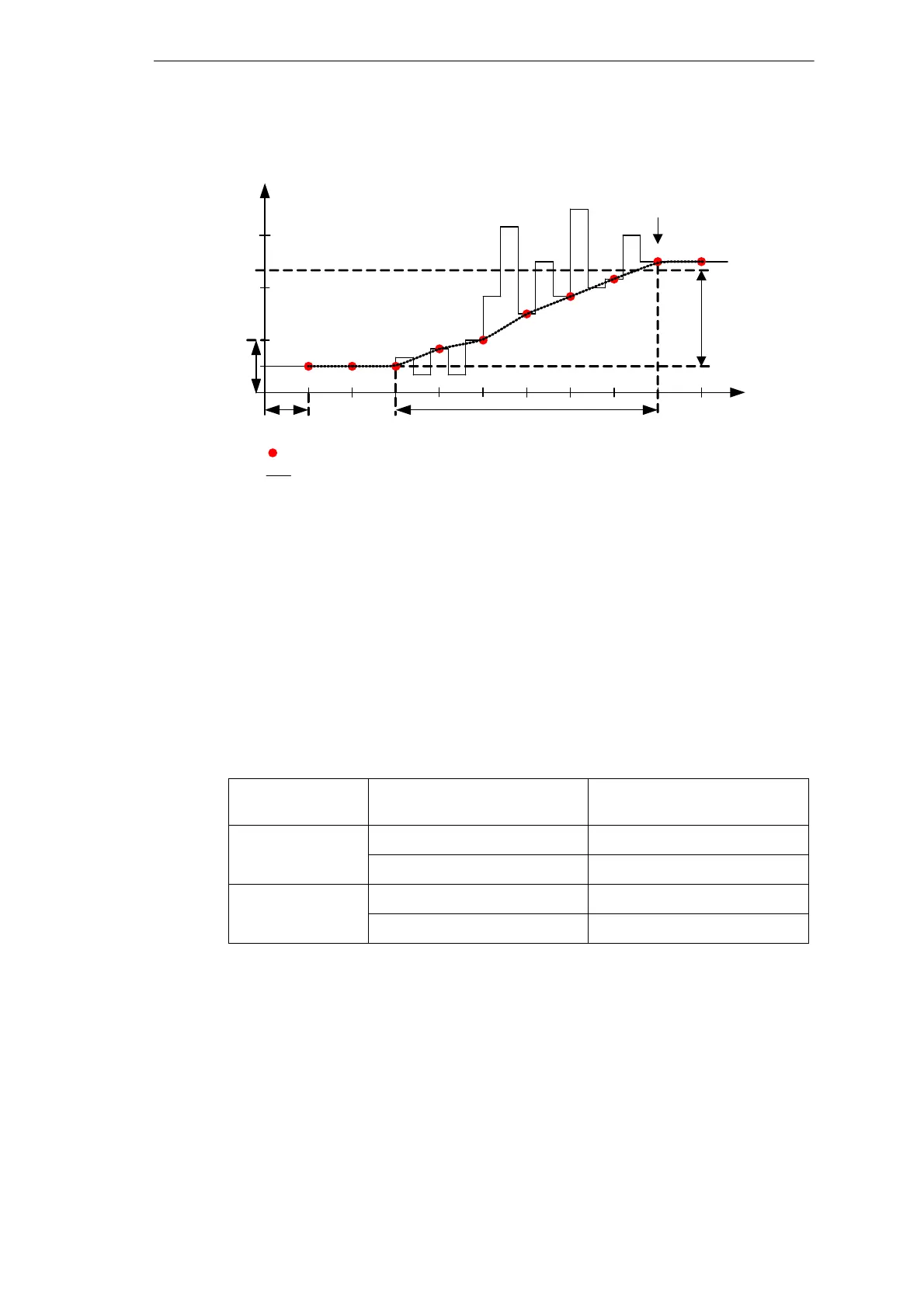
Figure 7-21 Triggering with recording rate = 5 nominal cycles
7.2.2.2.2 Binary Trigger
Status changes of the binary DAU inputs can be defined as trigger conditions. Thus, a record
can be started, if a sensor changes to or leaves from the alarm state or for each state change.
The correspondence between physical and logical state change depends on the sensor type
(see table 7-14 and chapter 12.11.1).
For the definition of high and low levels, refer to chapter 16.1.5.
Retrigger blocking for binary signals
The retrigger blocking can be activated separately for every binary input. It is used to suppress
repeated recordings in the event of fast successive binary signal changes while recording. The
corresponding binary trigger is disabled for the preset retrigger blocking time. If the same binary
input is retriggered within the retrigger blocking time, the retrigger blocking will be restarted for
this input. All other active channels can retrigger the TPR and thus extend the fault record.
f
n
Filter time
30 nominal cycles
Trigger
f
1/3 f
n
t [nominal cycles]
Recording rate = 5 nominal cycles
5 nominal cycles
Trigger threshold,
gradient trigger
Recorded value
Actual signal
Table 7-21 Sensor types
Sensor Logical
state change
Physical
state change
Make contact Change to alarm state Low → High
Change from alarm state High → Low
Break contact Change to alarm state High → Low
Change from alarm state Low → High

 Loading...
Loading...











