RUN XT: Service & Maintenance Manual - rev. 2.0
Page 3.6
3.3. UP-DOWN MOTOR DRIVE
The elevation of the machine is varied by the up-down motor which, by means of a timing belt, turns
the lead screw nuts on the 2 elevation bars. The motor has an integral encoder wheel which, by
means of a photocell, provides the motor motion control signal: each motor revolution corresponds
to a predetermined number of pulses and to a predetermined displacement on the elevation bars.
The direction of rotation of the motor determines whether the treadmill moves upward or
downward.
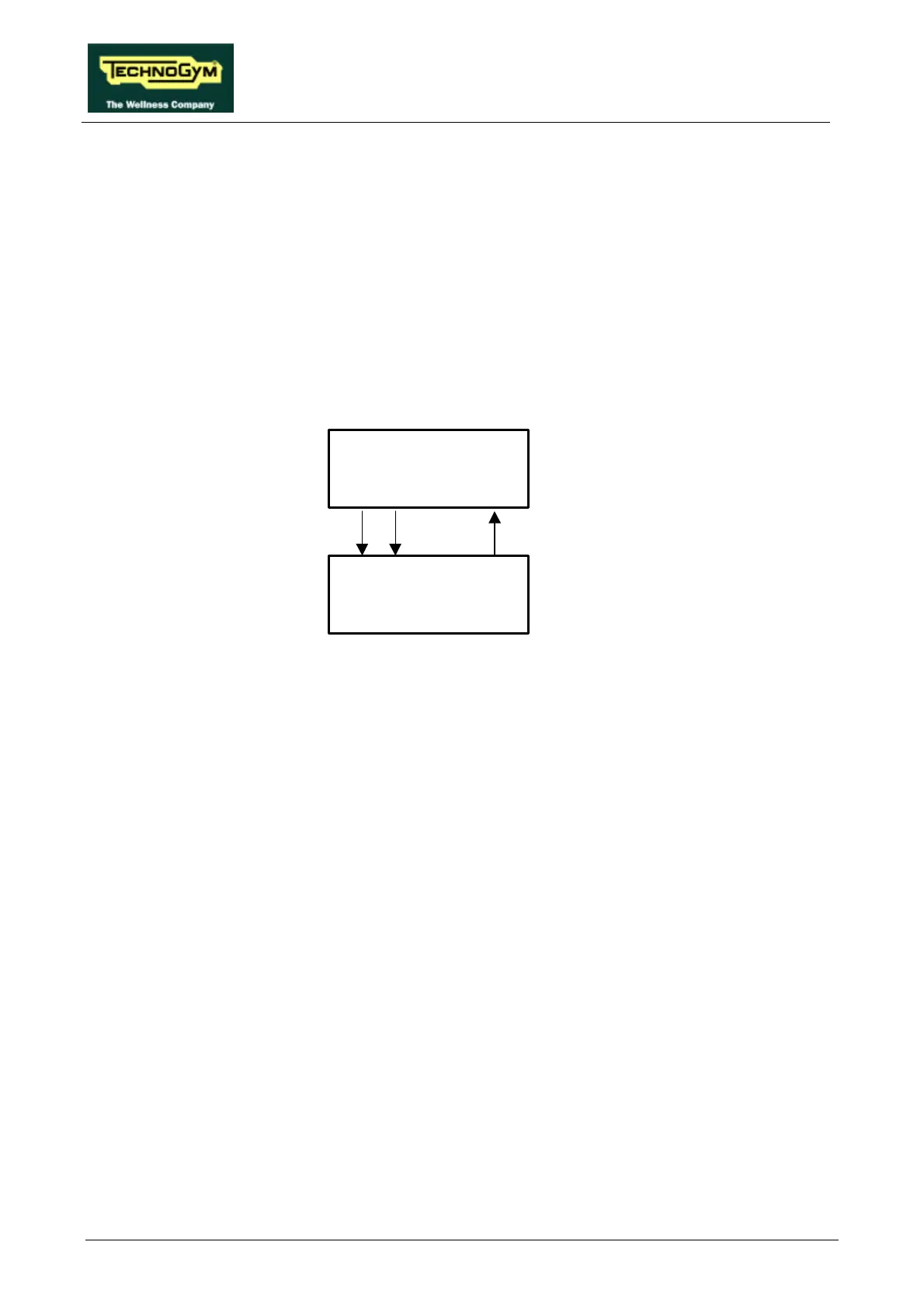
The machine controls the elevation through the CPU board and the up-down interface board as
shown in the figure below:
The elevation control utilizes 3 signals:
• Up signal
This is the signal generated by the CPU (pins 10-12 of connector CN1) to enable movement of
the up-down motor in the upward direction. Under normal conditions the signal is at logic level
low (0 Vdc), and it goes high (5 Vdc) to actuate the motor. The signal remains high for the entire
duration of the movement.
The signal enters the up-down board (pin 2-4 of connector CN2) and enables movement of the
motor in the desired direction.
• Down signal
This is the signal generated by the CPU (pin 11-12 of connector CN1) to enable movement of the
up-down motor in the downward direction. Under normal conditions the signal is at logic level
low (0 Vdc), and it goes high (5 Vdc) to actuate the motor. The signal remains high for the entire
duration of the movement.
The signal enters the up-down board (pin 3-4 of connector CN2) and enables movement of the
motor in the desired direction.
• Status signal
This is the signal generated by the up-down board whenever the photocell detects a number of
pulses corresponding to an 0.5% variation in the elevation. This signal (pin 1-4 of connector CN2
of the up-down board) is normally at logic level low (0Vdc) and goes high (5 Vdc) for a few
msec.
The CPU board receives this signal (pin 9-12 of connector CN1) which indicates the actual
elevation of the machine. Comparing it with the desired elevation value, the CPU determines
CPU board
Up-down
interface board
StatusDownUp
 Loading...
Loading...











