Note
All calibration steps that require accessing data on MACData() must begin read operations starting
at MACSubcmd() to ensure the data portion of the block is properly refreshed per the intended
MACSubcmd() subcommand (in this case 0xF081 or 0xF082). The first two bytes returned are the
MACSubcmd() subcommand followed by the counter, status, and raw ADC values, as shown in Table
10-1.
11.1 Cell Voltage Calibration
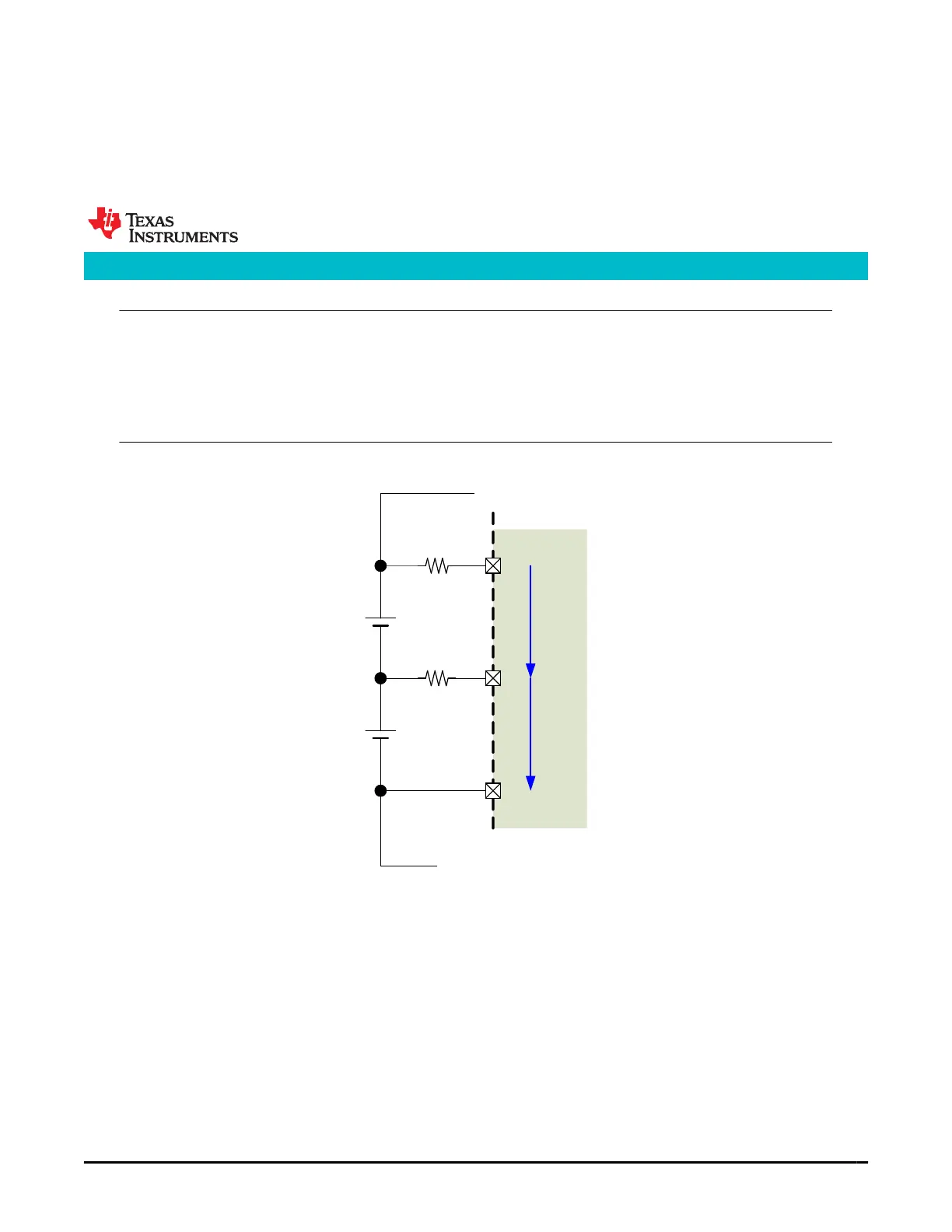
VC2
R
VC
VC1
R
VC
VSS
V
CELL
1
V
CELL
2
1. Apply known voltages in mV to the cell voltage inputs:
• V
CELL1
between VC1 terminal and VSS terminal
• V
CELL2
between VC2 terminal and VC1 terminal
2. If ManufacturerStatus()[CAL_EN] = 0, send 0x002D to MACSubcmd() to enable the [CAL_EN] flag.
3. Send 0xF081 or 0xF082 to MACSubcmd() to enable raw cell voltage output on MACData().
4. Poll MACData() until the 8-bit counter value increments by 2 before reading data.
5. Read the ADC conversion readings of cell voltages from MACData():
• ADC
CELL1
= AAaa of MACData()
• ADC
CELL2
= BBbb of MACData()
6. Average several readings for higher accuracy. Poll MACData() until ZZ increments, to indicate that updated
values are available:
• ADC
CELLx
= [ADC
CELLx
(reading n) + ...+ ADC
CELLx
(reading 1)]/n
7. Calculate gain value:
Chapter 11
Calibration
www.ti.com Calibration
SLUUCO0 – APRIL 2022
Submit Document Feedback
BQ28Z610-R2 59
Copyright © 2022 Texas Instruments Incorporated

 Loading...
Loading...











