5
1.3 Differences between the 2G, 3G, 3GA, 4G, 4GA and WiFi models
The only difference between the 2G, 3G and 4G models is the type of the modem used.
The 3G (UMTS) and the 4G (LTE) communication makes possible higher speed, thereby
increasing the speed of reporting. The 2G, 3G and the 4G models can be used in Europe, while
the 3GA model is equipped with a pentaband UMTS/HSPA modem that can be used worldwide.
The 4GA model is equipped with a multiband LTE modem which can be used in North America.
There is no difference between the mentioned models regarding the available functions or
configuration. For the 2G model, calls made through the GSM network will delay all other
communication, since 2G modems are unable to use multiple communication channels
simultaneously.
The WiFi model can only be used with a WiFi network. SMS and call-based functions are not
available in this model since it does not have a GSM modem. In turn, this model does not require
a SIM card.
1.4 Under Voltage Lock Out (UVLO) function
The Adapter2 is provided with built-in automatic power disconnection (Under Voltage
Lock Out) function. The device will turn off automatically when the supply voltage drops
below critical level, and turns back on when the voltage restores to operational level.
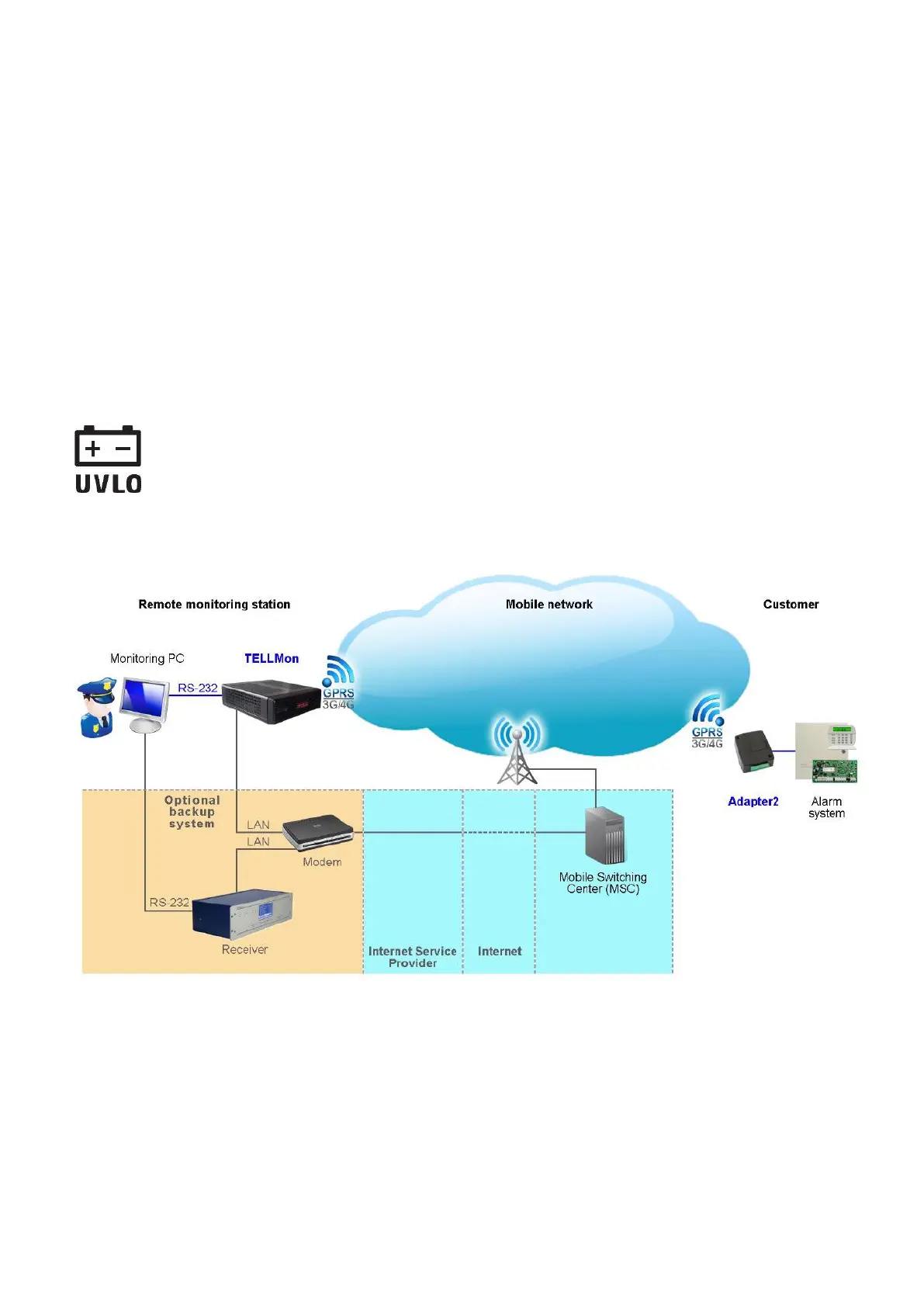
1.5 Remote monitoring application overview
The Adapter2 models equipped with a modem communicate with the TELLMon or SIA DC-09
receivers and MVP.next or TEX-MVP servers through the GSM service provider’s mobile
switching center using the GPRS/UMTS/LTE network, and then through the Internet. After
processing and conversion, the server forwards the received data packages through serial port
towards the monitoring PC that runs the alarm monitoring software. Alternative reporting channels:
voice call and SMS.
The WiFi product model connects to the Internet via a local WiFi router and does not support
alternative reporting via voice call or SMS.
 Loading...
Loading...