1.1 Basic Understanding of AC Servos
9
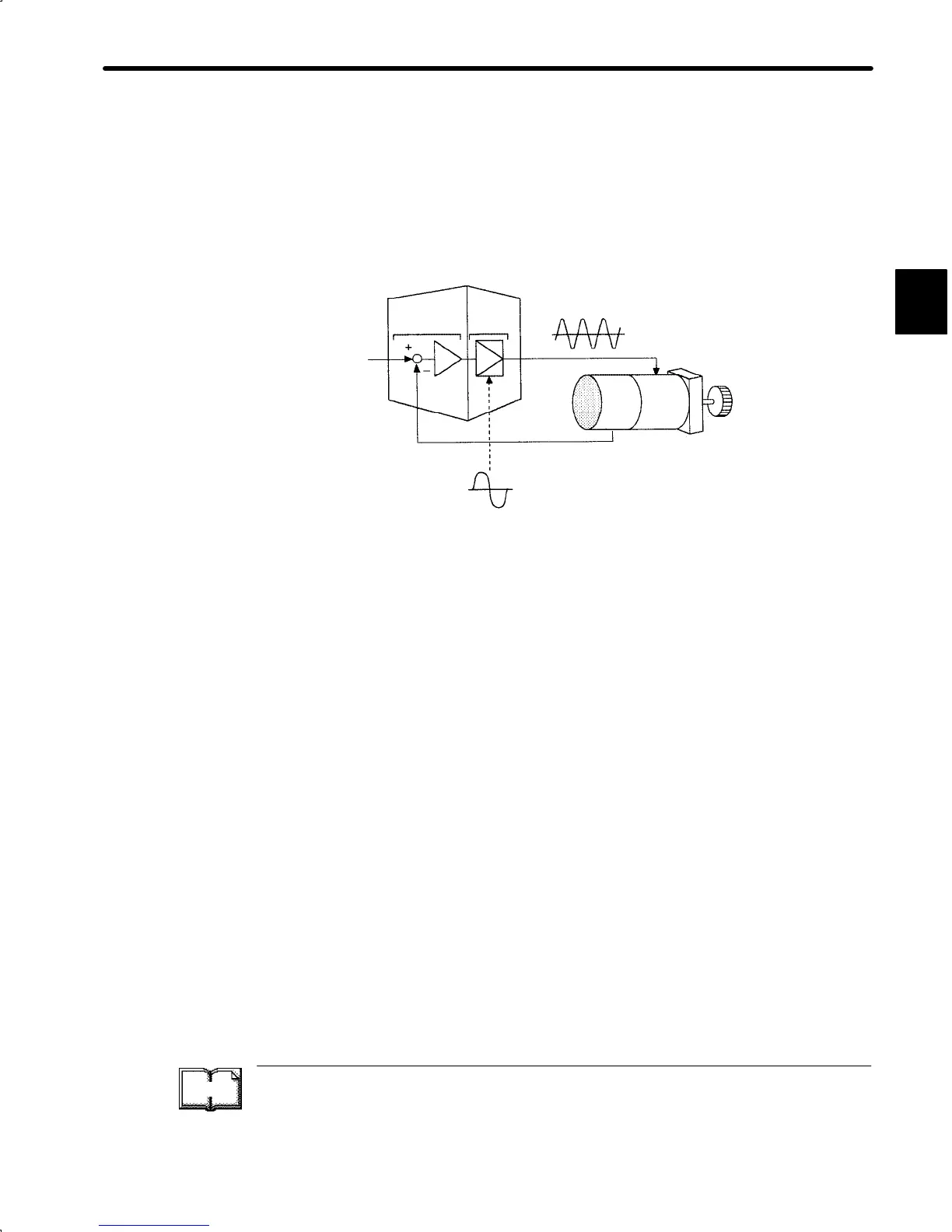
(4) Servo amplifier
A servo amplifier is required to operate an AC servomotor.
The following figure illustrates the configuration of a servo amplifier:
Servo amplifier
Reference
input
Motor driving AC power
Comparator
Power
amplifier
Feedback
Servomotor
Commercial AC power
A servo amplifier consists of the following two sections:
(a) Comparator
A comparator consists of a comparison function and a control function. The com-
parison function compares reference input (position or speed) with a feedback
signal and generates a differential signal.
The control function amplifies and transforms the differential signal. In other
words, it performs proportional (P) control or proportional/integral (PI) control.
(It is not important if you do not understand these control terms completely at this
point.)
(b) Power Amplifier
A power amplifier runs the servomotor at a speed or torque proportional to the
output of the comparator. In other words, from the commercial power supply of
50/60 Hz, it generates alternating current with a frequency proportional to the ref-
erence speed and runs the servomotor with this current.
TERMS
Proportional/integral (PI) control
PI control provides more accurate position or speed control than proportional control, which
is more commonly used.
1

 Loading...
Loading...











