Free Running and Jamming
Your UltraSync ONE has a Free Run/Jam-Ext mode, which has two different
purposes. You should use this mode if you want to use your UltraSync ONE to:
l Run as a standalone unit and provide its timecode to an external device (see
Free Running - UltraSync ONE as a Standalone Device on page 39).
l Synchronise with external devices in a third-party system rather than a
Timecode Systems network (see Jamming to an External Timecode Source on
page 40).
Note: To preserve battery life, RF is automatically disabled in Free
Run/Jam-Ext mode, as it is not needed in a free running or external
jamming workflow.
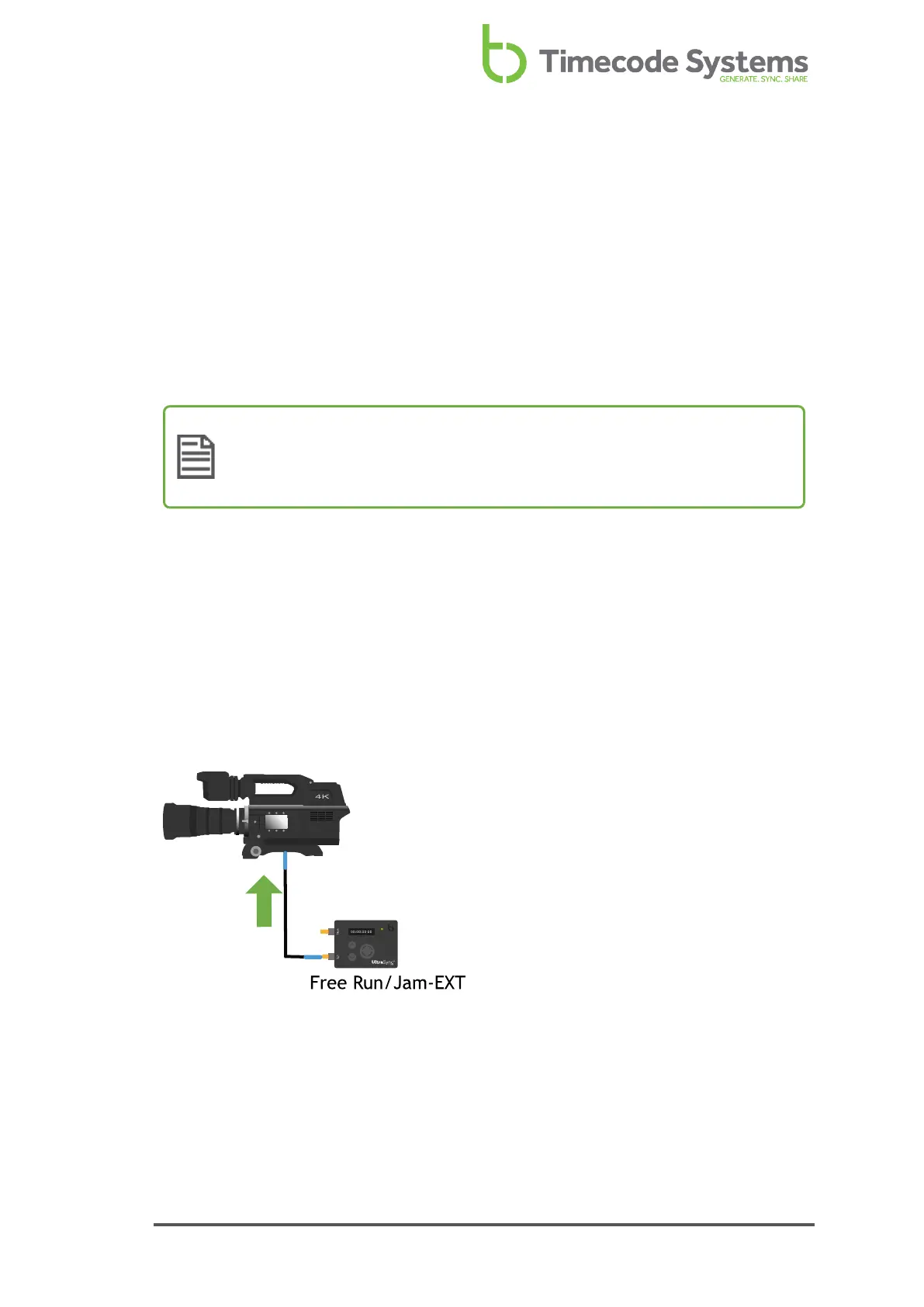
Free Running - UltraSync ONE as a Standalone Device
UltraSync ONEs are most commonly used in a network, where they will synchronise
with a master device. But you do not have to use your UltraSync ONE in a network -
if you prefer, you can use it as a standalone device.
When a UltraSync ONE is used as standalone device, it is 'free running'. This means
that the UltraSync ONE uses its own internal timecode settings and does not receive
timecode from other devices. It can output its timecode to other devices via the
SYNC or LTC ports, so that the other devices synchronise with the UltraSync ONE.
To run your UltraSync ONE as a standalone device, you need to set it to run in Free
Run/Jam-Ext mode (see Jam UltraSync ONE to a Signal on page 61).
UltraSync ONE User Guide 39
 Loading...
Loading...