7
7.3 Continuous Recorder
92 Digital Fault Recorder, SIMEAS R-PMU, Manual
E50417-H1076-C360-A5, Release 10.2012
7.3 Continuous Recorder
The SIMEAS R-PMU features six continuous recorders: 5 Continuous Recorders (CR) and the
Event Recorder (ER). Continuous Recorders are used for data acquisition of the analog values
over longer periods of time, in order to be able to perform long-term analyses of the system
behaviour. The Event Recorder records the state changes of binary signals. Table 7-22 provides
an exact overview of the available recorders.
The individual recorders use different methods of data acquisition:
The CPR records the values as instantaneous values at the end of the parameterized
recording interval.
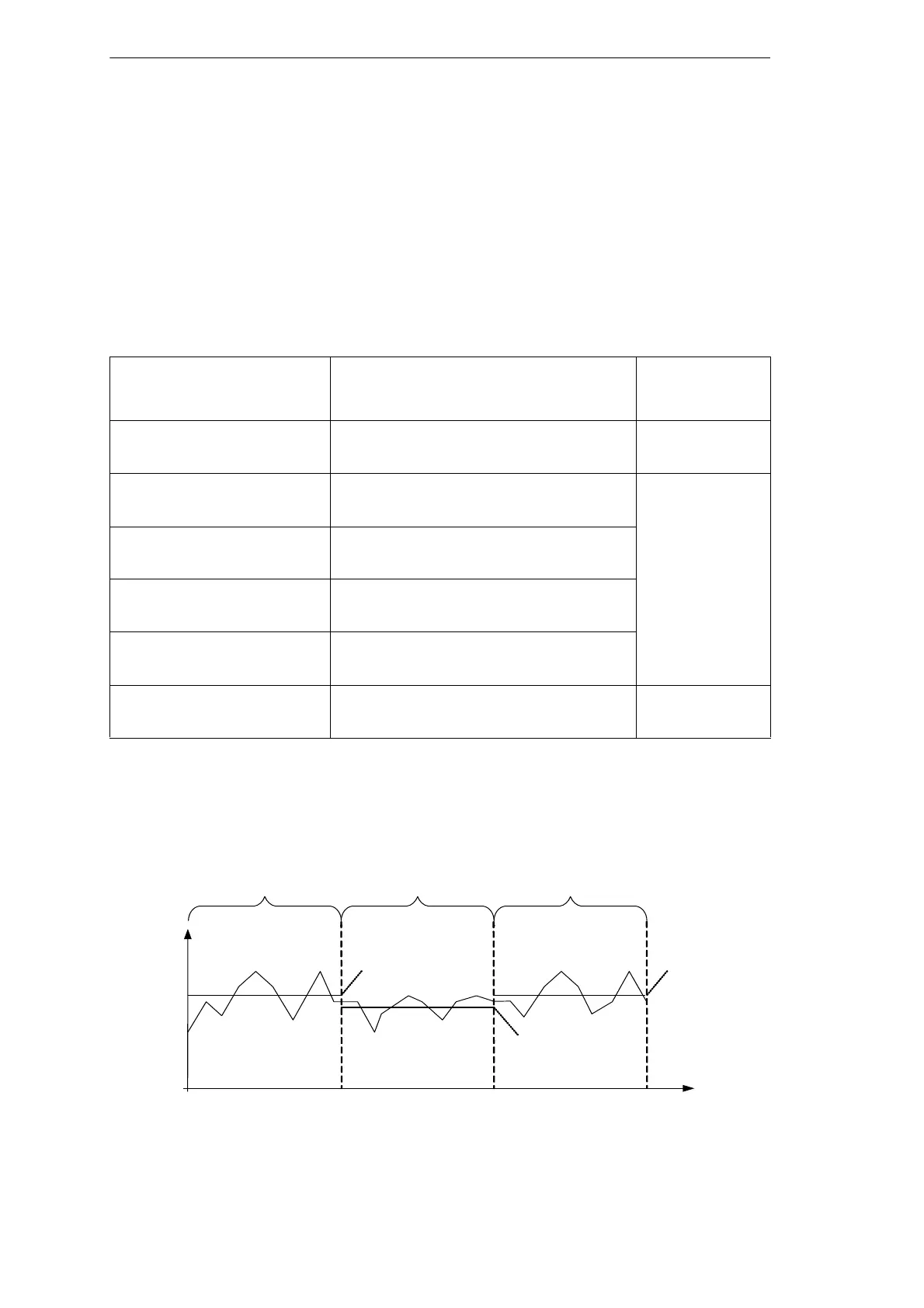
The CFR, CRR, CQR and CDR recorders calculate the arithmetic mean of the cycle-based
measured values using the averaging interval (see figure 7-22).
Figure 7-22 Calculating the arithmetic mean at the end of each averaging interval for CFR, CRR, CQR and CDR
Table 7-22 Continuous recorder overview
Designation Recorded values Recording interval
(to be
parameterized)
Continuous Phasor Recorder
(CPR)
Phasors, frequencies Cycle time:
1 s to 10 min
Continuous Frequency Recorder
(CFR)
Frequencies
Arithmetic mean value
Averaging time:
1 s to 10 min
Continuous RMS-value Recorder
(CRR)
rms values (V, I)
Arithmetic mean value
Continuous Power Recorder
(CQR)
Active and reactive powers
Arithmetic mean value
Continuous DC Recorder
(CDR)
Process signals
Arithmetic mean value
Event Recorder
(ER)
Binary signals Event-controlled
Averaging interval Averaging intervalAveraging interval
Arithmetic mean
value
Arithmetic mean
value
Arithmetic mean
value
t
Signal

 Loading...
Loading...











