Publication 1766-RM001A-EN-P - October 2008
482 Socket Interface Using CIP Generic Messaging
The exact sequence of sending and receiving data depends on the
application protocol.
Typical Sequence of Transactions For UDP Without OpenConnection
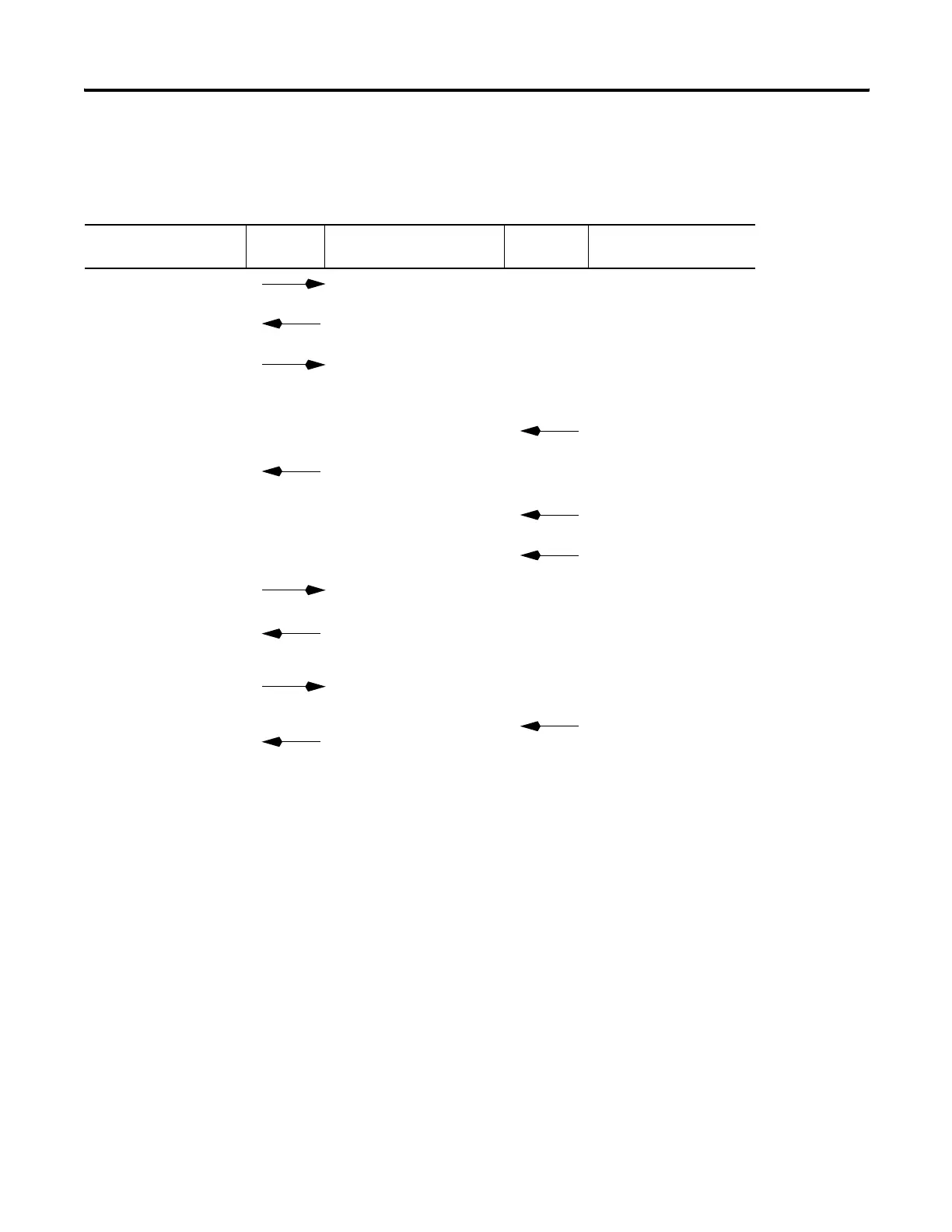
The following diagram shows a typical sequence of socket interface
transactions for UDP communications without using the OpenConnection
service to specify the destination address. In this case, the MicroLogix
controller specifies the destination for each datagram and receives the
sender's address along with each datagram it receives.
The example below shows the MicroLogix controller sending data to a
device and then the device sending a response. This is a typical sequence
of transactions. Depending on the application protocol, the device could
instead initiate sending data to the MicroLogix controller. Additionally,
Typical Sequence of Transactions for a TCP Server
MSG in Ladder
Program
Ethernet Subsystem
10.10.10.10
Remote Ethernet Device
10.10.10.11
CreateSocket
Port=49100
CreateSocket Response
Instance=102
AcceptConnection
Timeout = 10000 ms
(ListenTCP Connection)
Open TCP Connection
Port=49100
(Accept TCP Connection)
AcceptConnection Response
Send Data
Data = abc
Data = abc
Read
Timeout = 10000 ms
Read Response
Data = abc
Write
Data = xyz
Data = xyz
Write Response
The response is returned to the
controller as soon as the data is sent
Receive Data
efesotomasyon.com - Allen Bradley,Rockwell,plc,servo,drive

 Loading...
Loading...