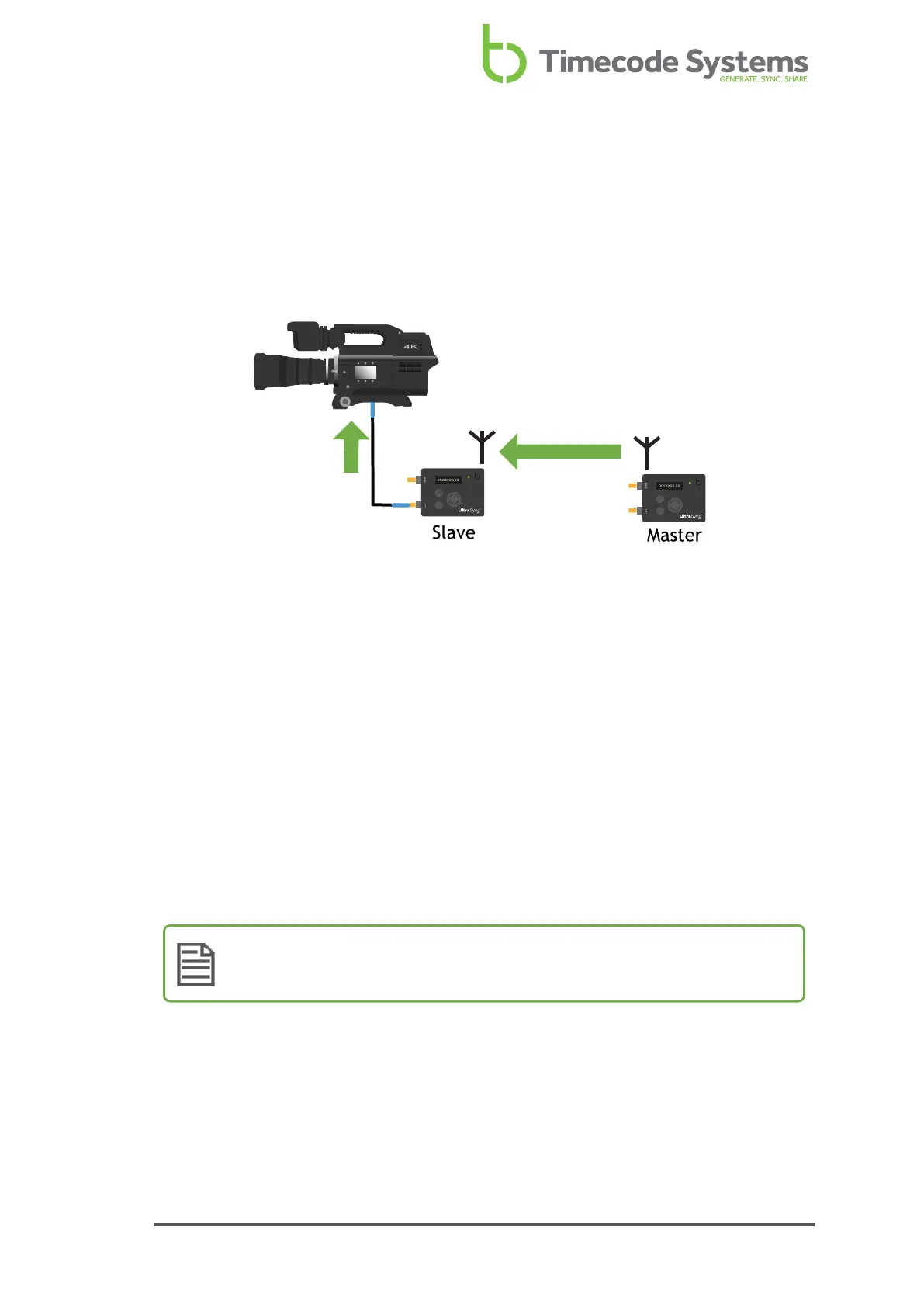
RF Slave
If you want your UltraSync ONE to receive its timecode from another Timecode
Systems device, set it to run in RF Slave mode. It will then try to connect with the
master device in the network. If it is in range of the master, it will synchronise with
the master's timecode (see RF Network on page 29).
You should use the RF Slave mode if you want your UltraSync ONEs to synchronise
with the timecode of the master device in the network.
As a slave, your UltraSync ONE will receive its timecode from the master device, as
long as the master is in range and is communicating on the same RF channel as your
UltraSync ONE.
The master sends the following data to the slaves via RF:
l Timecode
l Frames-Per-Second
l User bits (metadata).
When a slave receives this data, it updates its own internal settings to match, so
that it is synchronised with the master.
Note: If your slave cannot connect to a master, it runs in free mode (see
Master and Slaves on page 24).
To set your UltraSync ONE to be a master in an RF network, see Run UltraSync ONE
as an RF Slave on page 52.
UltraSync ONE User Guide 35
 Loading...
Loading...